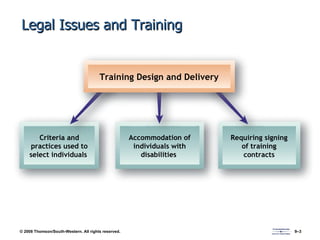
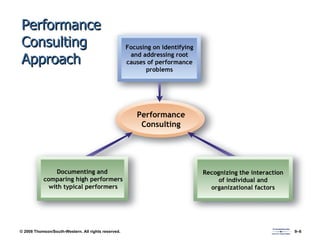
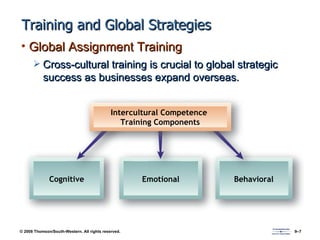
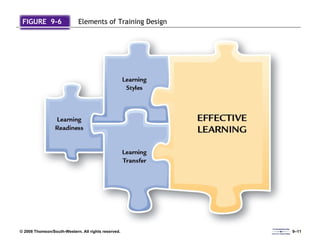
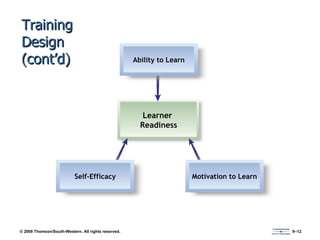
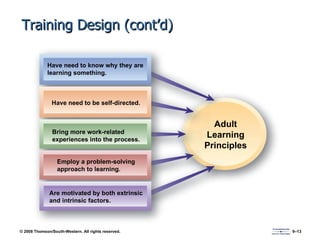
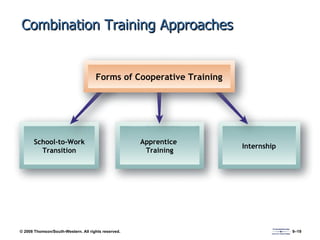
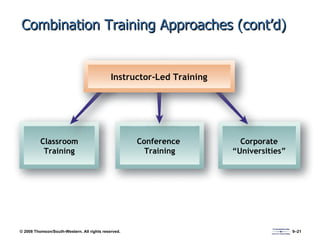
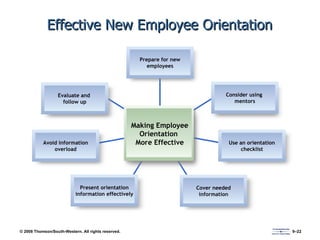
The document discusses various aspects of developing human resources through training. It covers the nature of training, legal issues, how training supports organizational strategy and competitiveness, knowledge management, performance consulting, global strategies, developing strategic training plans, establishing objectives and priorities, training design principles, internal and external training approaches, and methods for evaluating training.