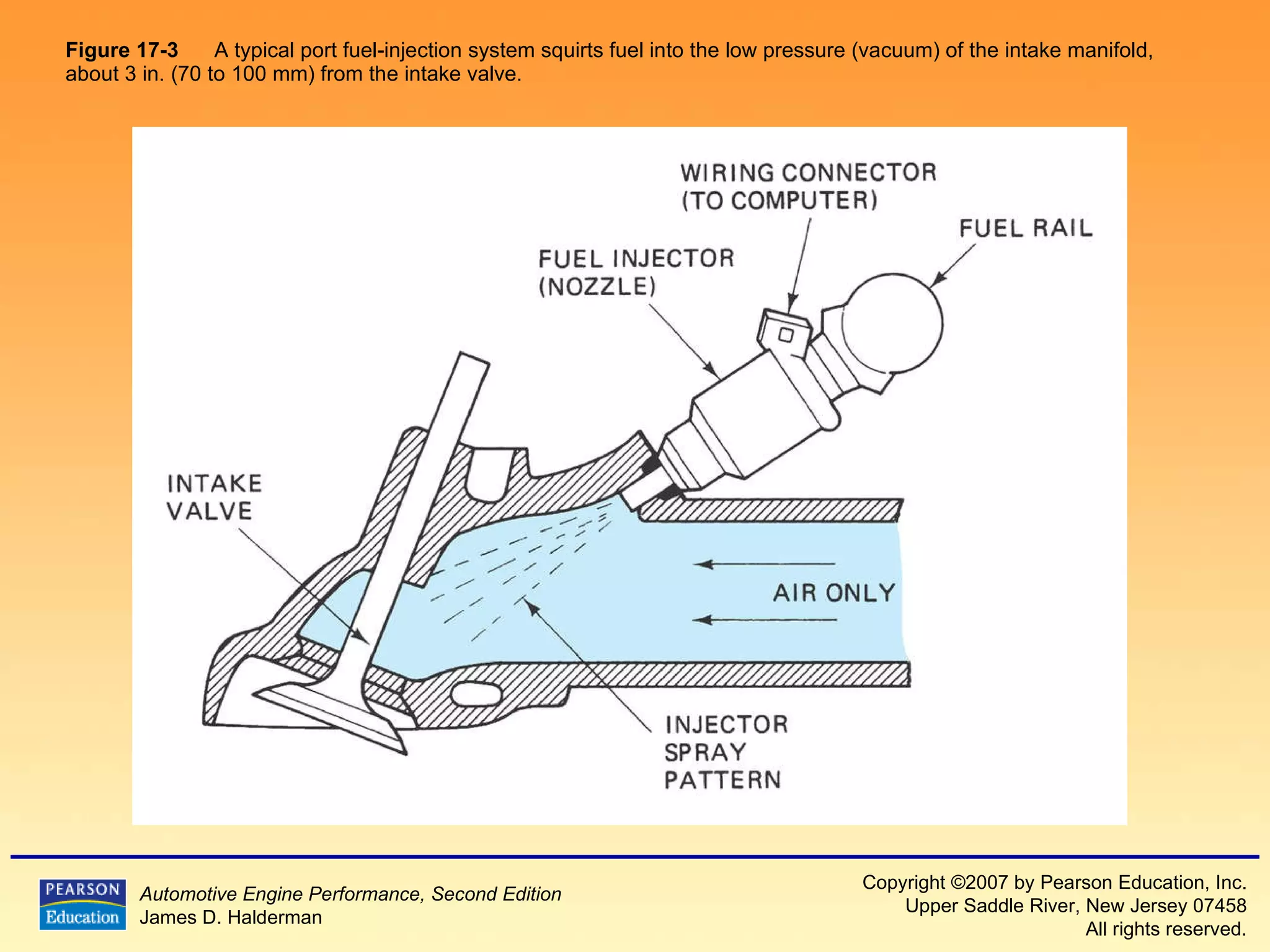
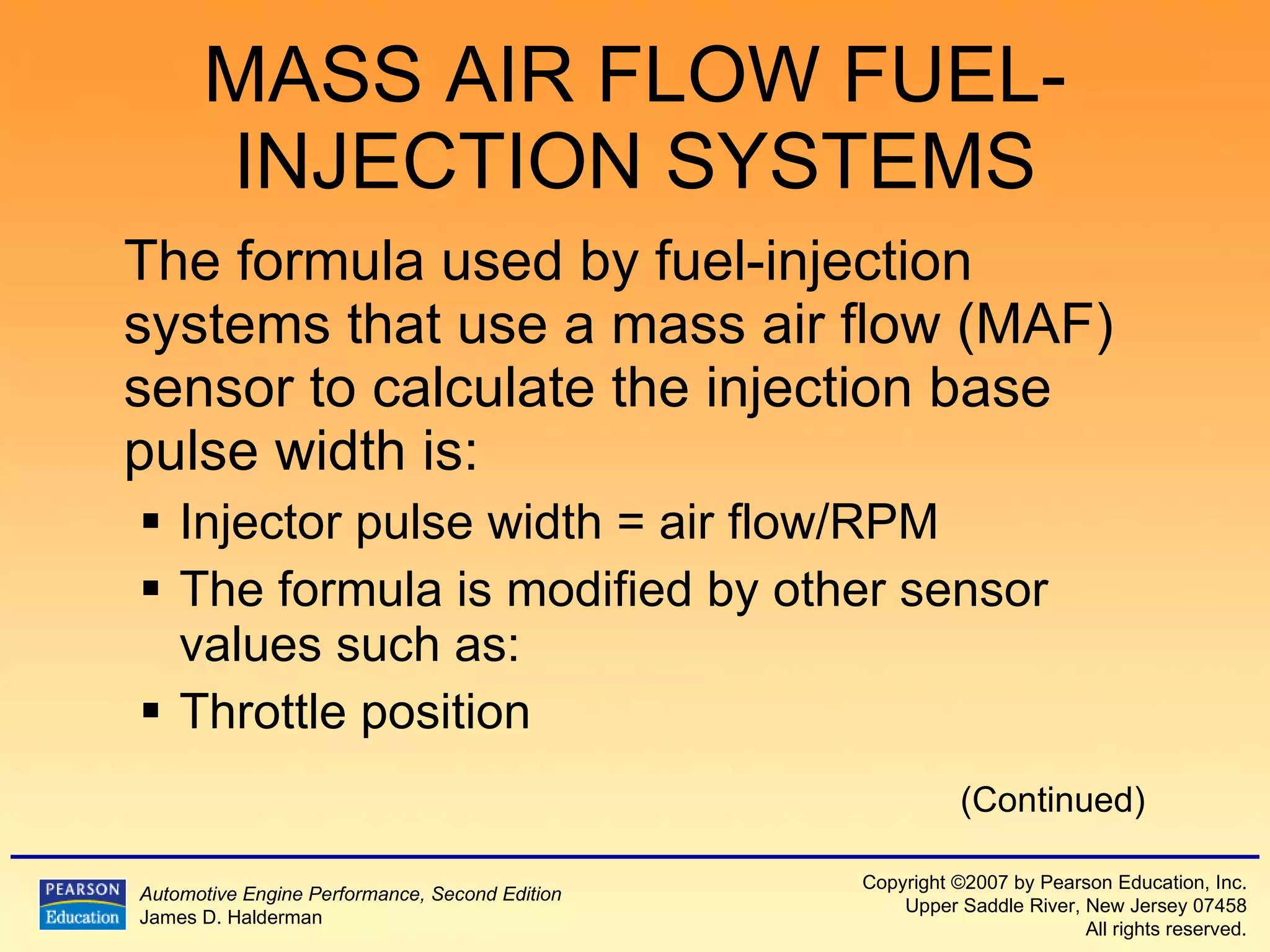
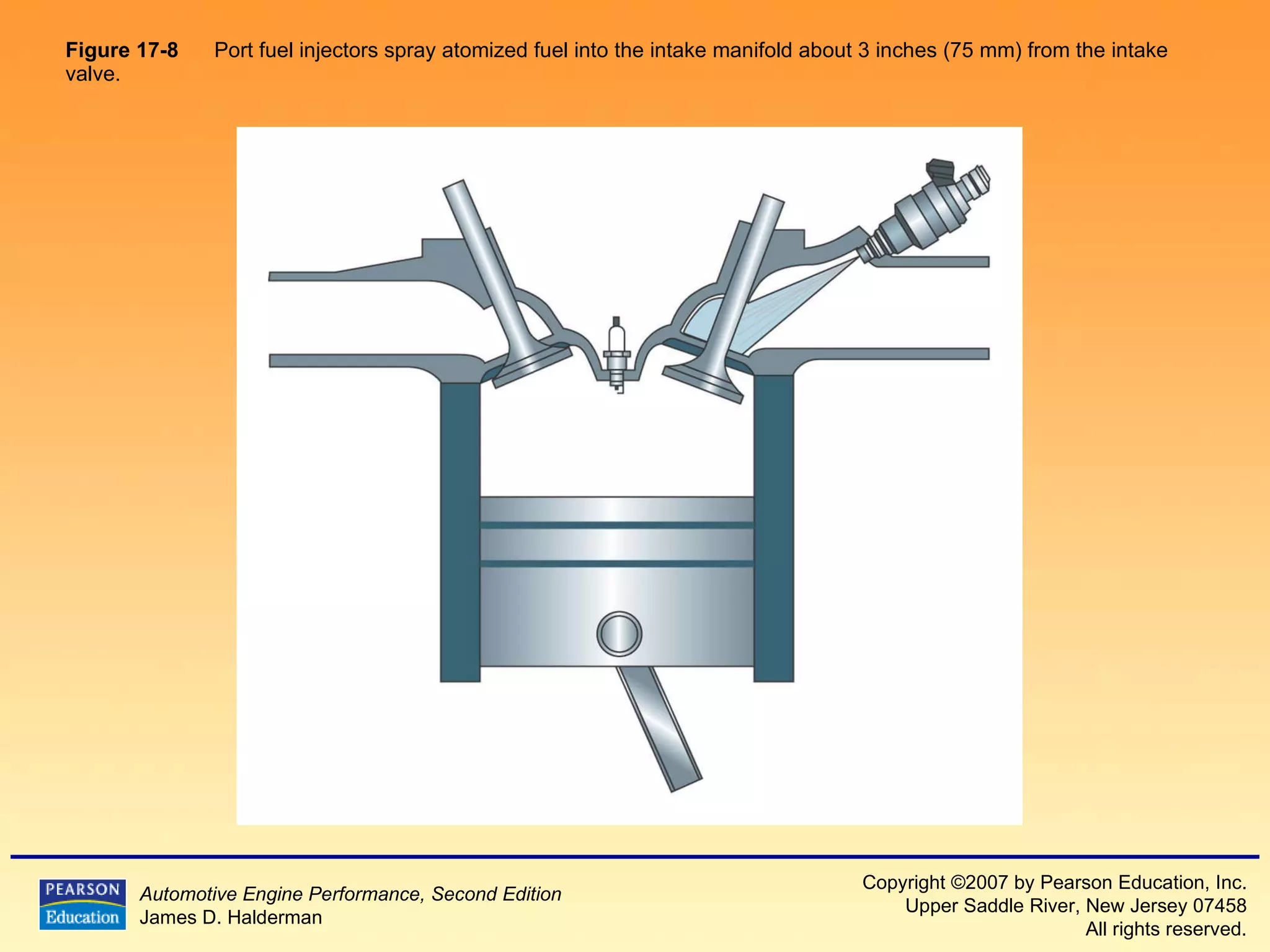
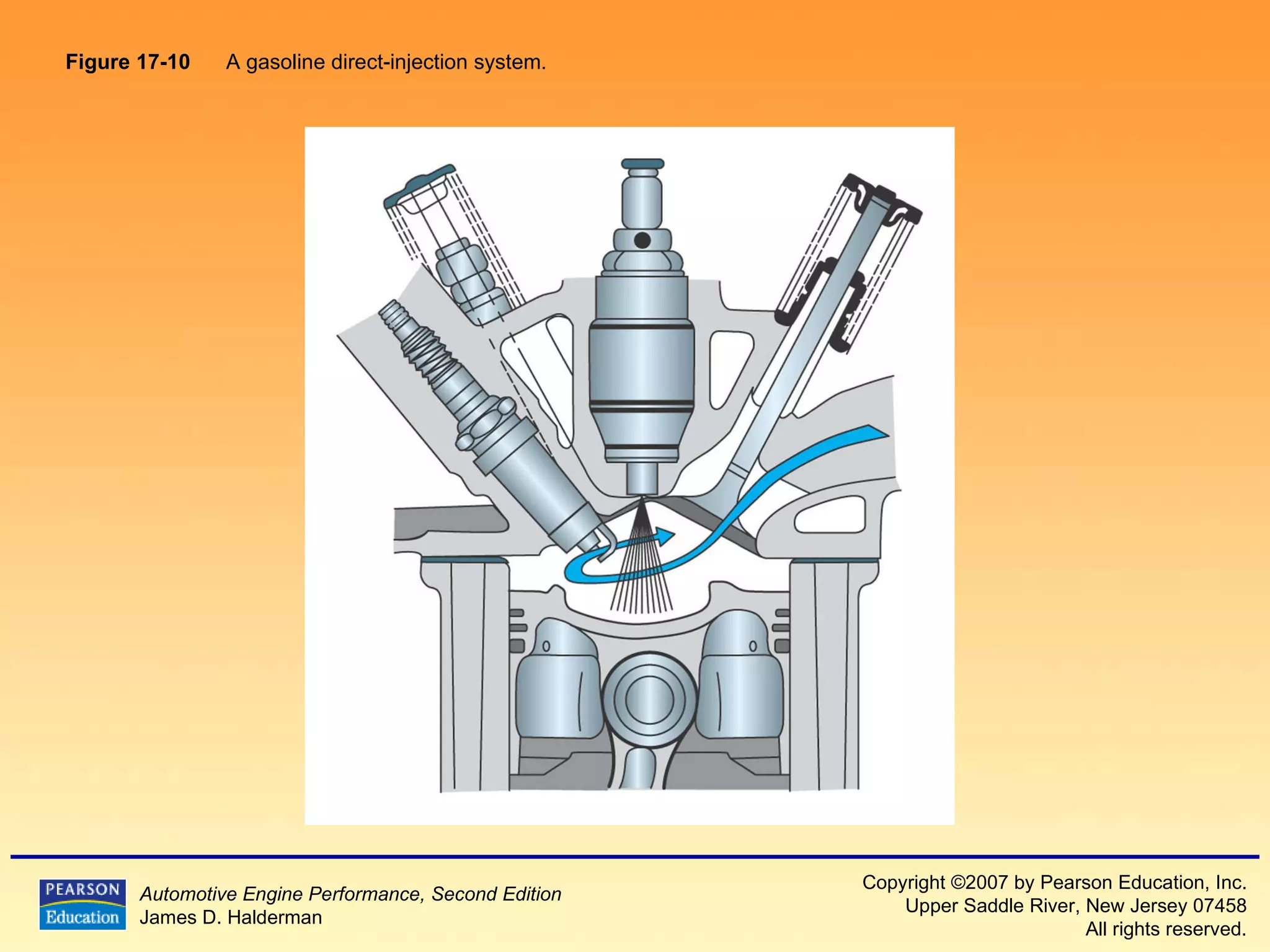
