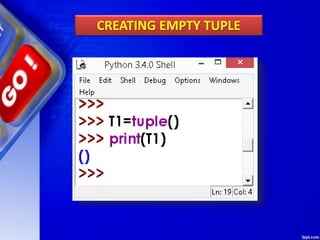
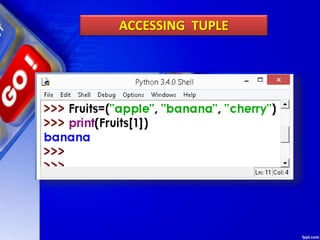
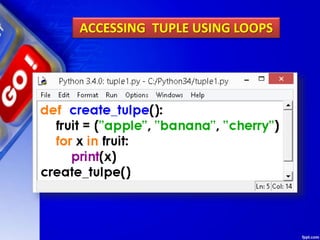
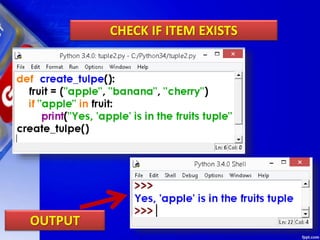
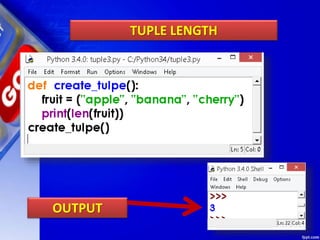
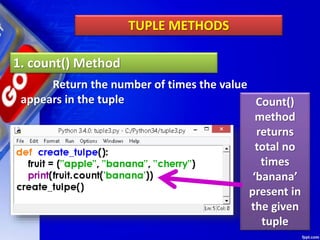
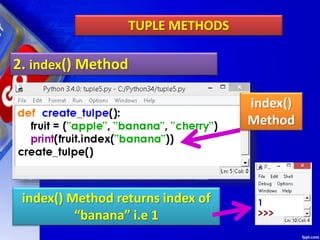
This document discusses tuples in Python. It begins by defining a tuple as a sequence of values that can be of any type and are indexed by integers. Tuples are immutable, like lists but values cannot be changed. Various tuple functions are described such as creating empty tuples, accessing tuple elements using indexes and loops, checking if an item exists, getting the length, and removing a tuple. Built-in tuple methods like count() and index() are explained. The key differences between tuples, lists, and dictionaries are outlined. Finally, some example programs demonstrating tuple operations are provided.


















![DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LIST AND TUPLE
LIST TUPLE
Syntax for list is slightly
different comparing with
tuple
Syntax for tuple is slightly
different comparing with
lists
Weekdays=[‘Sun’,’Mon’,
‘wed’,46,67]
type(Weekdays)
class<‘lists’>
twdays = (‘Sun’, ‘mon', ‘tue',
634)
type(twdays)
class<‘tuple’>
List uses [ and ] (square
brackets) to bind the
elements.
Tuple uses rounded
brackets( and ) to bind the
elements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter17tuples-190528090344/85/Chapter-17-Tuples-26-320.jpg)













![5. Write a Python program to add an item in a
tuple.
#adding items in a specific index
tuplex = tuplex[:5] + (15, 20, 25) + tuplex[:5]
print(tuplex)
#converting the tuple to list
listx = list(tuplex)
#use different ways to add items in list
listx.append(30)
tuplex = tuple(listx)
print(tuplex)
TUPLE - AVERAGE PROGRAMS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter17tuples-190528090344/85/Chapter-17-Tuples-40-320.jpg)



