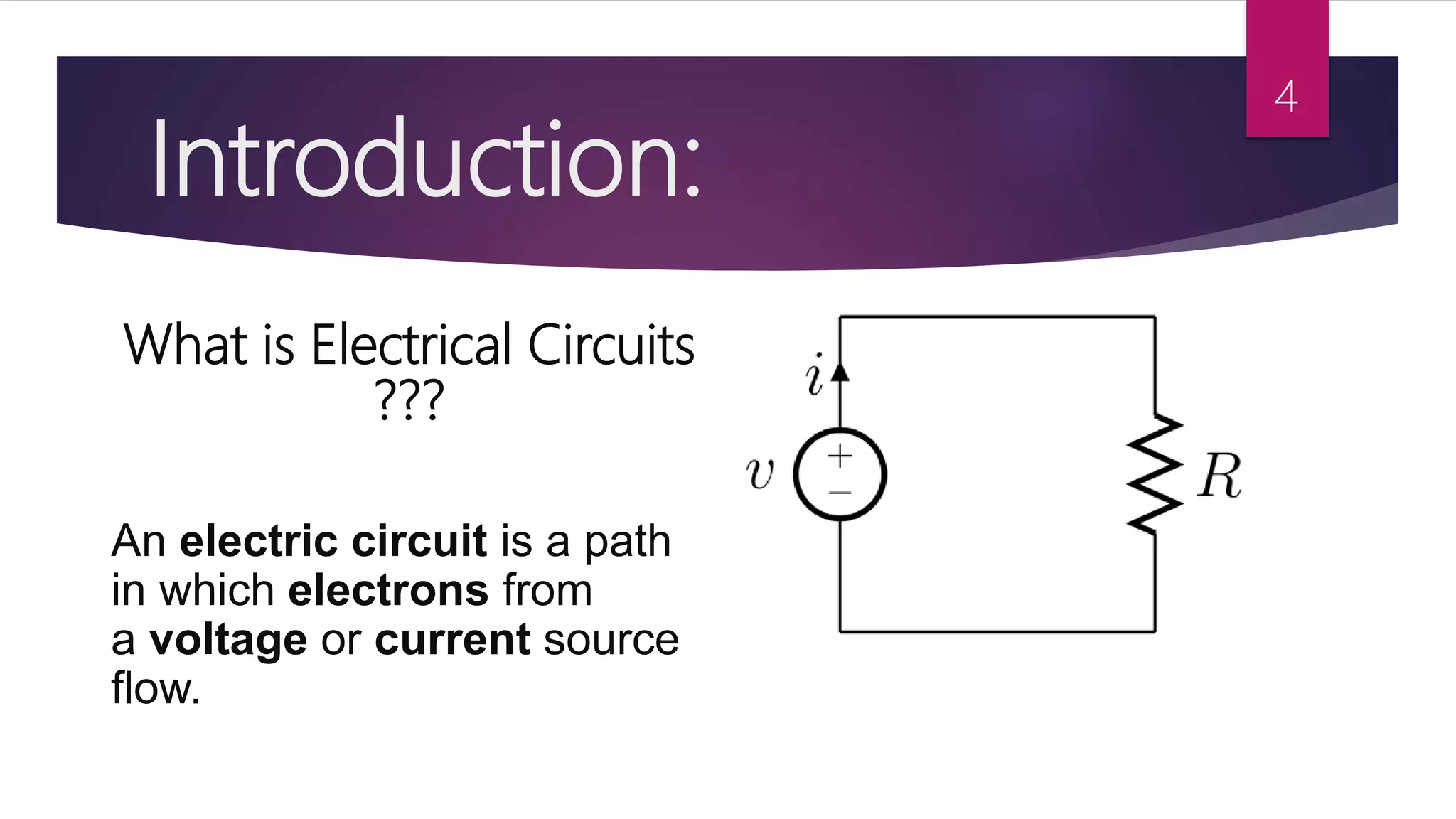
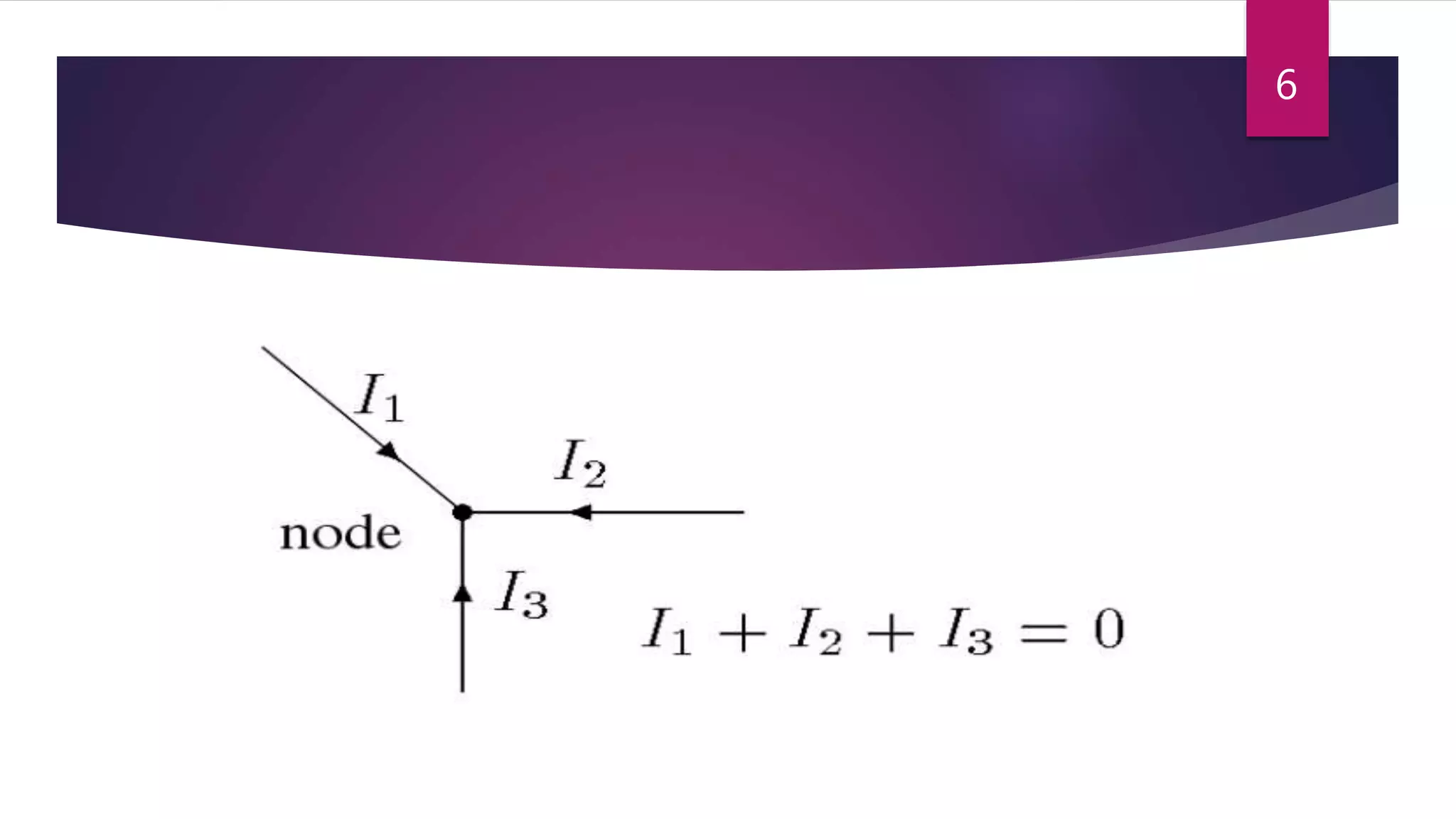
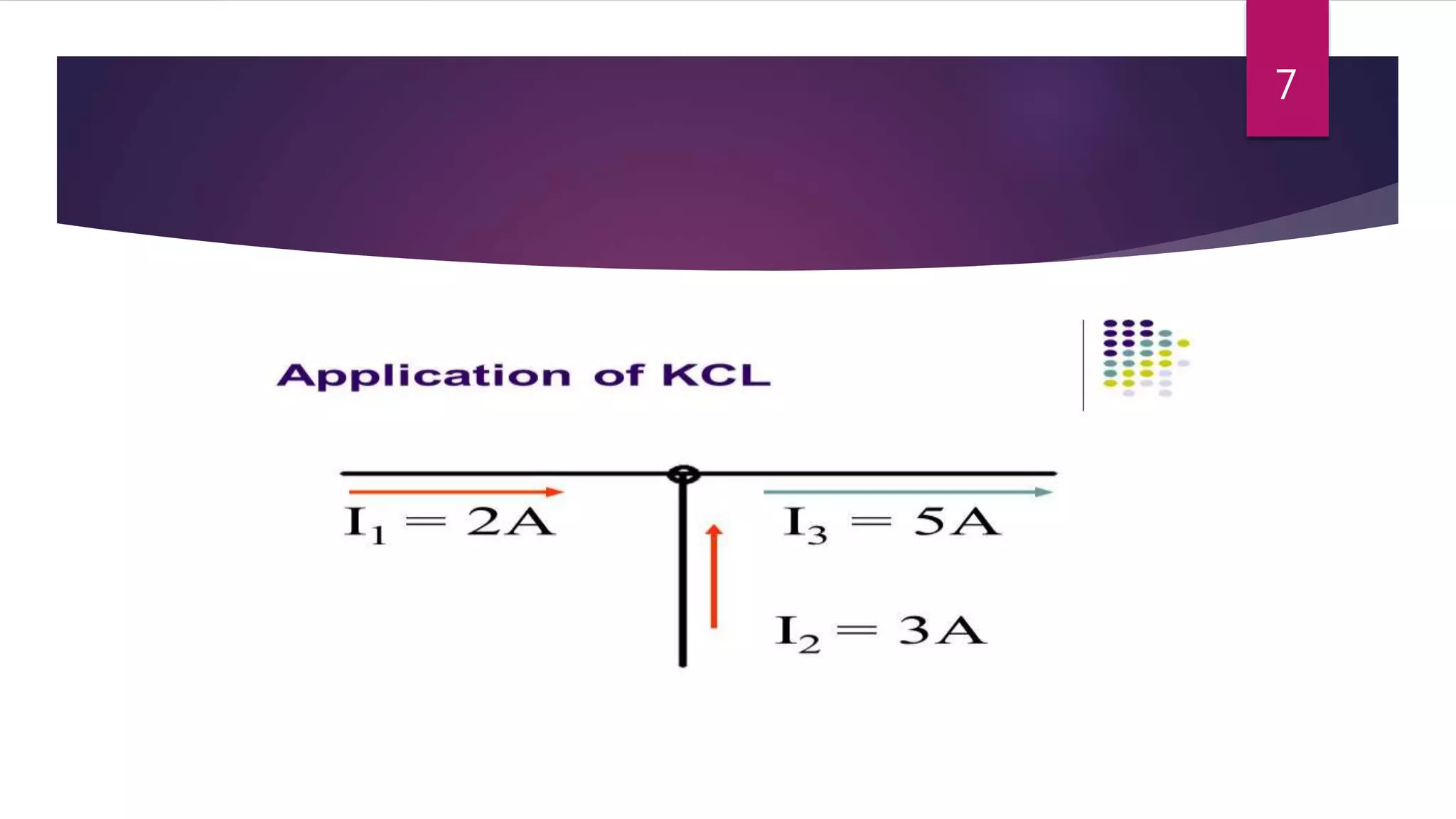
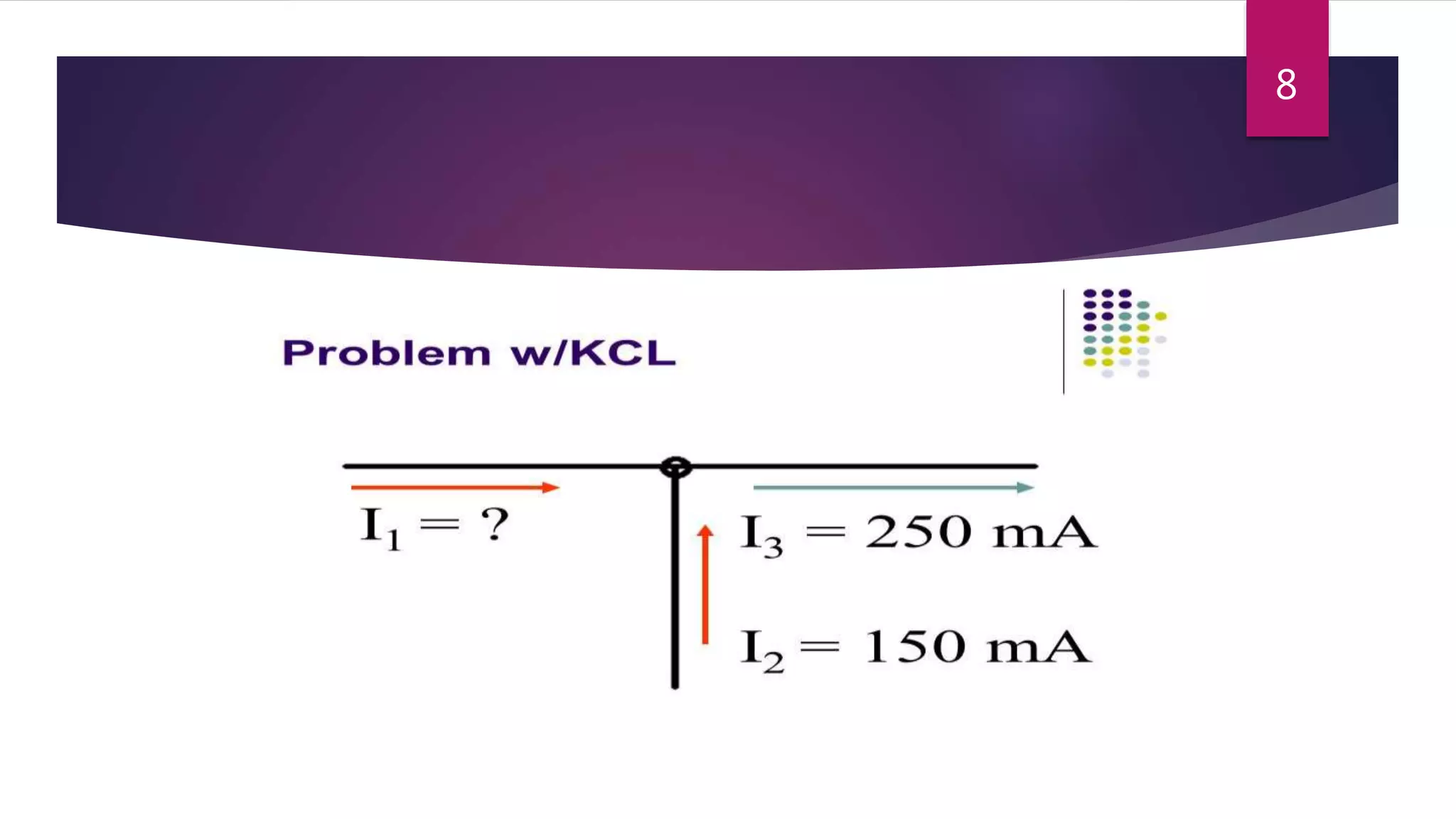
