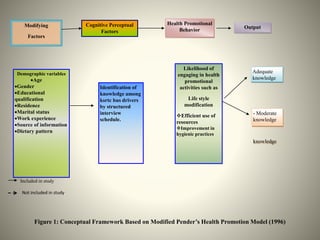
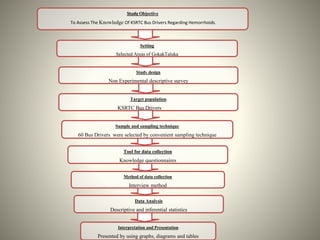
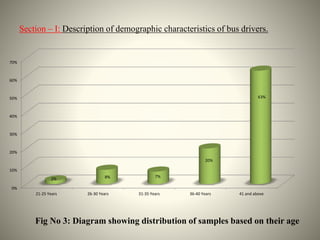
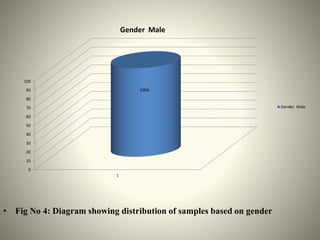
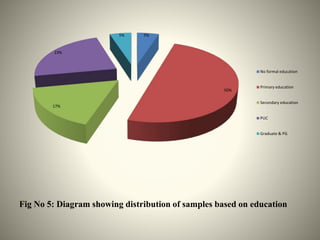
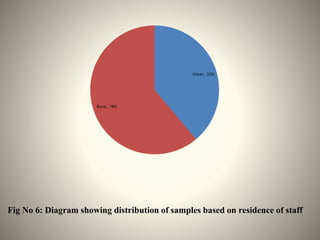
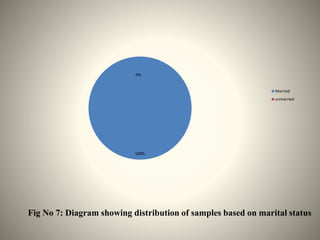
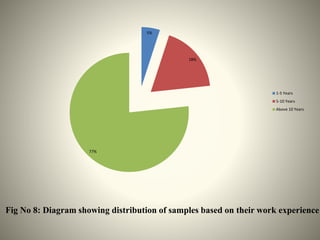
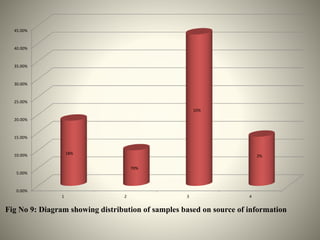
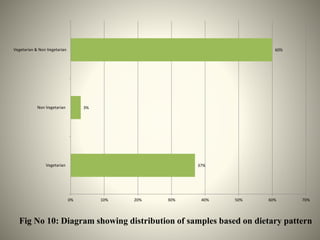
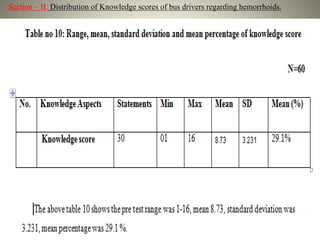
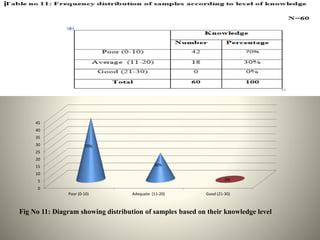
- The study aimed to assess the knowledge of hemorrhoids among 60 KSRTC bus drivers in Gokak taluka, India.
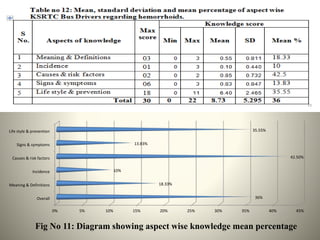
- Most drivers had poor overall knowledge of hemorrhoids, though they scored best on knowledge of causes and risk factors.
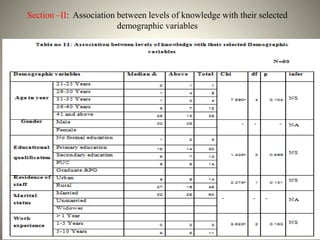
- The findings suggest that educational interventions are needed to improve drivers' understanding of hemorrhoids, including their meaning, incidence, signs and symptoms, and lifestyle prevention strategies.