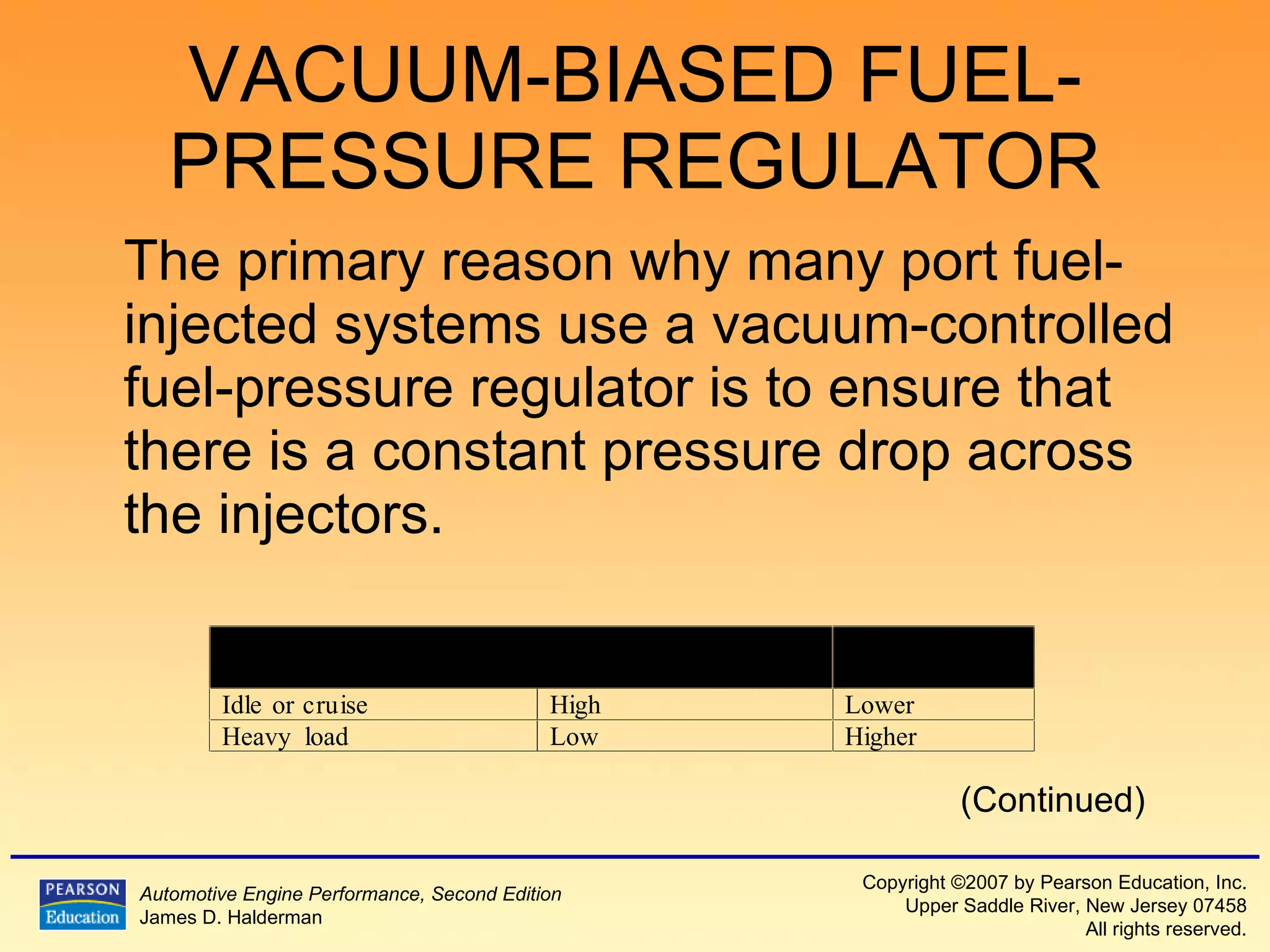
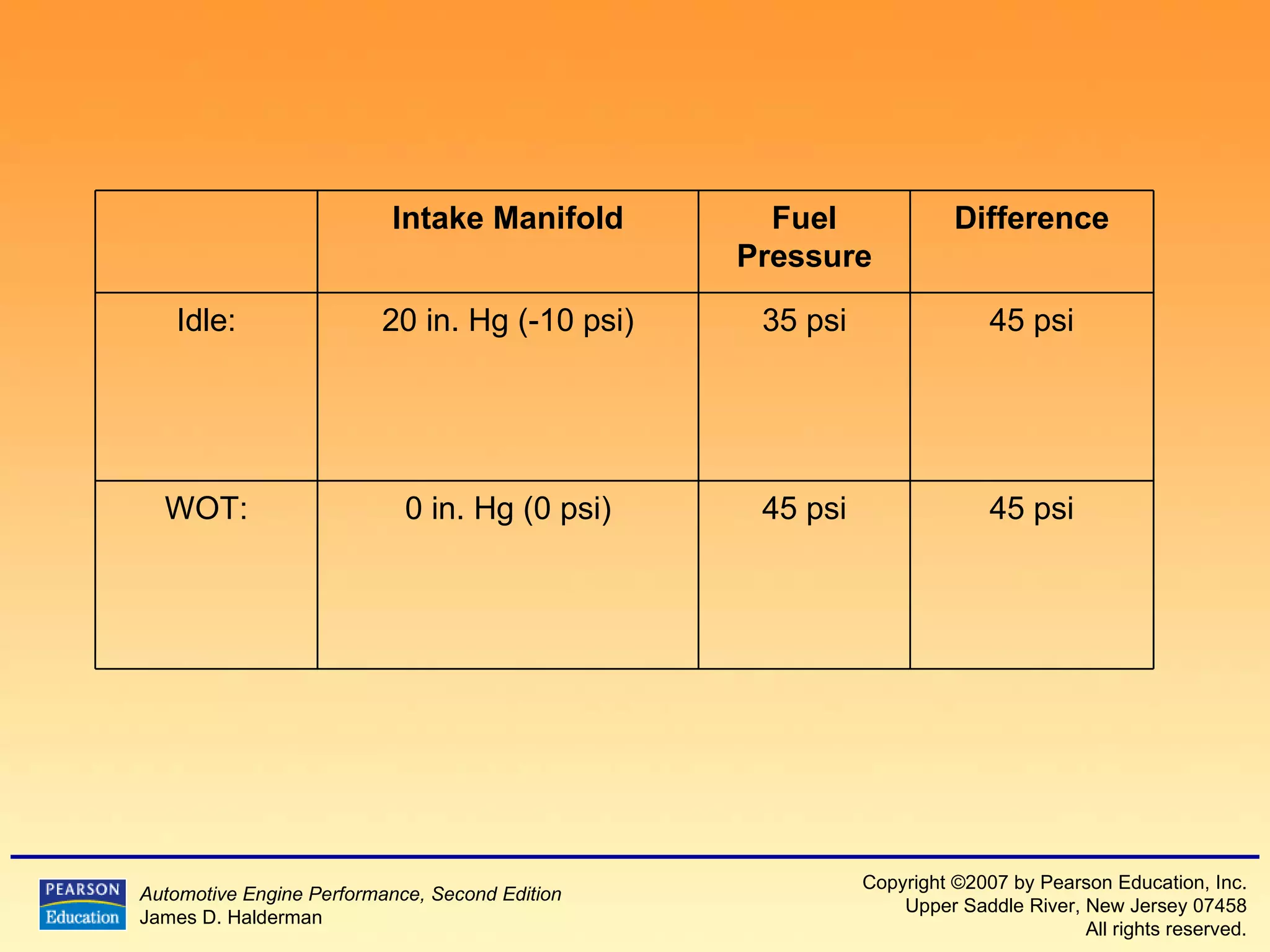
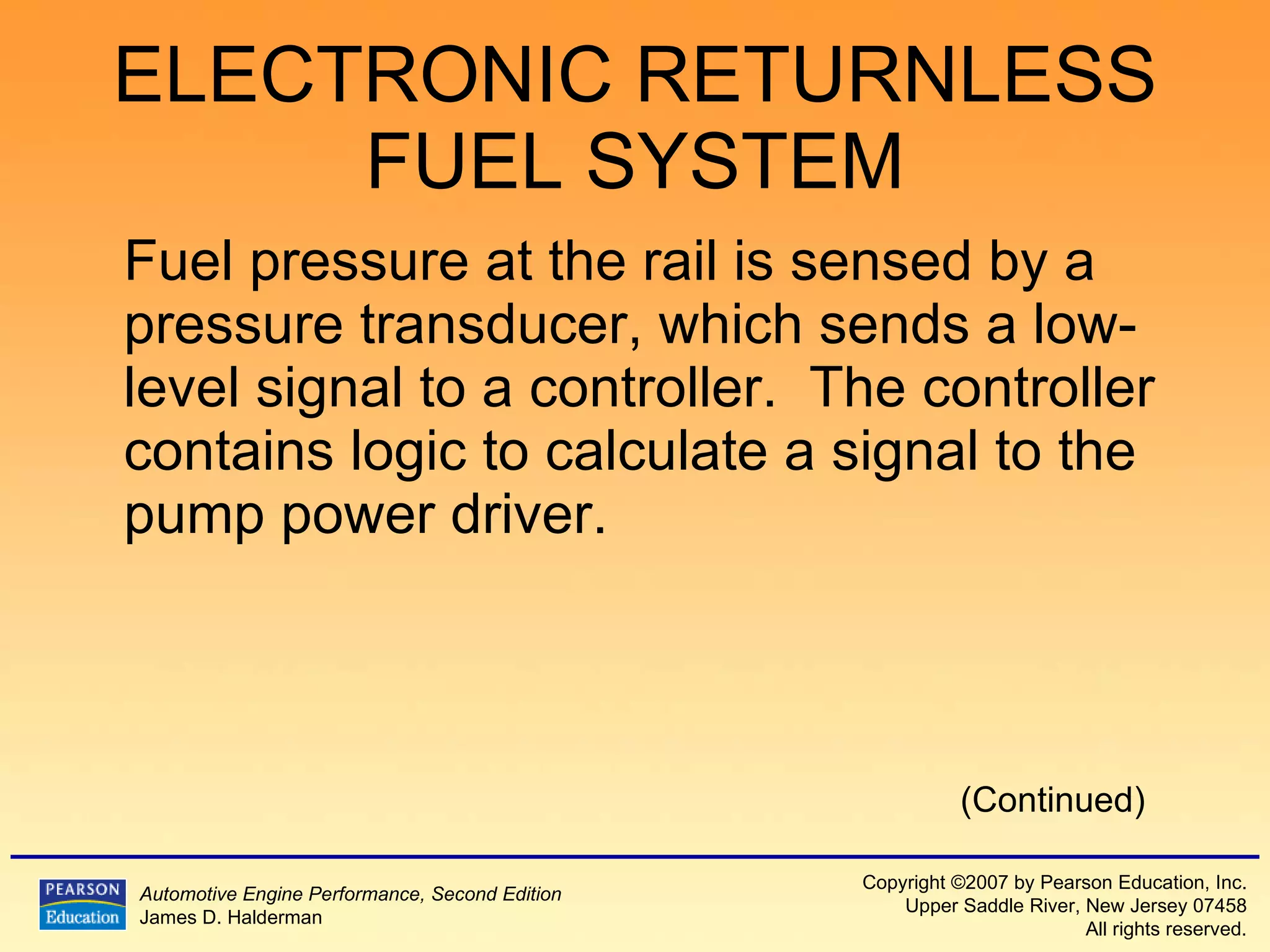
