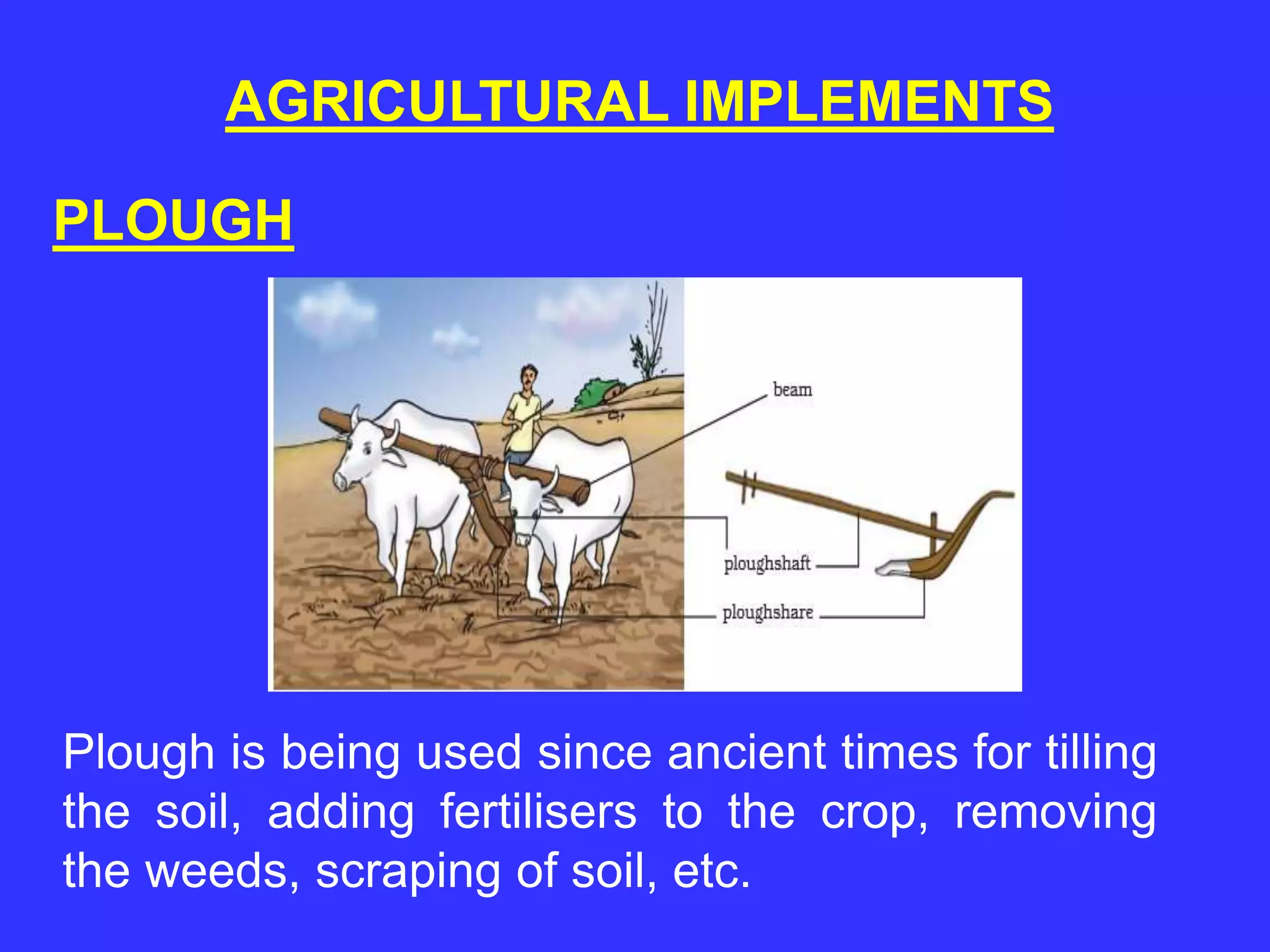
The document provides an overview of crop production and management, tracing the evolution of agriculture from nomadic lifestyles to settled farming practices. It details various processes involved in agriculture, including soil preparation, sowing, fertilization, irrigation, weed control, harvesting, and storage of crops. Additionally, it distinguishes between kharif and rabi crops and emphasizes the importance of proper agricultural techniques for enhancing crop yield.