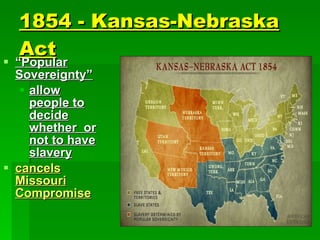
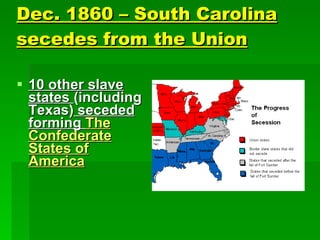
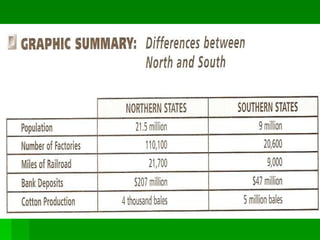
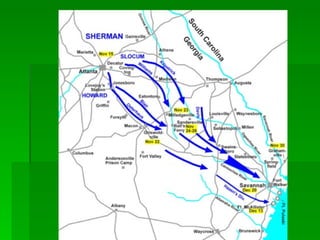
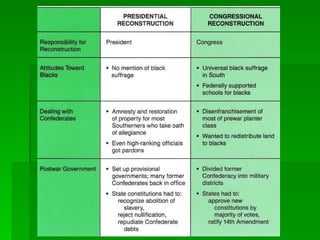
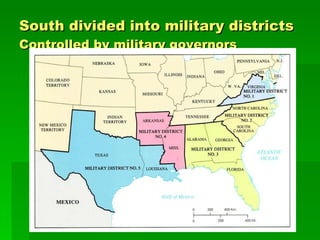
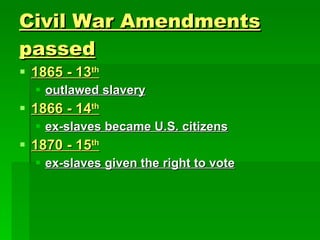
Frederick Douglas was an escaped slave who lectured against slavery and published an abolitionist newspaper called The North Star. The Missouri Compromise of 1820 maintained a balance of power in Congress by admitting Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state, dividing the Louisiana Territory between slave and free territories north and south of the line. The Dred Scott decision of 1857 ruled that slaves were property without rights, further fueling tensions between North and South. Abraham Lincoln was elected President in 1860 on a platform opposing the expansion of slavery, leading several Southern states to secede and form the Confederate States of America, precipitating the Civil War.