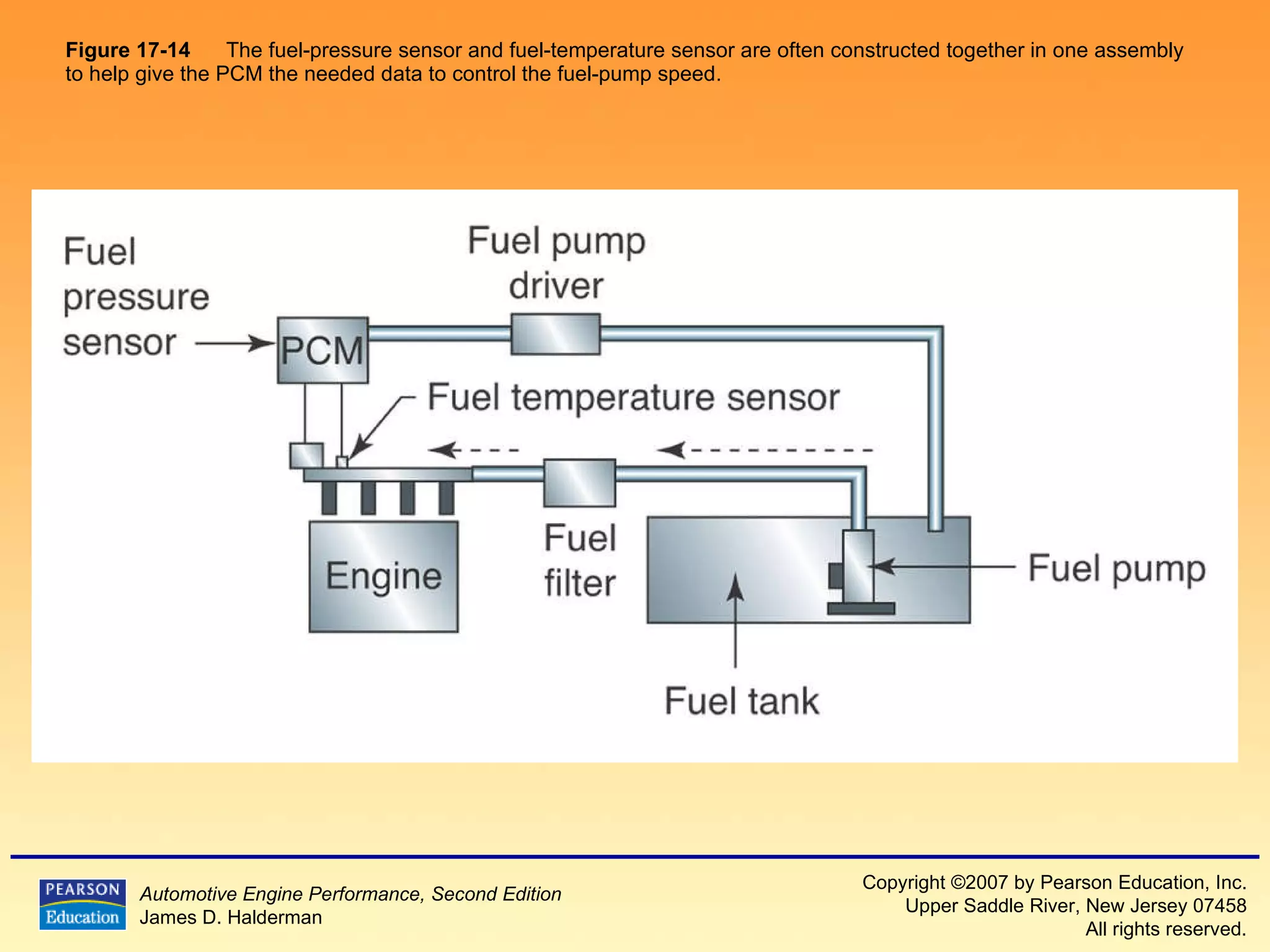
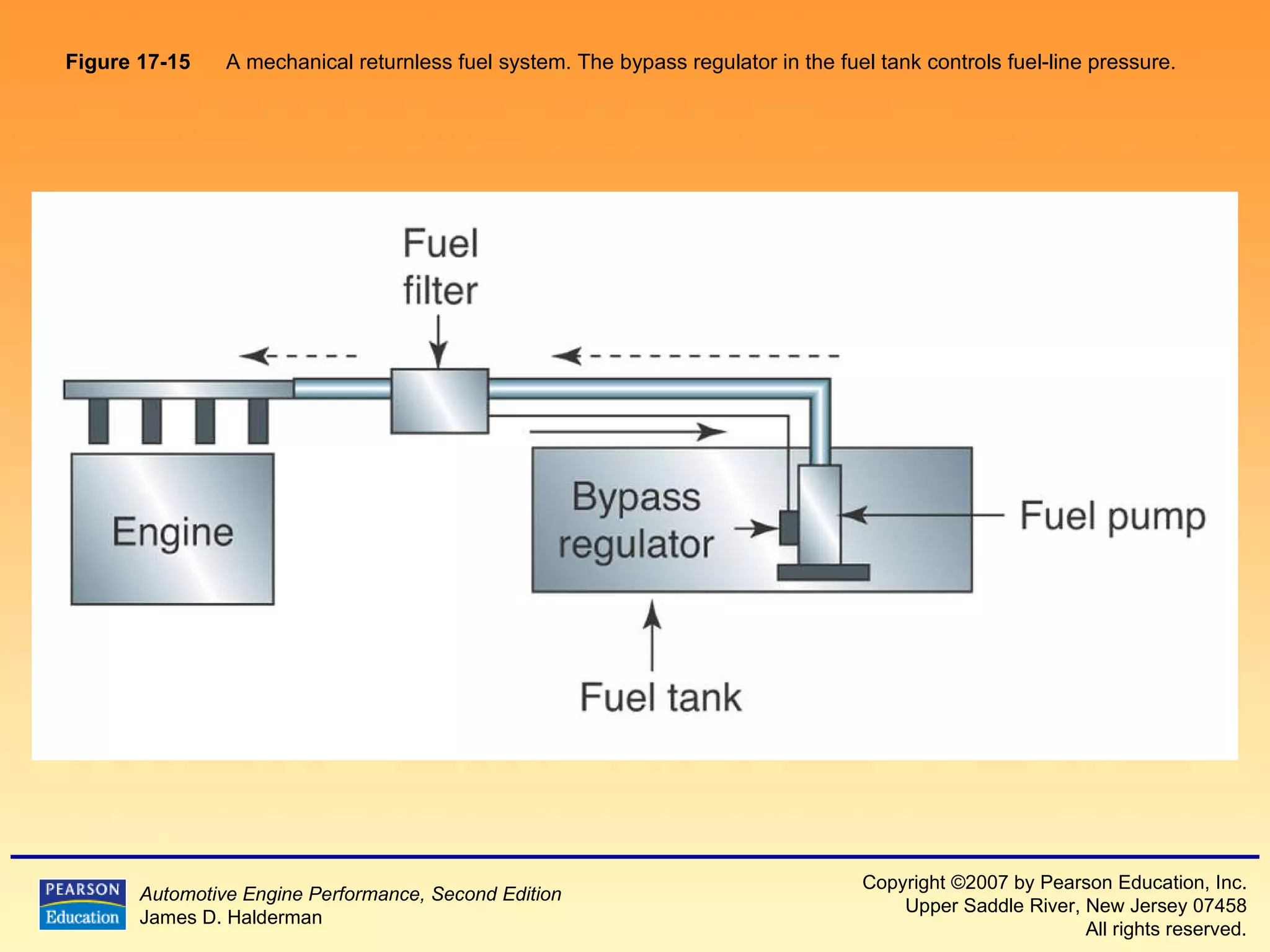
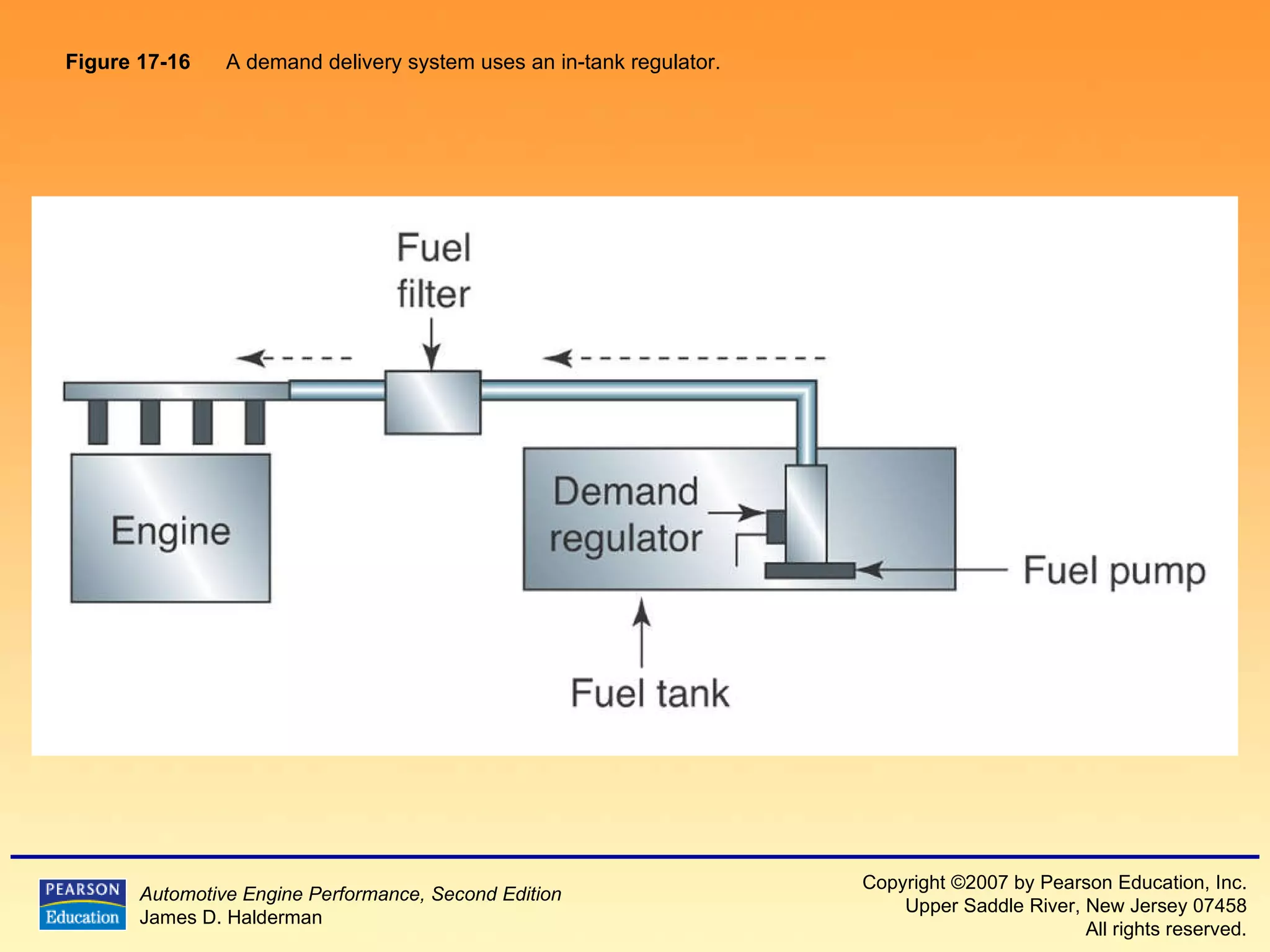
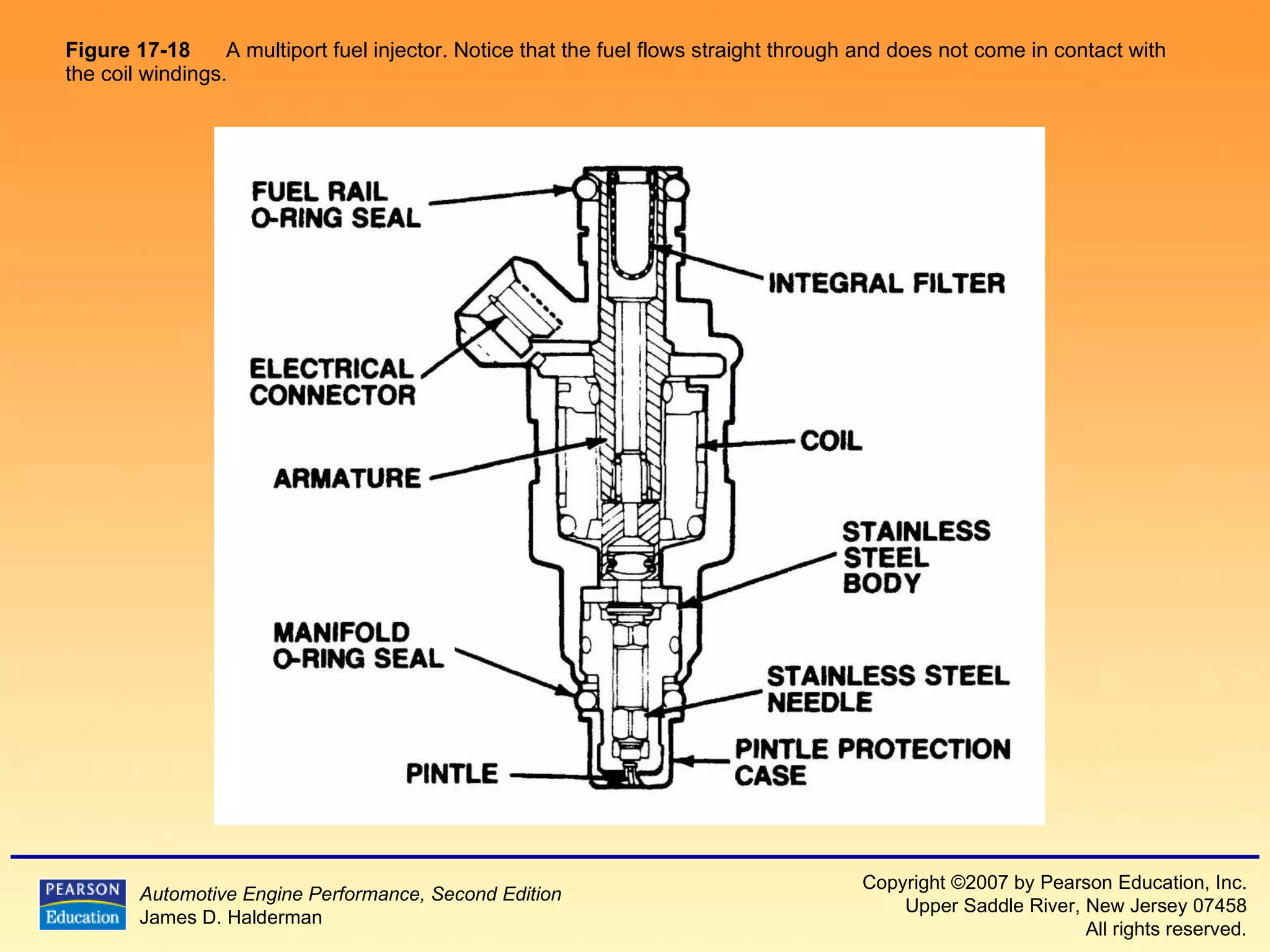