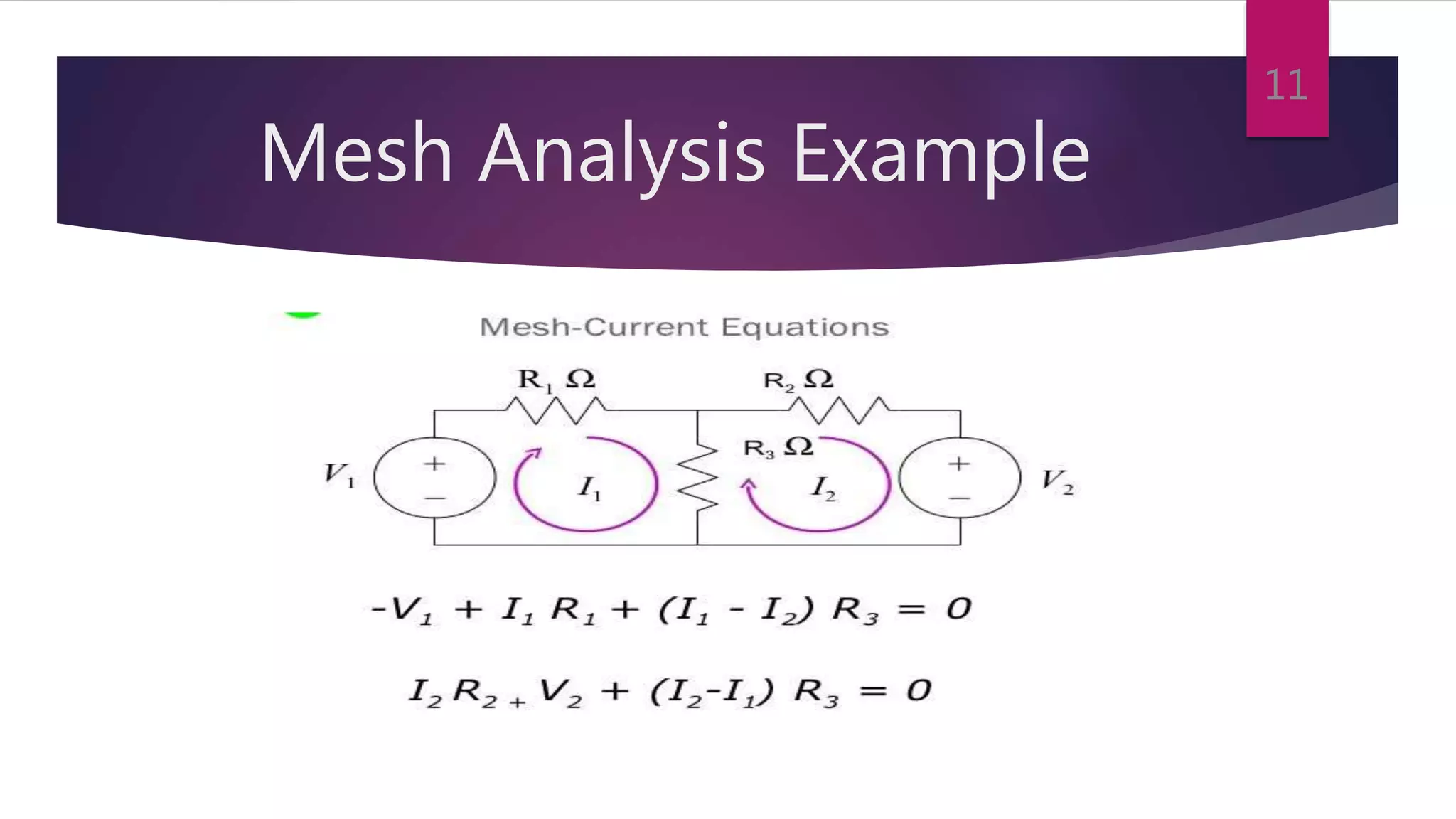
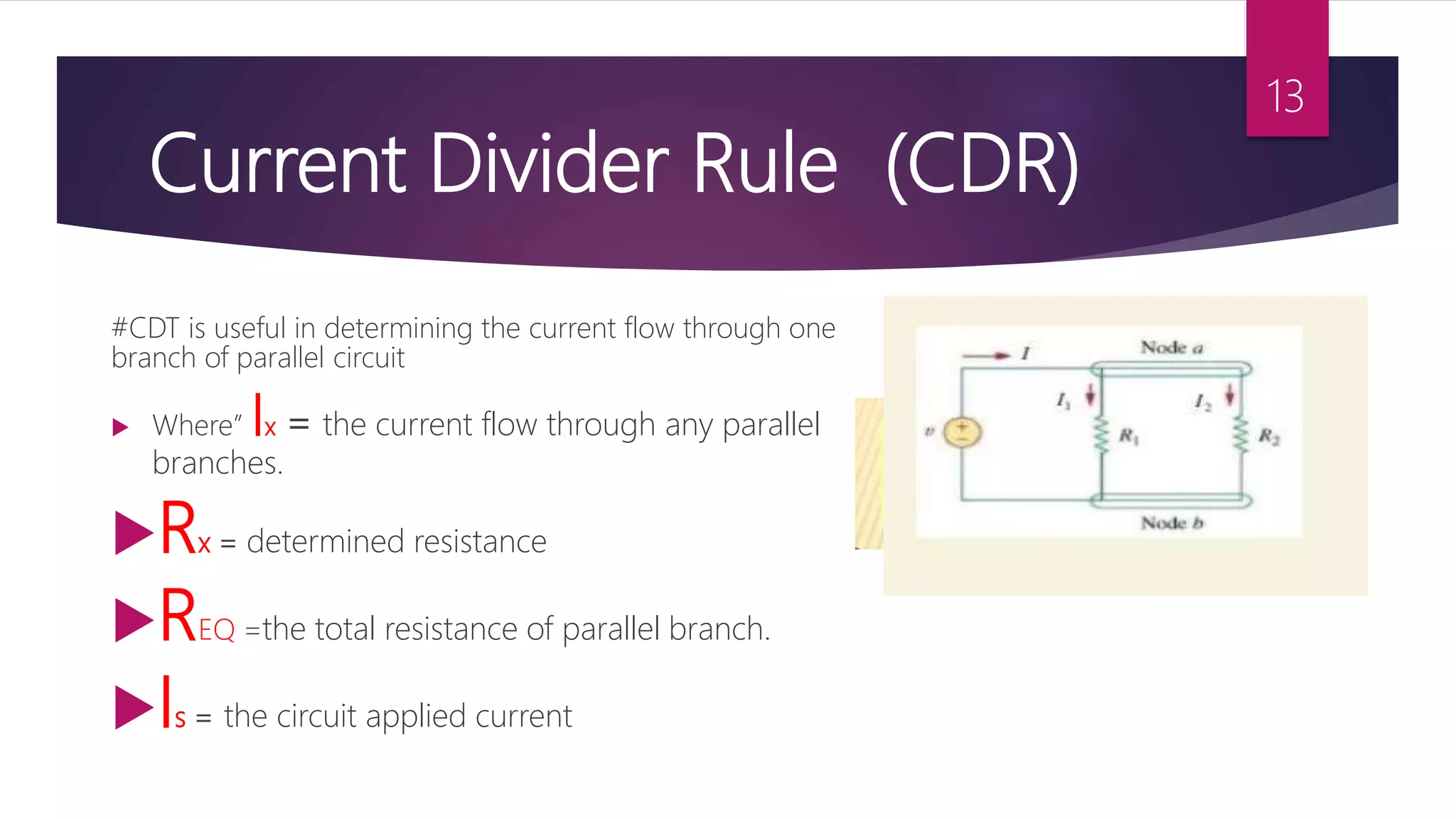
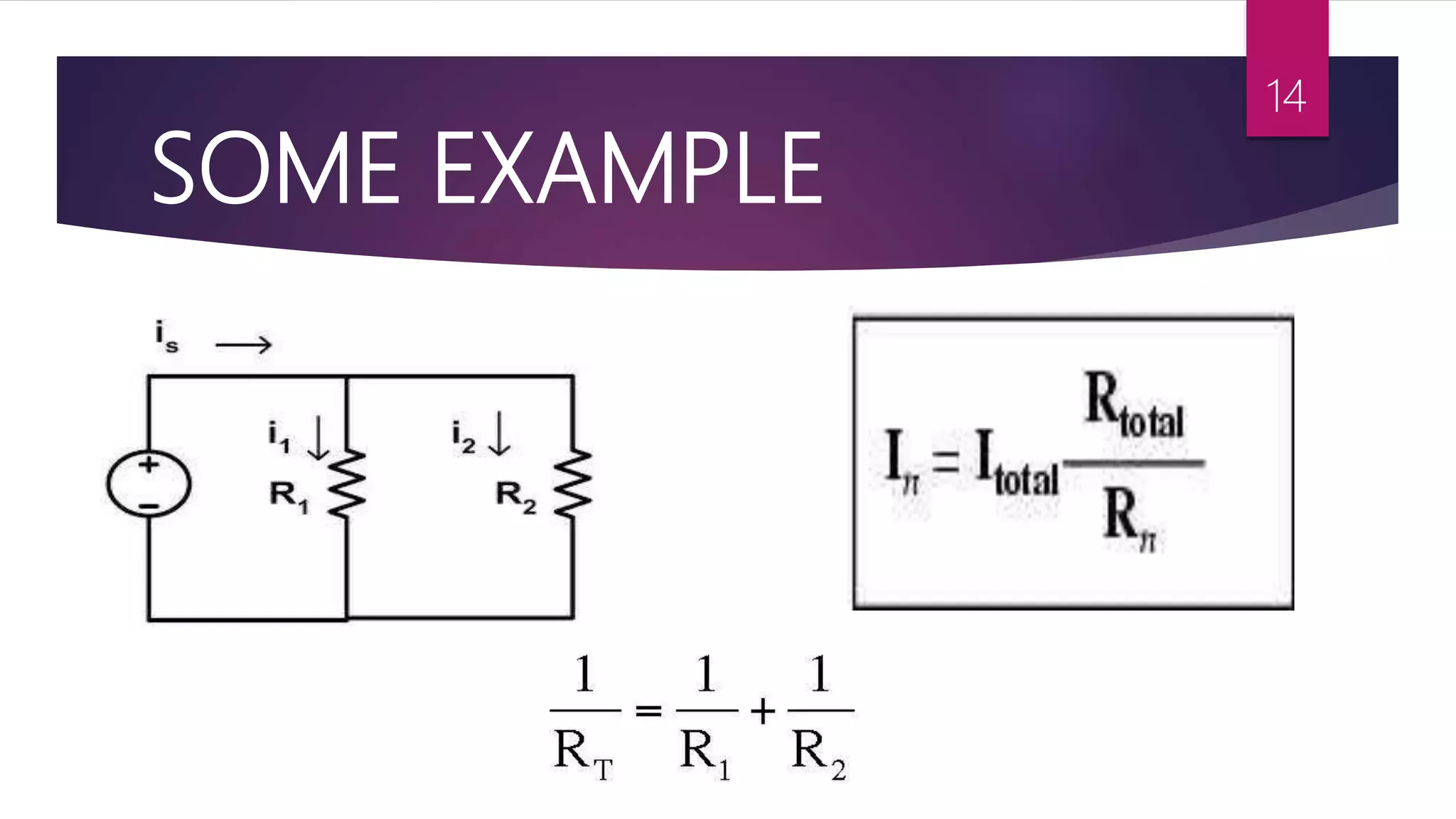
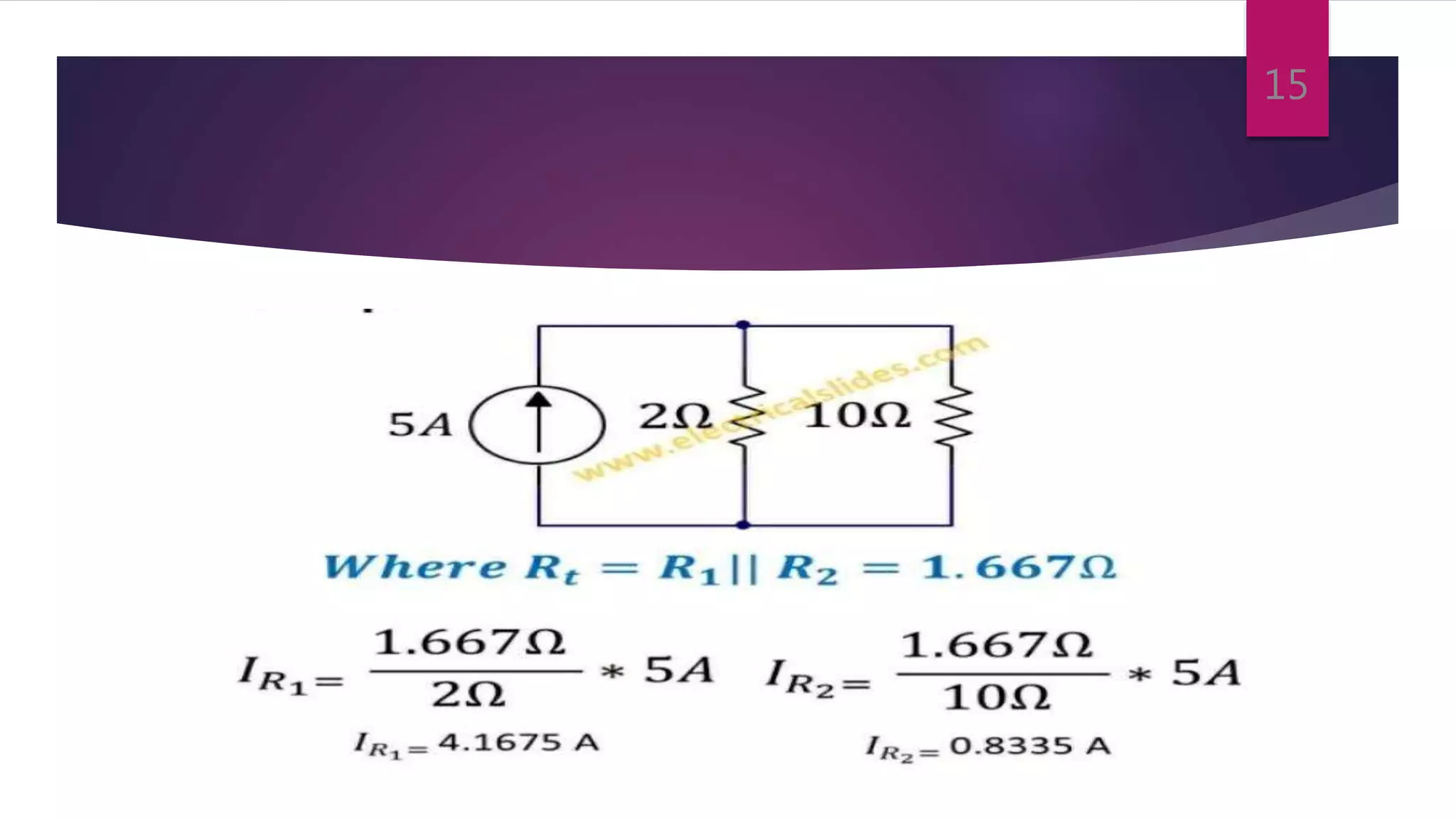
