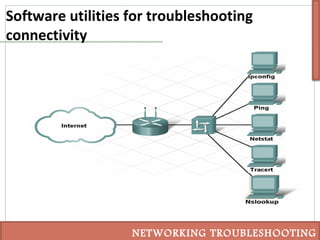
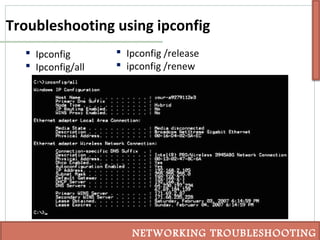
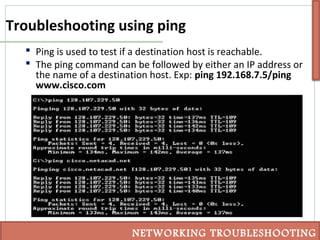
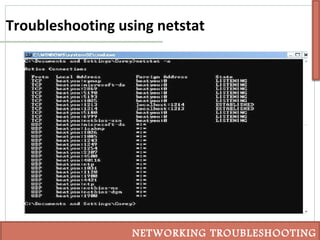
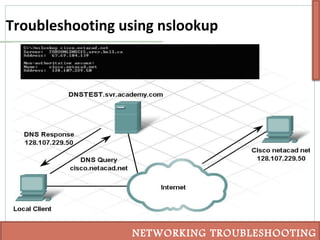
This document discusses various techniques for troubleshooting networking issues, including top-down, bottom-up, and divide-and-conquer approaches. It describes using the senses and tools like ipconfig, ping, tracert, netstat, and nslookup to diagnose physical layer problems, connectivity issues, and incorrectly configured devices. Thorough documentation of troubleshooting steps and results is recommended, as is obtaining assistance from outside sources like documentation, forums, or a helpdesk when issues cannot be resolved alone.