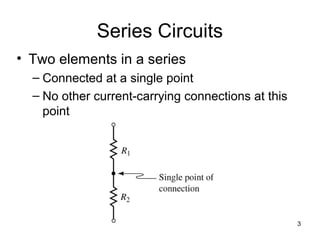
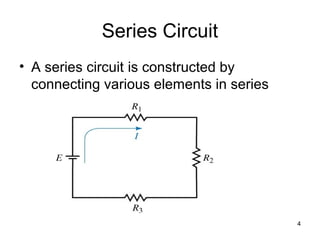
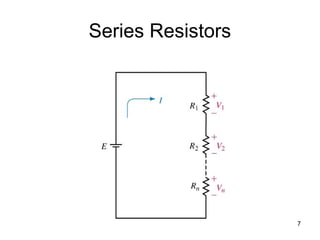
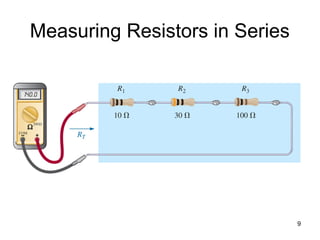
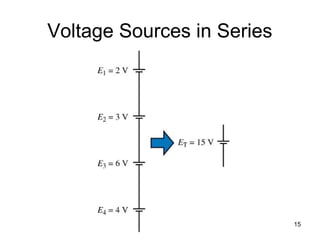
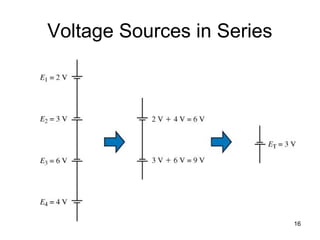
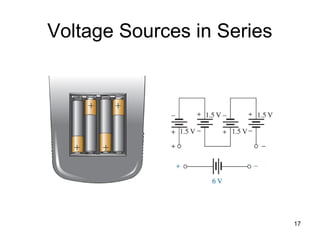
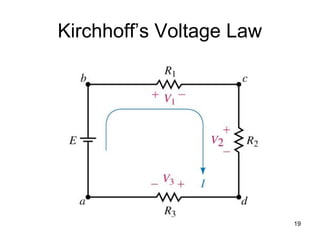
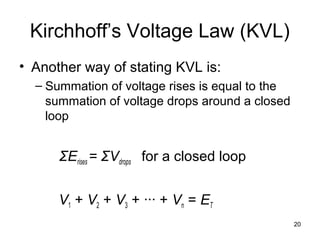
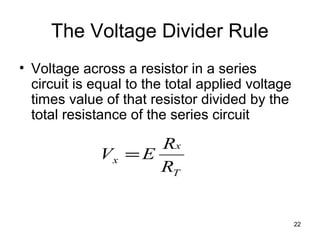
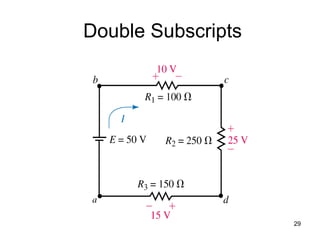
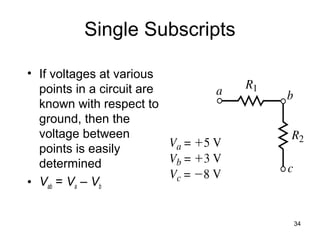
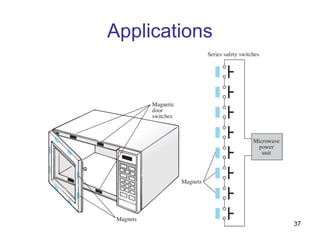
This document discusses series circuits. It defines a series circuit as one where two elements are connected at a single point with no other current-carrying connections. The total resistance of a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistances. The current is the same at every point in a series circuit. Kirchhoff's Voltage Law states that the sum of the voltage rises equals the sum of the voltage drops in a closed loop circuit. The voltage divider rule describes how voltage is divided across resistors in proportion to their resistances. Examples of series circuits applications include holiday lights and microwave oven safety switches.