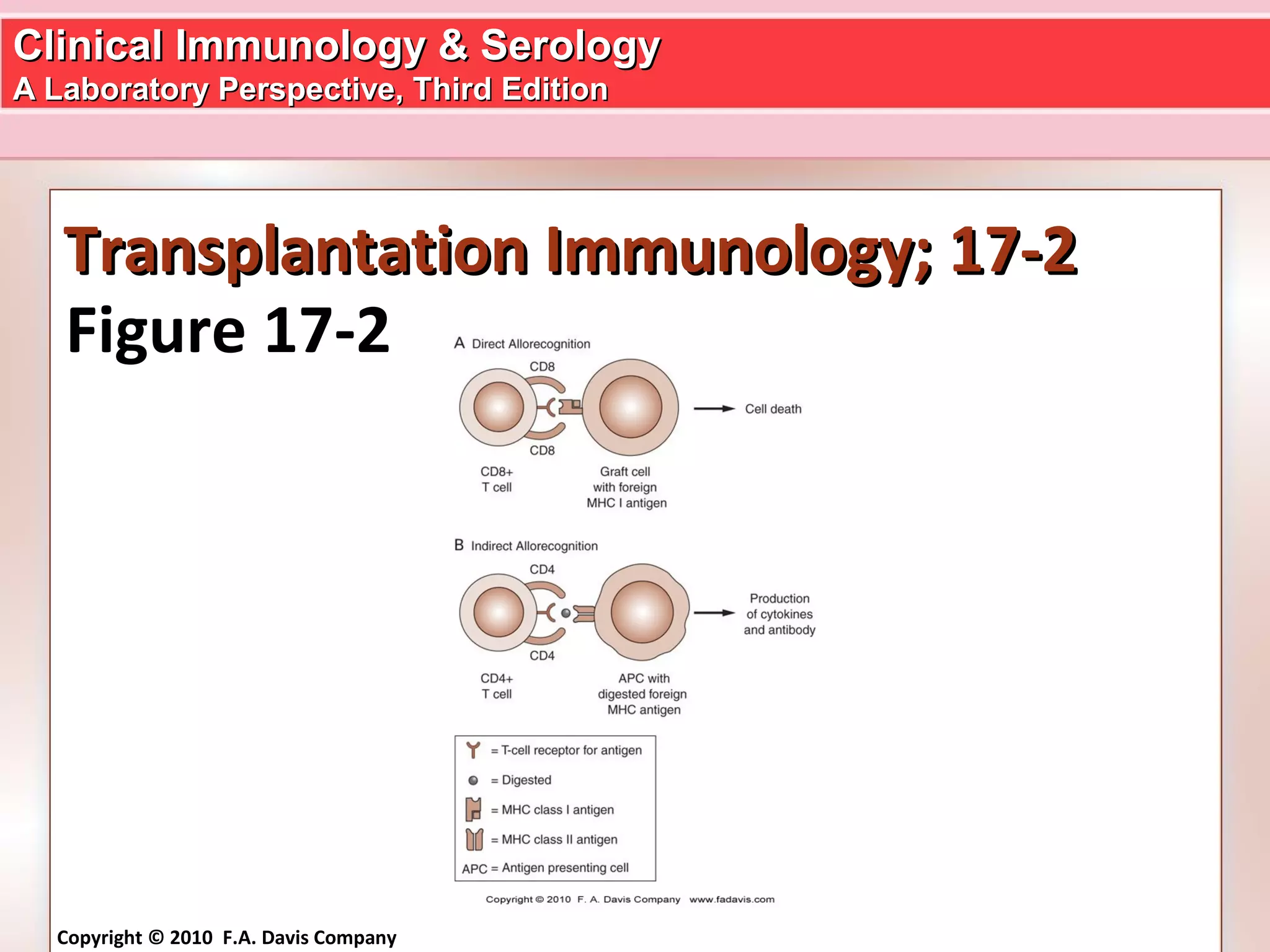
Transplantation involves transferring cells or tissues between individuals and can be lifesaving but also carries immunological risks. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins encoded by HLA genes are the main targets recognized by the recipient's immune system, leading to graft rejection. Careful HLA typing and screening for antibodies is crucial before transplantation to minimize immunological incompatibility between donor and recipient. Immunosuppressive drugs are used to reduce the immune response and prevent rejection after transplantation.