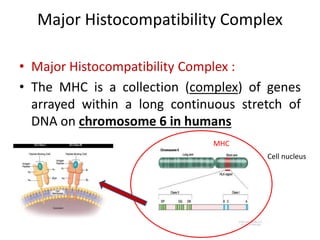
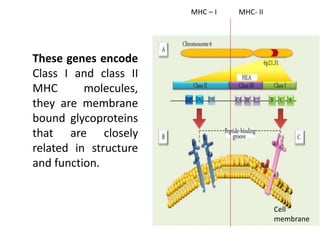
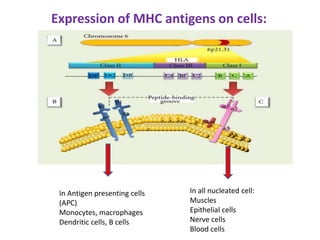
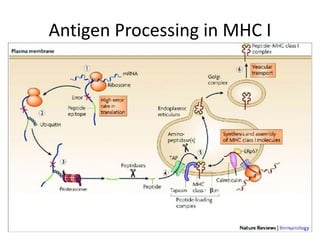
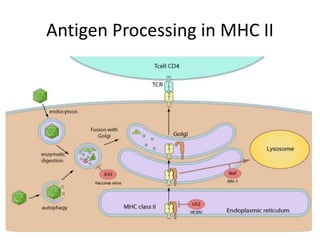
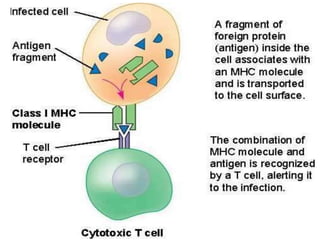
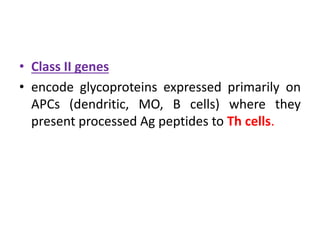
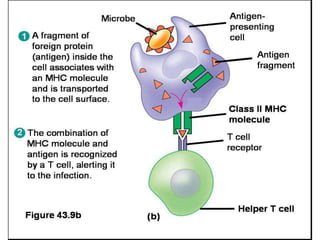
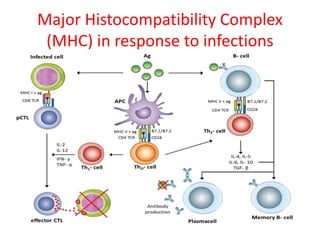
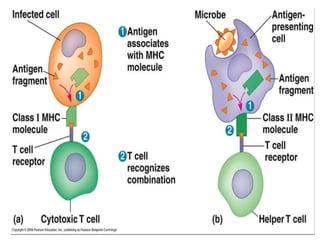
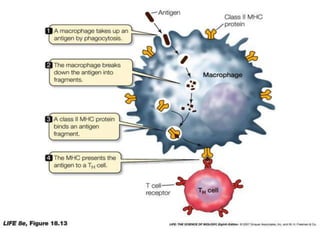
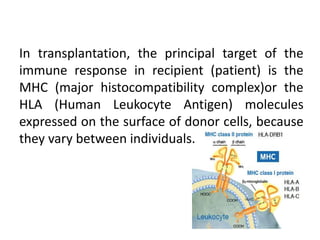
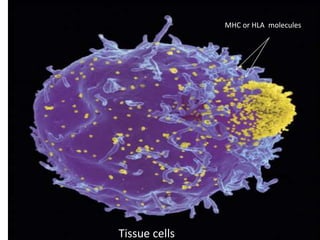
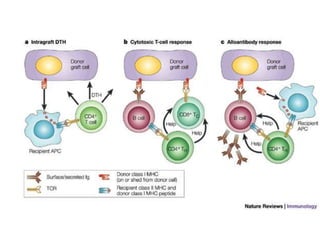
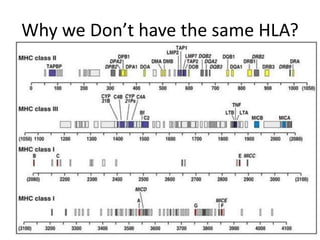
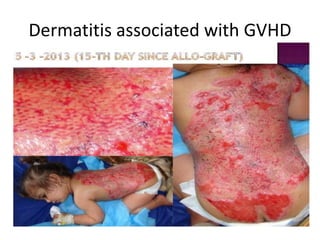
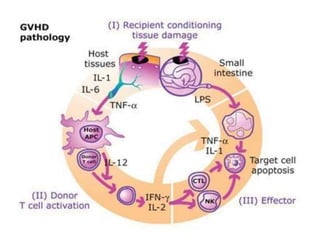
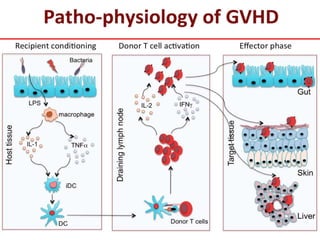
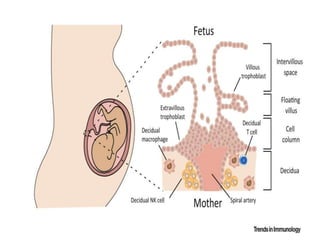
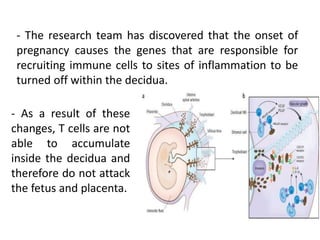
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) plays a key role in the immune system's response to transplants and infections. The MHC is a set of genes that encode MHC molecules which are expressed on nearly all cells and present antigen peptides. There are three main classes of MHC molecules - Class I presents antigens to CD8+ T cells, Class II presents antigens to CD4+ T cells, and Class III encodes proteins involved in immune processes. MHC molecules are important in transplant rejection, as mismatches can trigger an immune response against the donor tissue. Careful HLA typing and matching is done to minimize rejection.