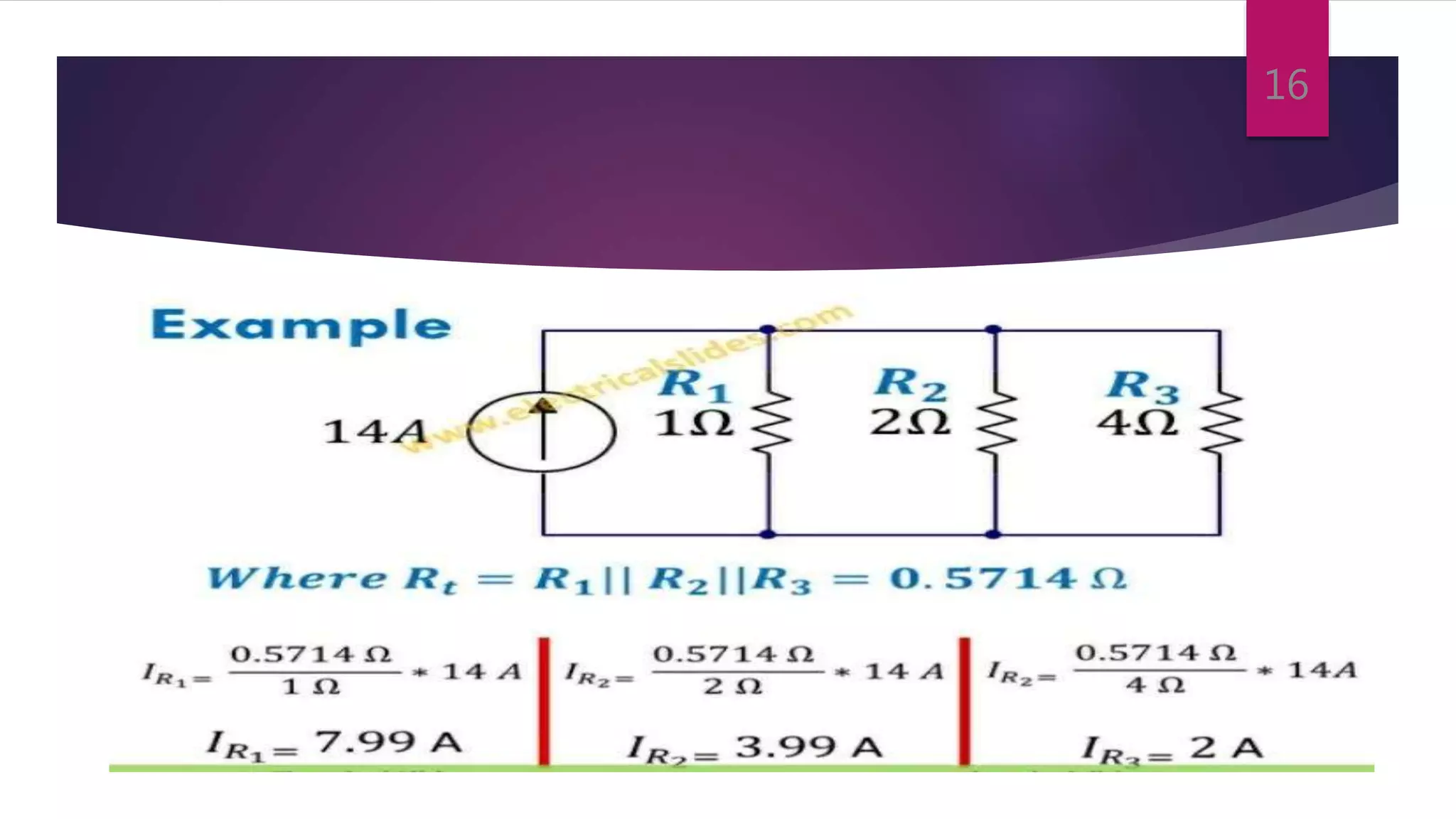
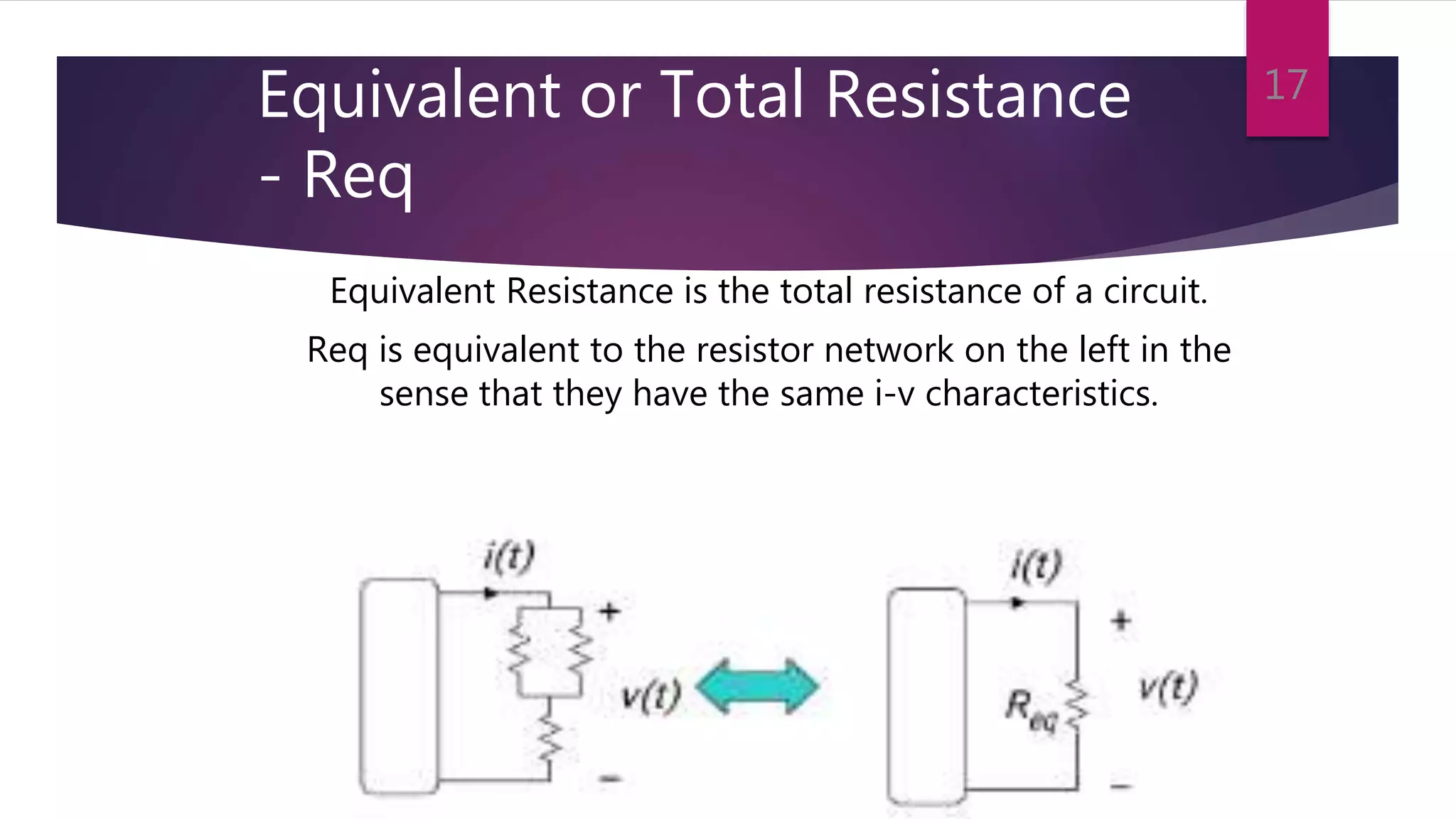
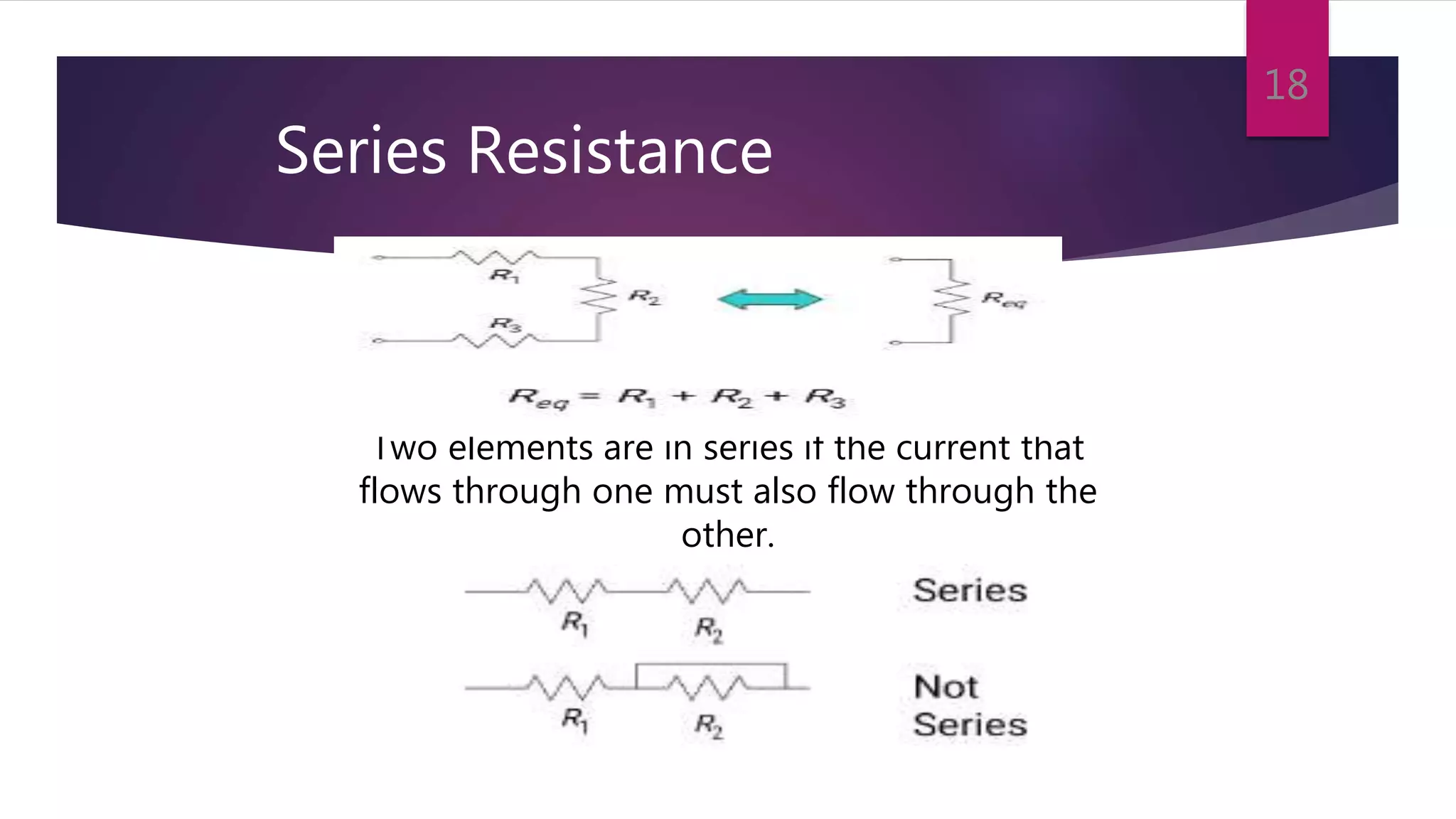
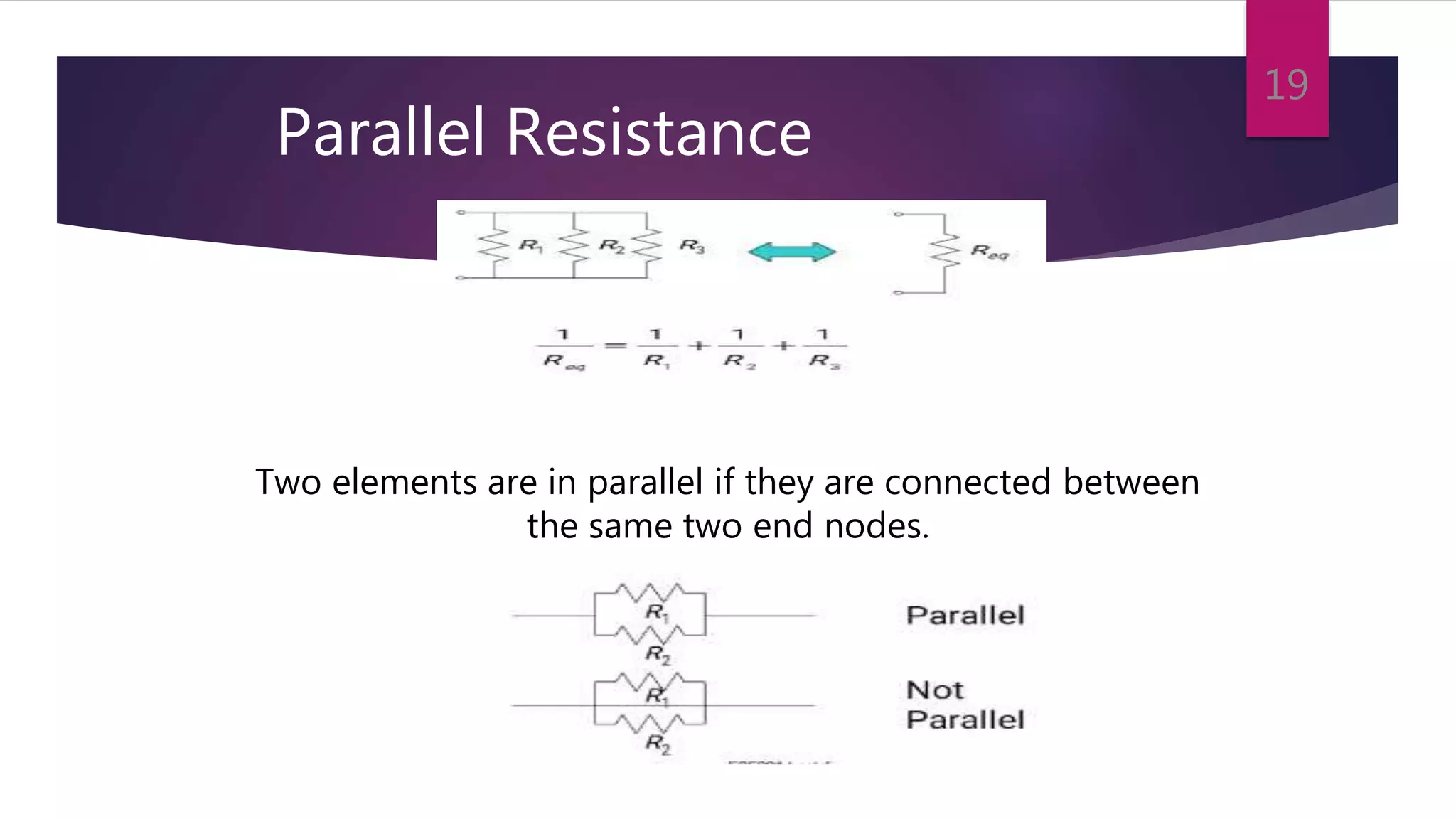