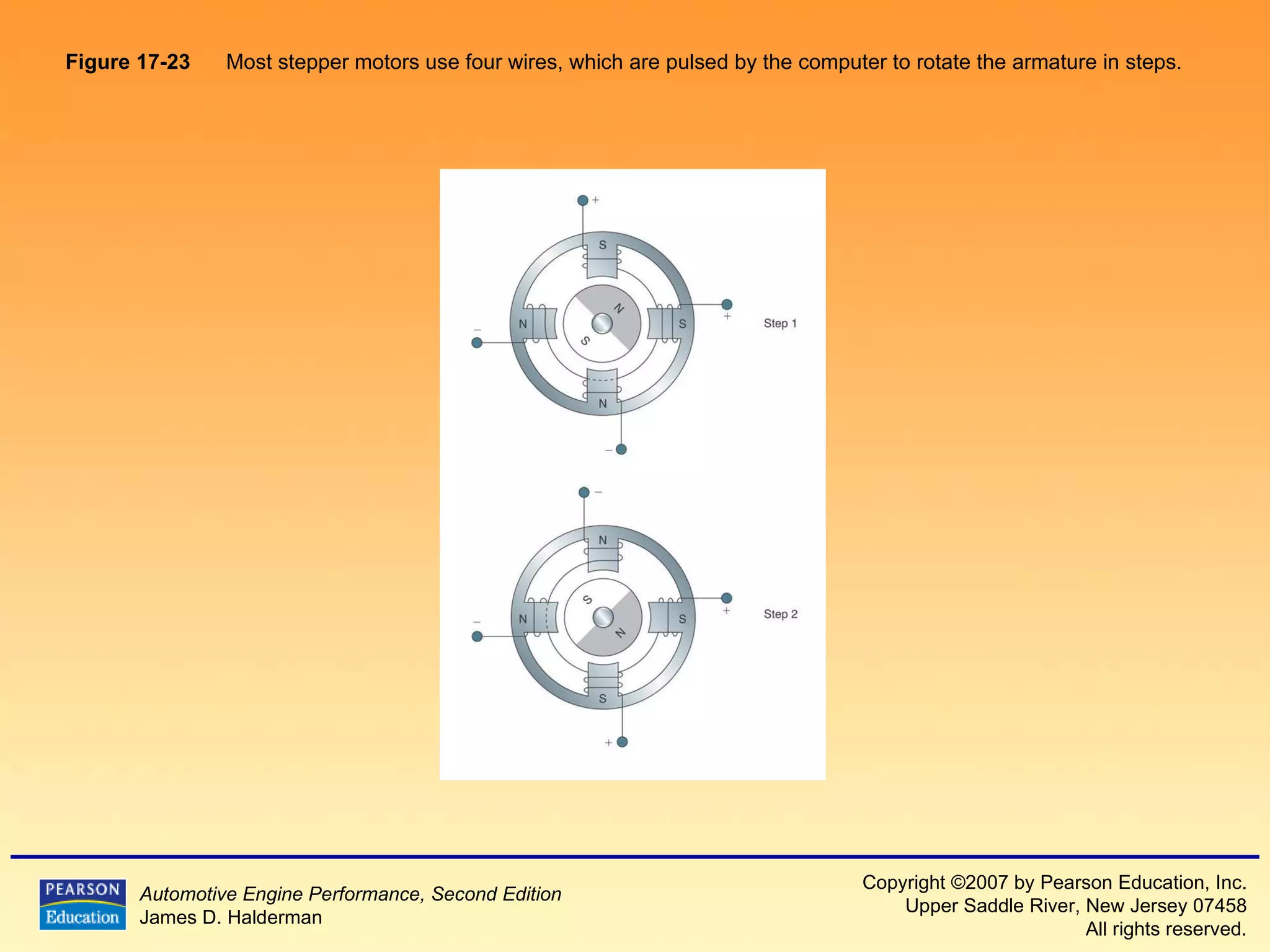
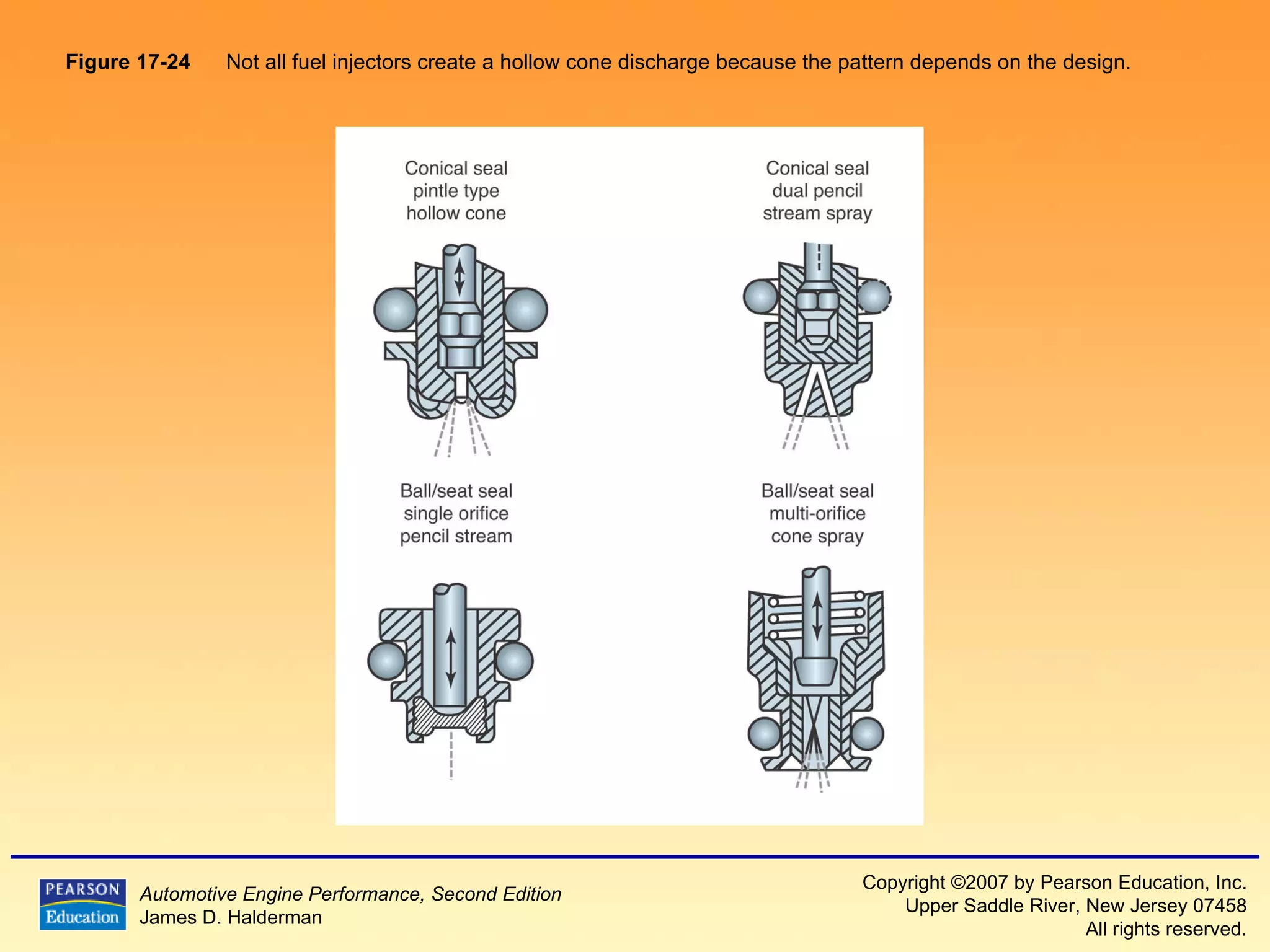
The document discusses various aspects of fuel injection systems, including:
