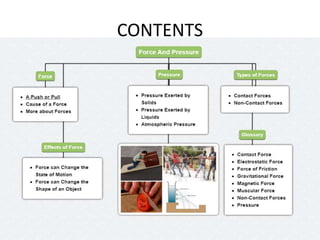
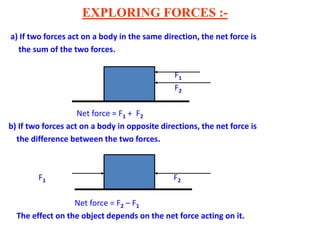
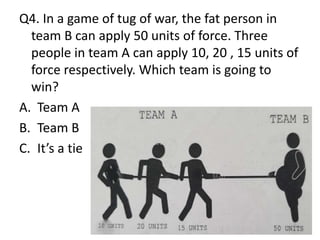
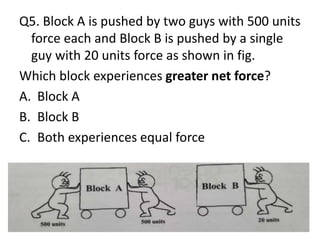
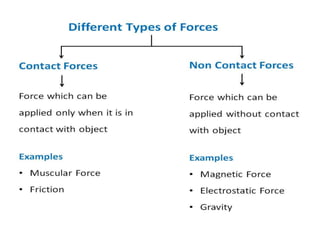
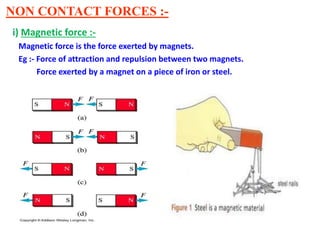
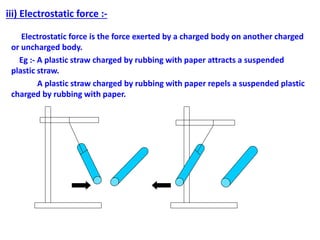
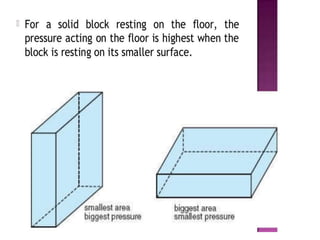
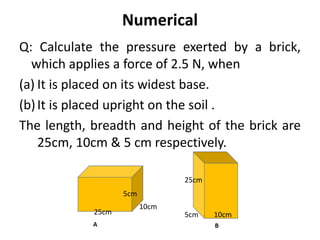
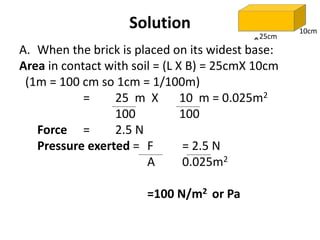
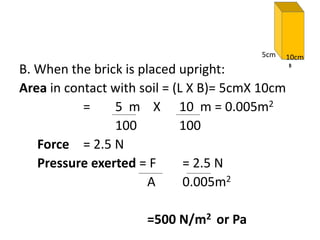
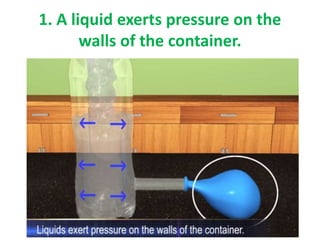
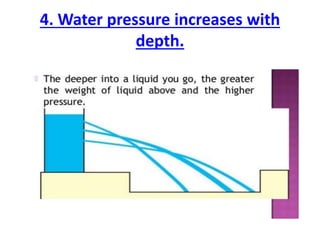
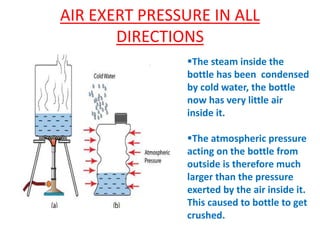
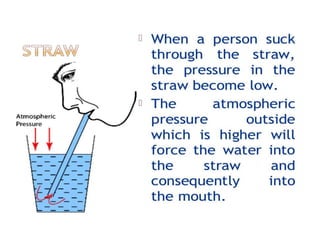
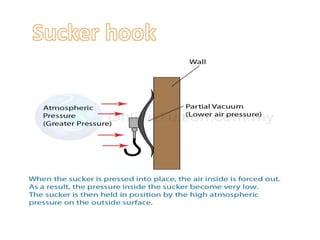
Force is a push or pull that can cause an object to be in motion or at rest by overcoming inertia. Forces act due to an interaction between two objects. The net force on an object is the sum of all forces acting on it and depends on both the magnitude and direction of individual forces. Pressure is the amount of force applied per unit area. Liquids and gases exert pressure due to the weight of the fluid above. Atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude and temperature and decreasing humidity.