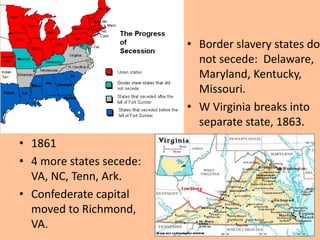
This document provides a summary of key events and developments in the United States leading up to and during the American Civil War from the 1850s to the 1860s. It outlines the political crises over slavery and states' rights that increased sectional tensions between the North and South. It discusses pivotal court cases like Dred Scott v. Sandford and events like the raid on Harper's Ferry that further divided the nation. The document also summarizes the secession of Southern states, the outbreak of the Civil War after the attack on Fort Sumter, and how the war expanded the powers of the federal government and ultimately led to the Emancipation Proclamation freeing millions of enslaved people.