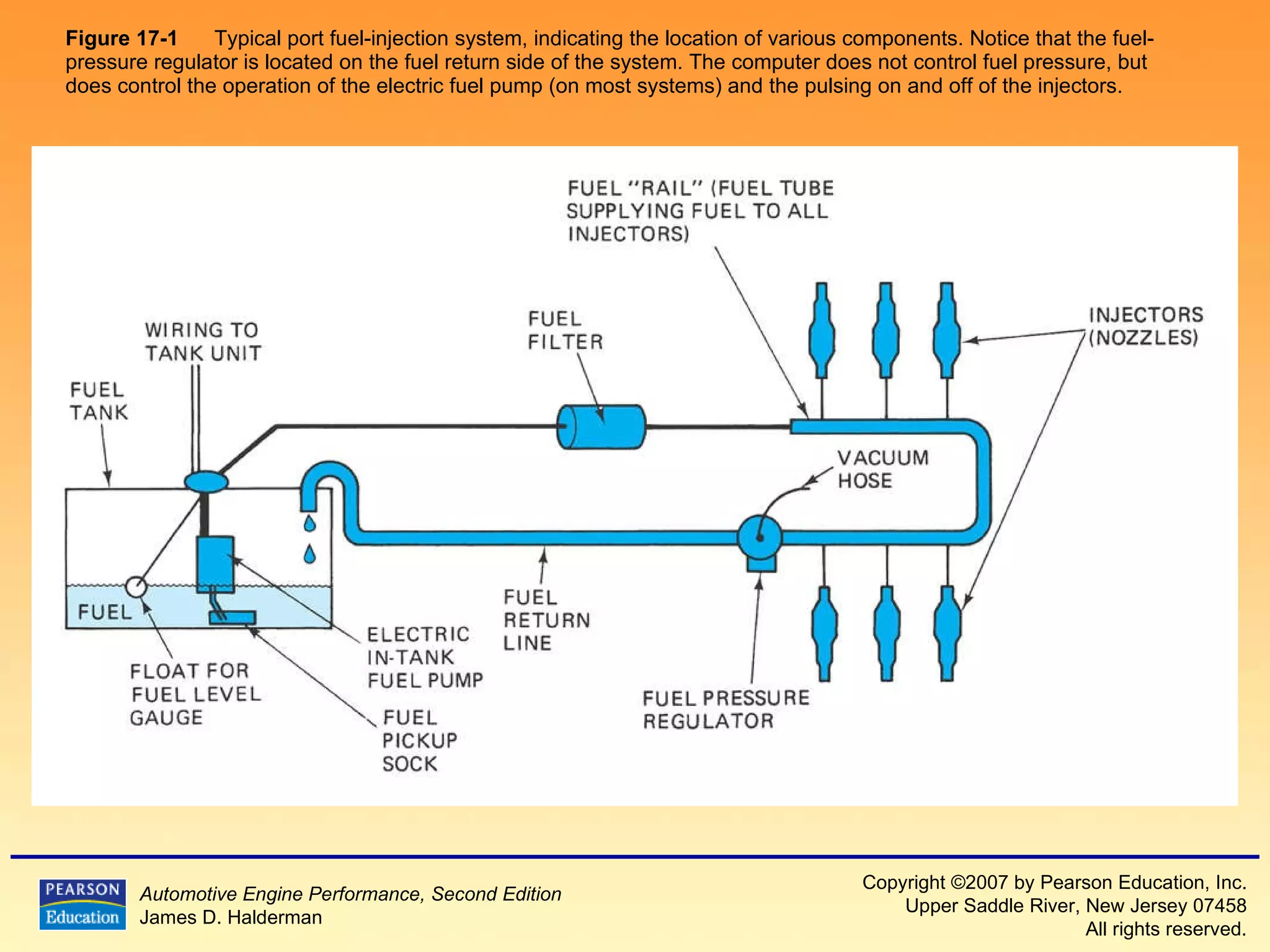
1) It describes the basic components and operation of port fuel injection and throttle body injection systems, including the fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, injectors, and how they are controlled by the computer.