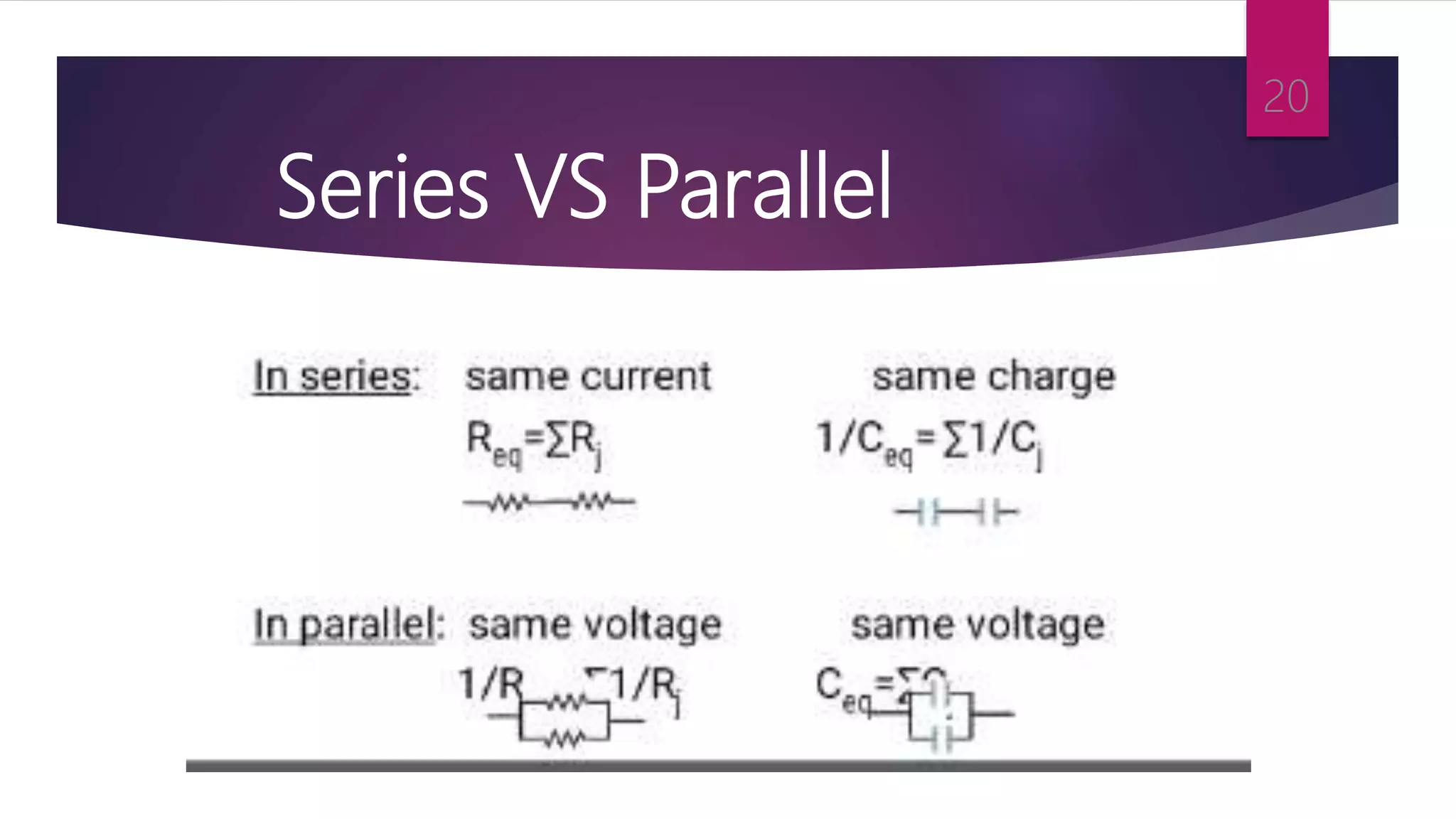
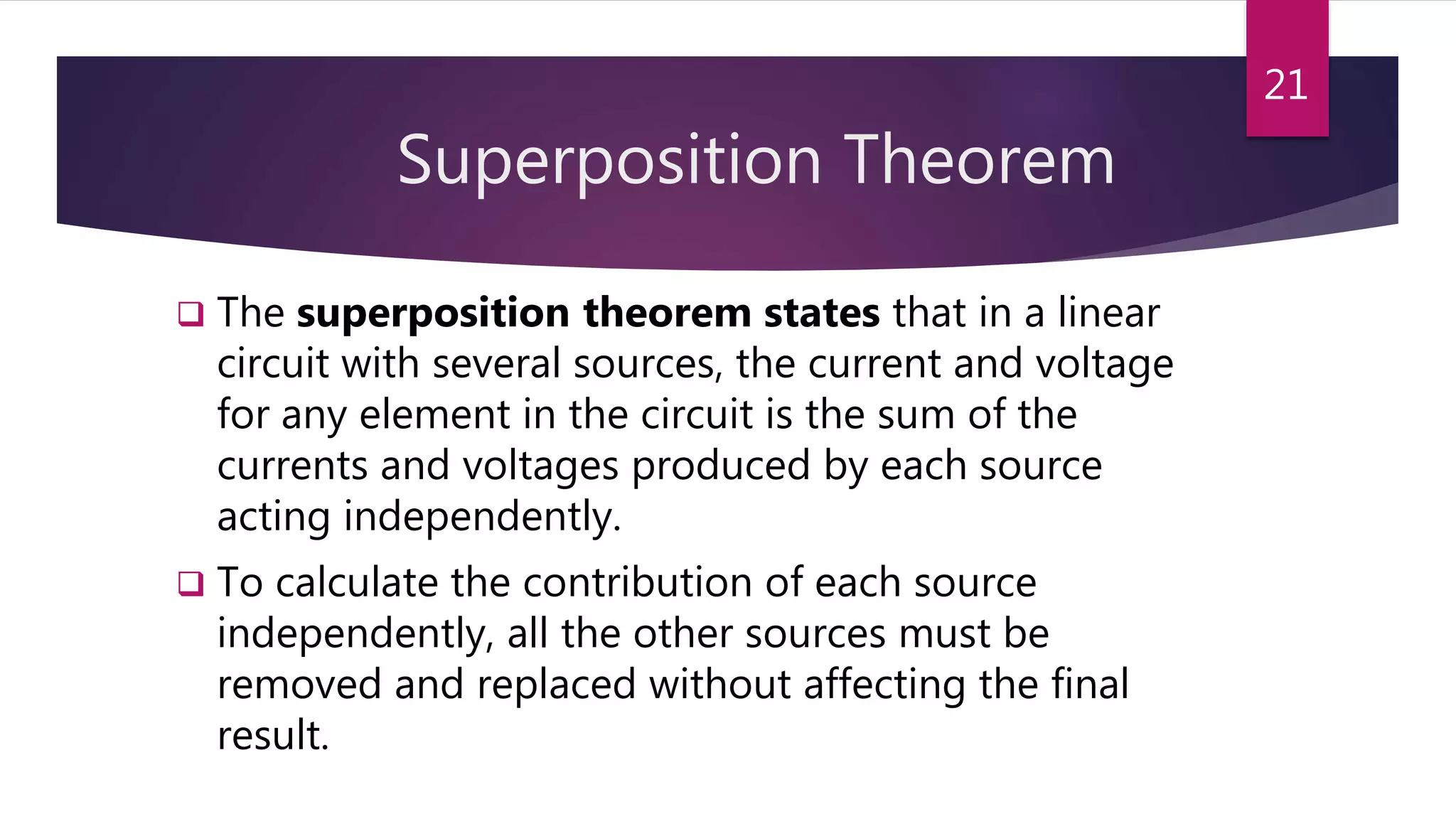
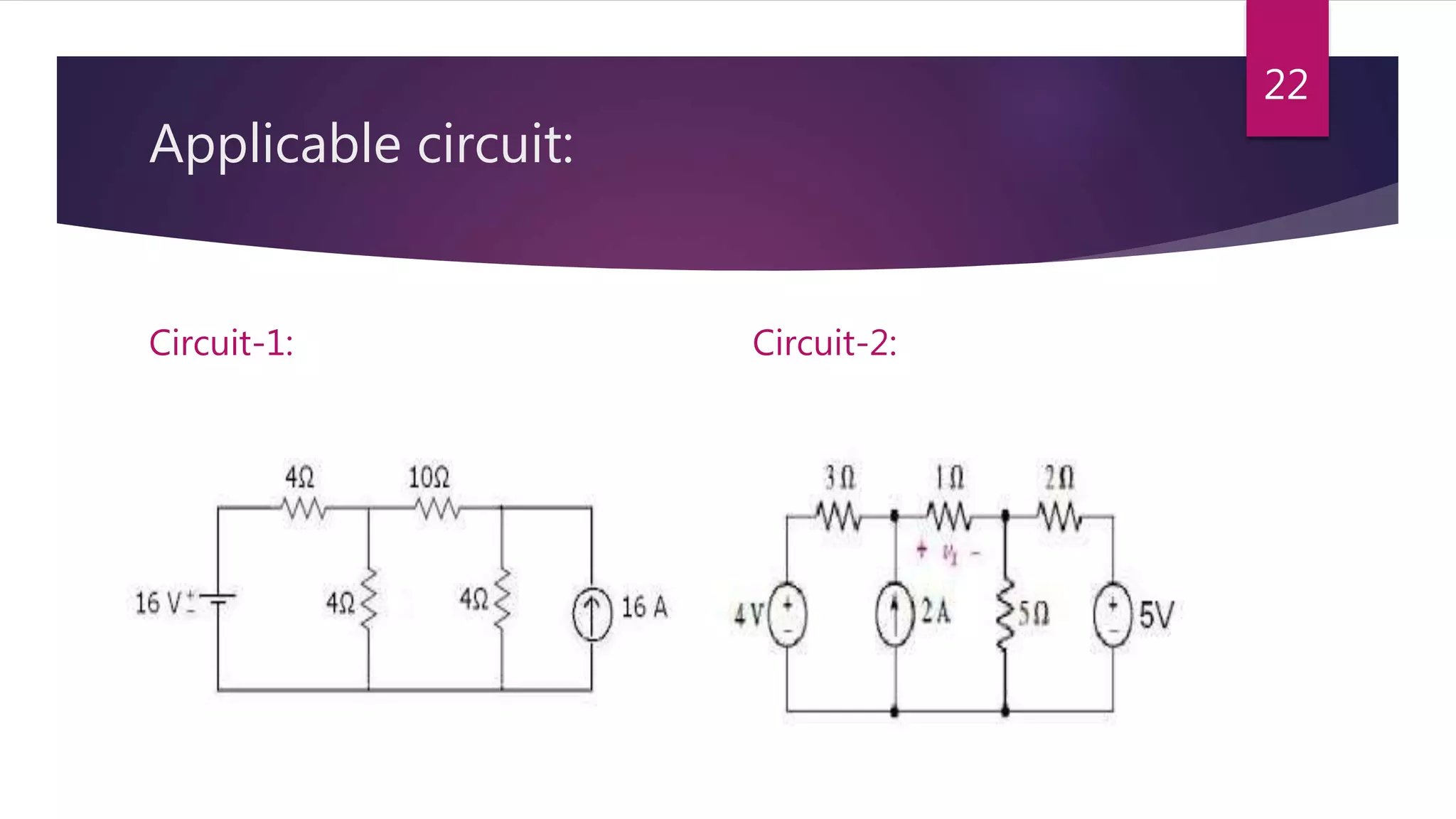
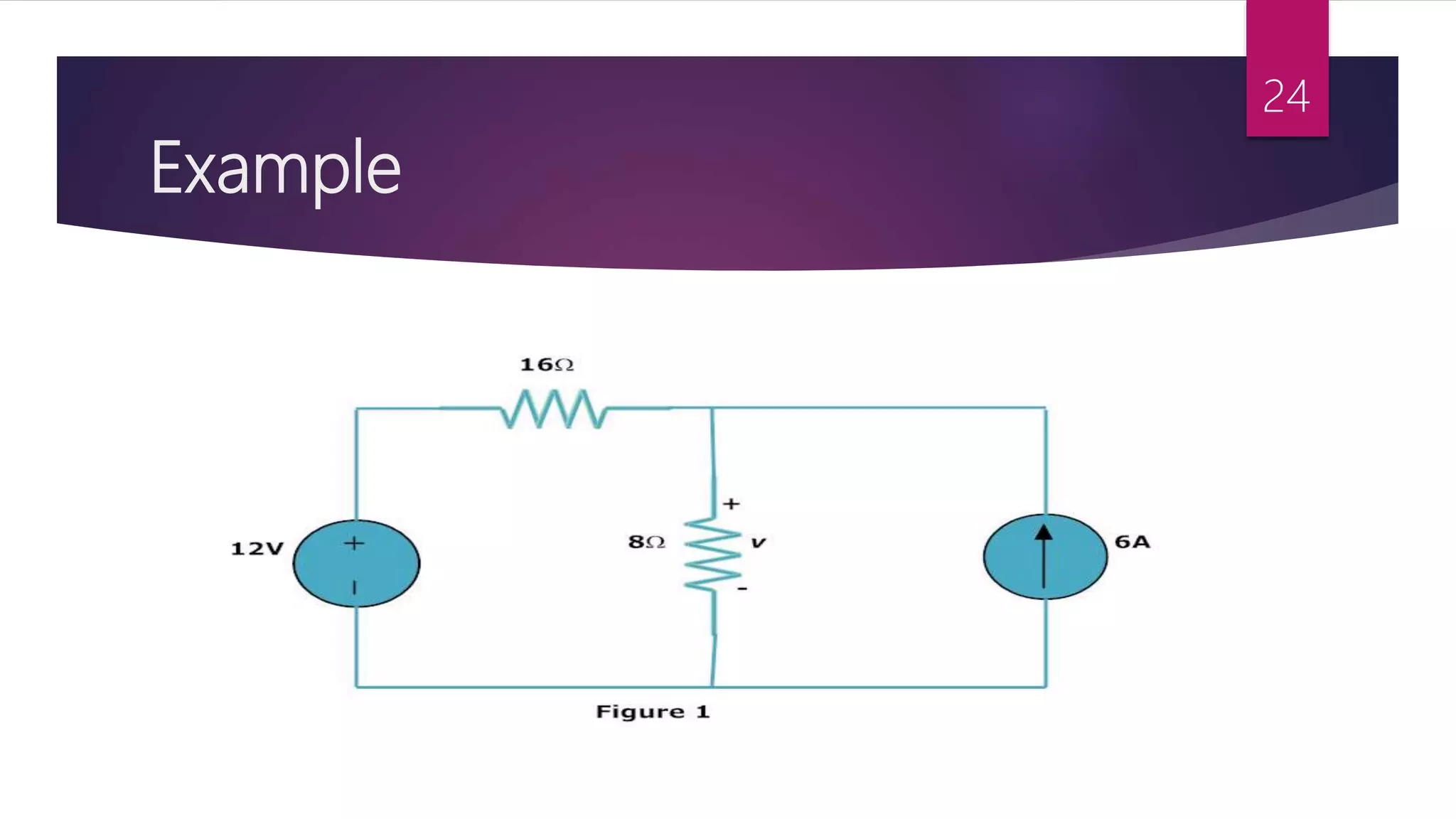
This presentation summarizes key concepts in electrical circuits including Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL), mesh analysis, current divider rule, equivalent resistance, series and parallel circuits, and superposition theorem. It introduces electrical circuits as paths for electron flow from a voltage or current source. Specific topics covered include KCL, mesh analysis techniques and examples, using the current divider rule to determine current flow in parallel branches, calculating equivalent resistance, distinguishing series and parallel components, and applying the superposition theorem by considering one source at a time in linear circuits.