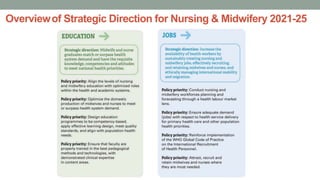
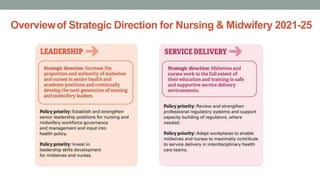
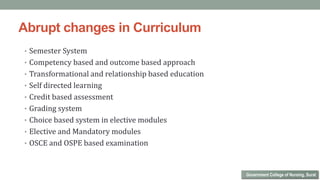
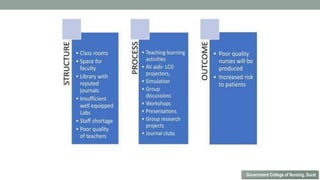
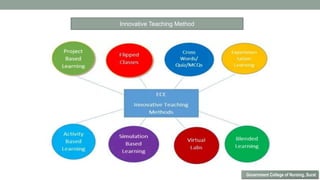
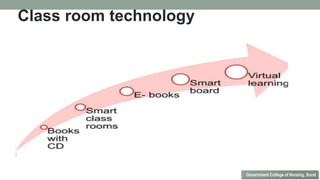
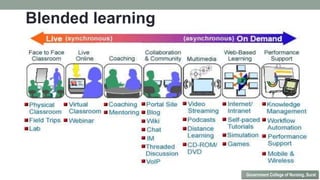
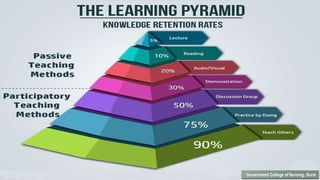
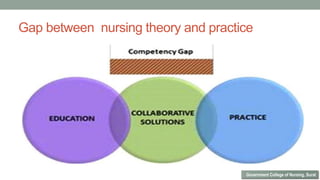
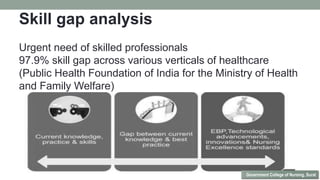
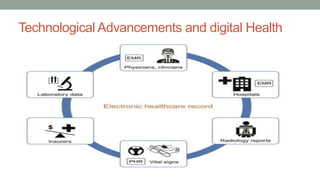
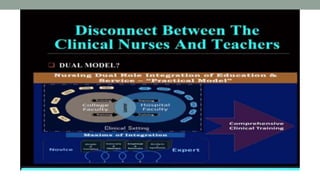
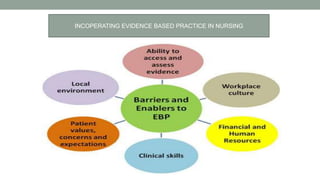
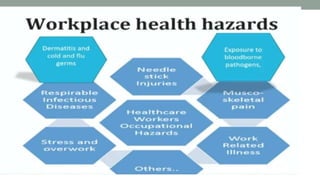
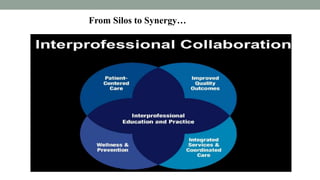
Nurses play a vital role in healthcare but face many challenges in nursing education and practice. The document discusses issues like nursing shortages, disparities in rural healthcare access, and the increasing workload and complex healthcare environment exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. It also outlines strategies recommended by WHO like increasing investments in nursing education, leadership training, and service delivery to address the global shortfall of nurses by 2030. The presentation highlights specific challenges faced by nurses in India such as inadequate salaries, lack of promotion criteria, workplace violence, and staffing shortages. It proposes managing these challenges through excellence, research, advocacy, career development, and collective bargaining.