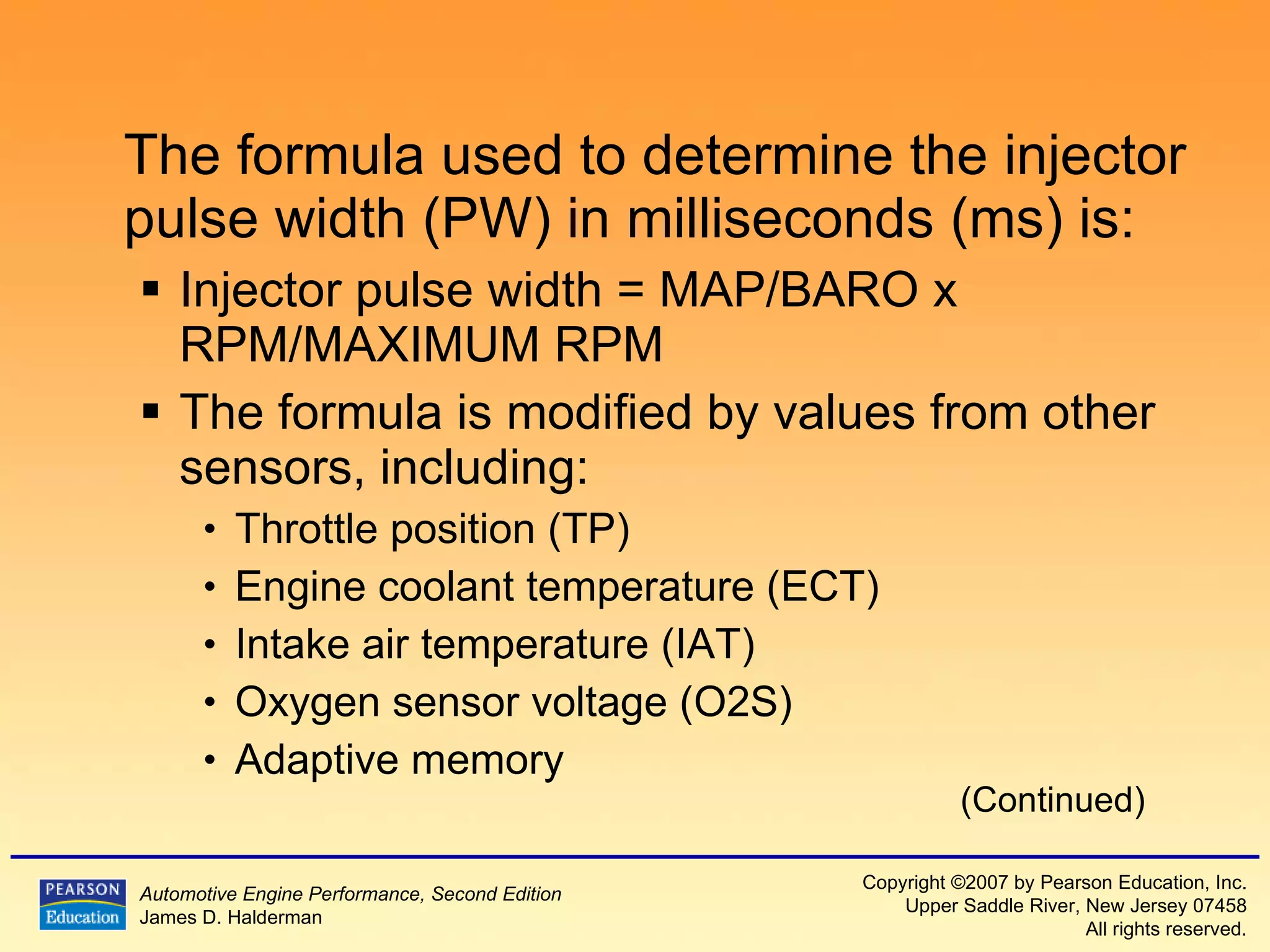
2) It explains the different types of fuel injection systems and how they determine the proper fuel amount, such as speed density and mass air flow systems.
