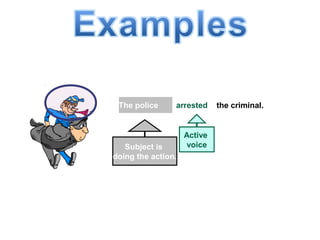
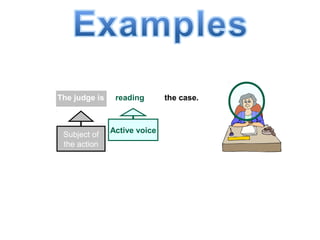
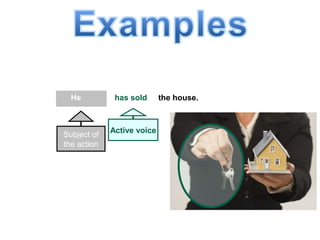
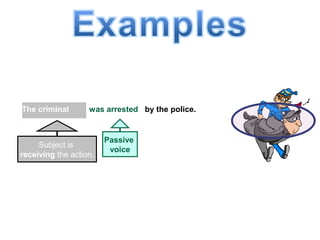
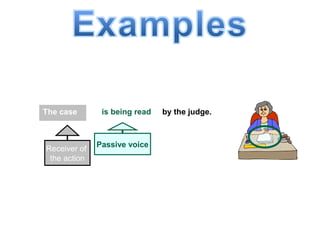
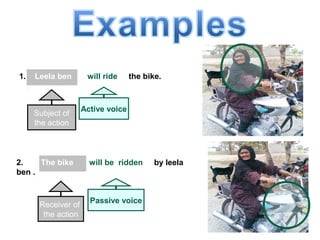
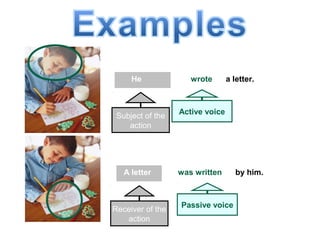
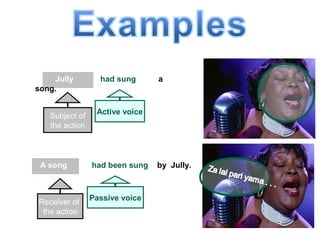
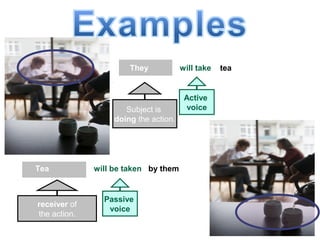
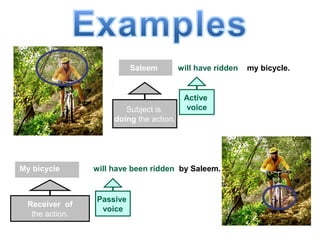
The document discusses active and passive voice in sentences. Active voice indicates that the subject of the verb performs the action, while passive voice indicates the subject receives the action. There are generally three rules for converting between active and passive voice: 1) make the object of the active sentence the subject of the passive sentence, 2) use an appropriate auxiliary verb, and 3) make the main verb of the active sentence the past participle in the passive sentence. While active voice is usually preferred for being more direct, passive voice can be used when the performer of the action is unknown or less important than the recipient of the action.