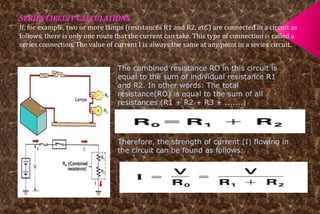
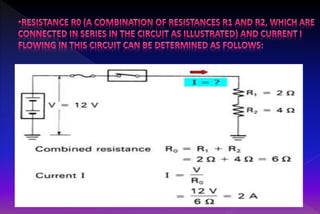
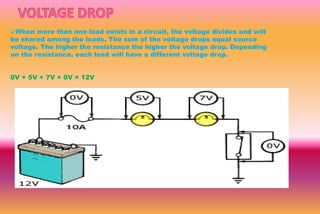
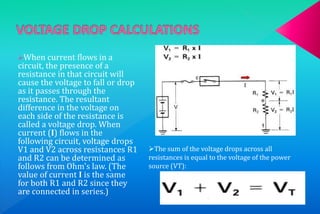
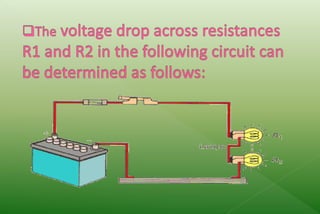
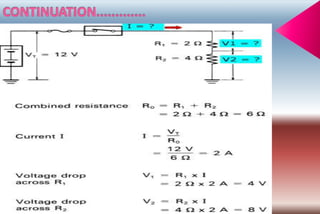
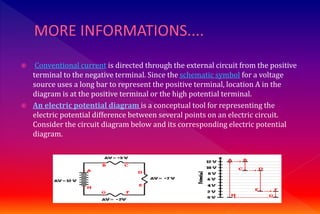
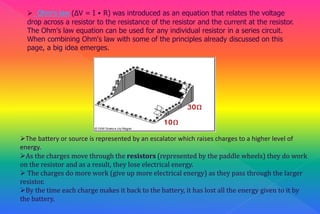
A series circuit consists of components connected in a single path, where the same current flows through each component, but the voltage is divided among them. If any part of the circuit is interrupted, the entire circuit fails, and the equivalent resistance can be calculated as the sum of individual resistances. Ohm's law relates the voltage drop across resistors to their resistance and the current flowing through them, indicating how energy is lost as charges move through the circuit.