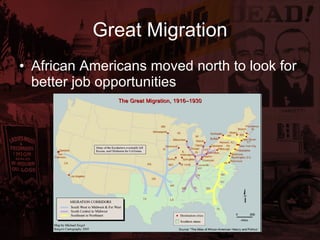
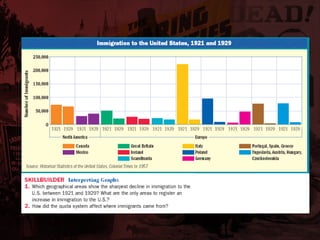
The Roaring 20s saw many social and political changes in the US following WWI. There was a Red Scare where suspected communists were persecuted following the Russian Revolution. Immigration was greatly restricted through the Emergency Quota Act of 1921. The Ku Klux Klan grew due to anti-immigrant sentiment. Politically, the Harding administration was rocked by scandals like Teapot Dome, where the Secretary of Interior illegally leased oil-rich lands. Culturally, the 1920s saw the rise of mass consumption fueled by new industries like automobiles and air travel, though some warned that unchecked prosperity could not last.