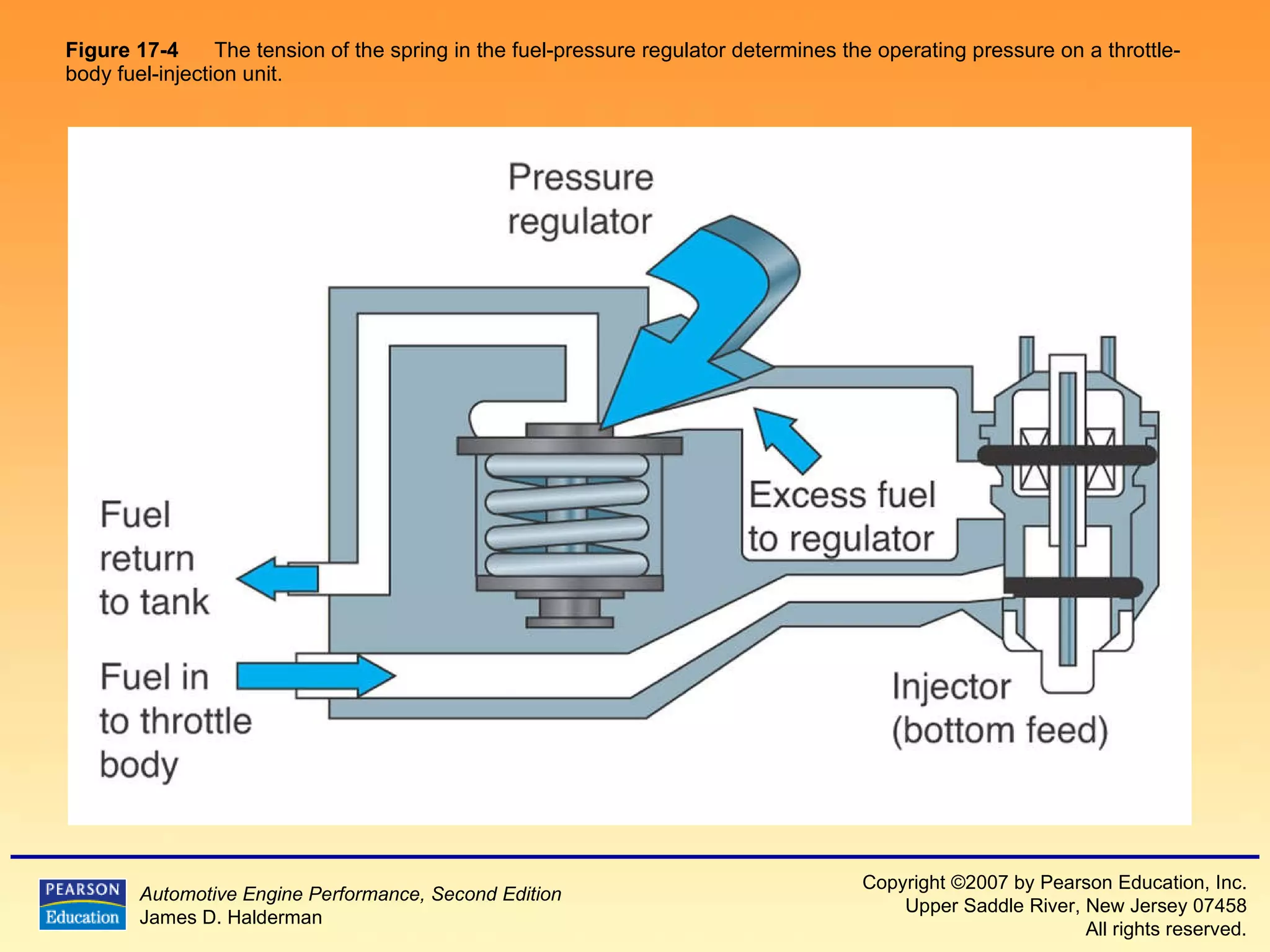
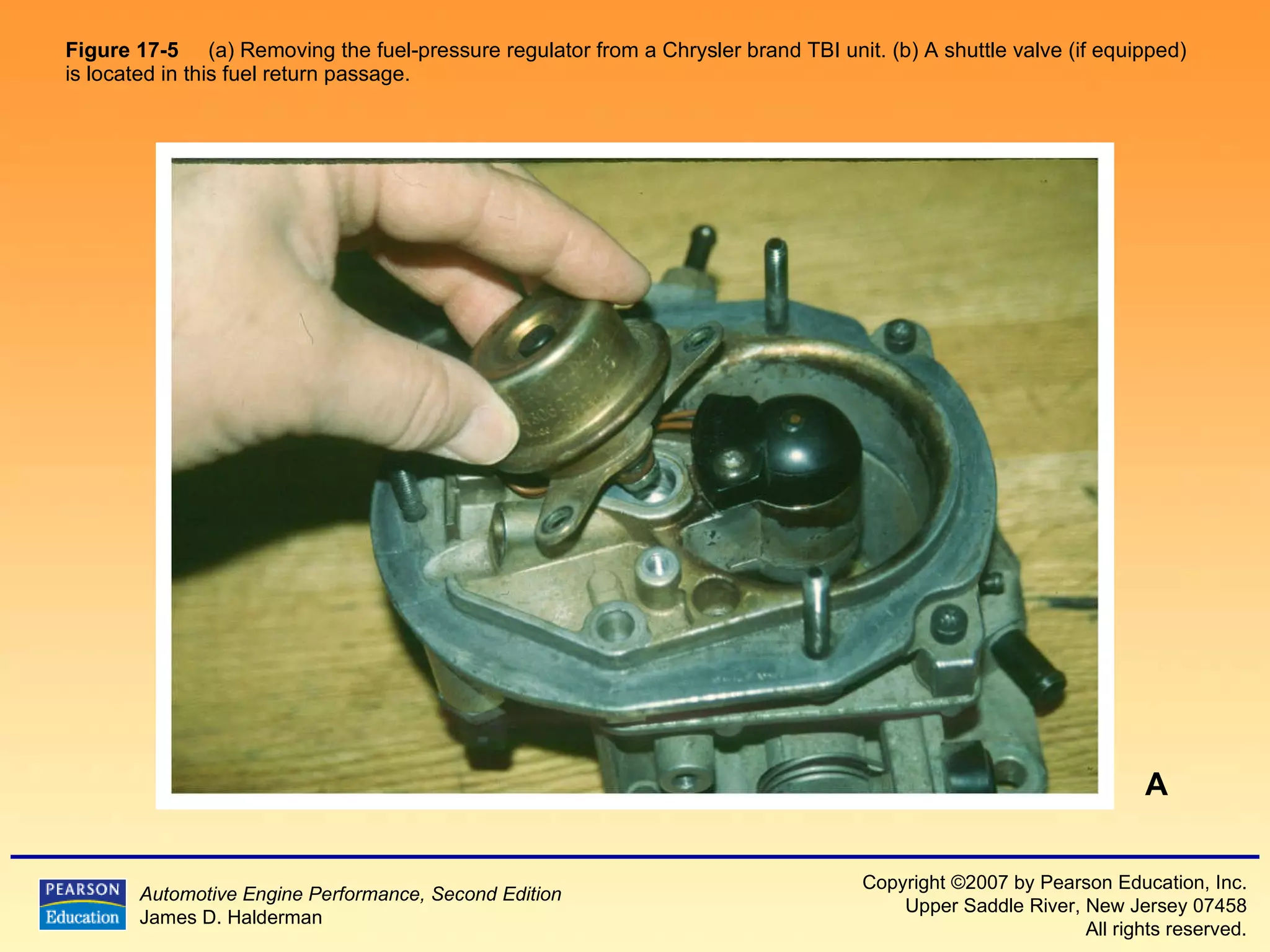
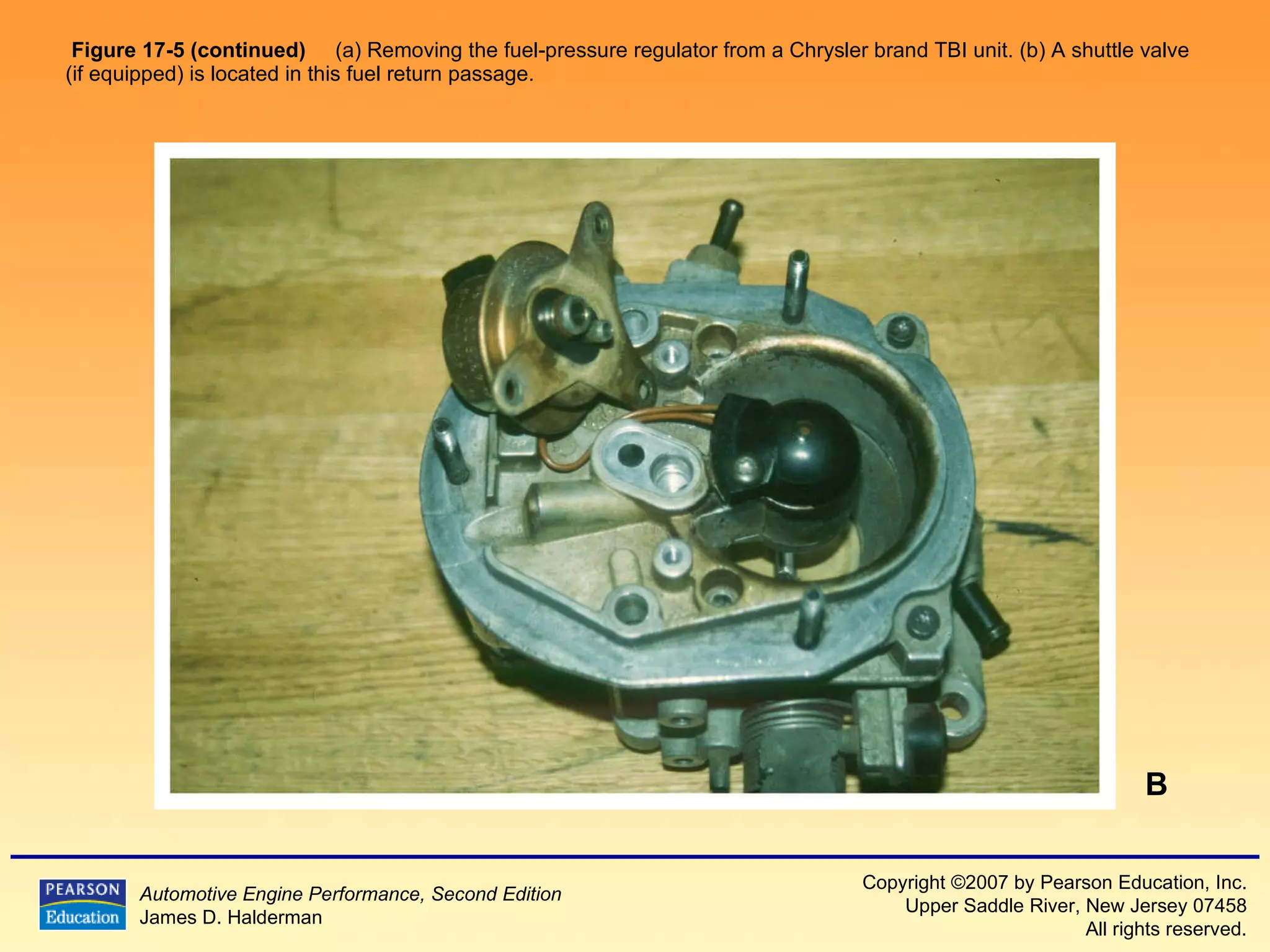
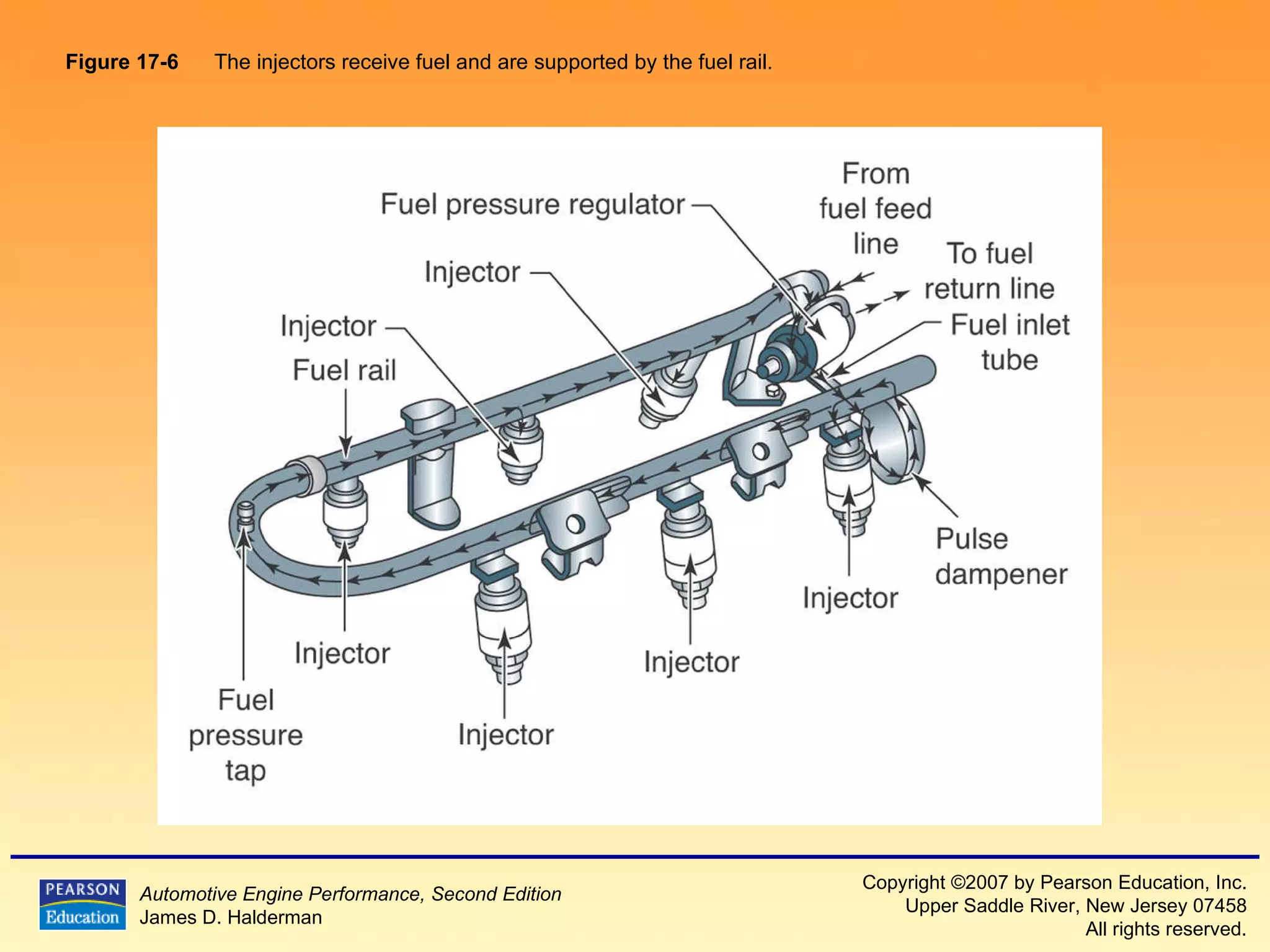
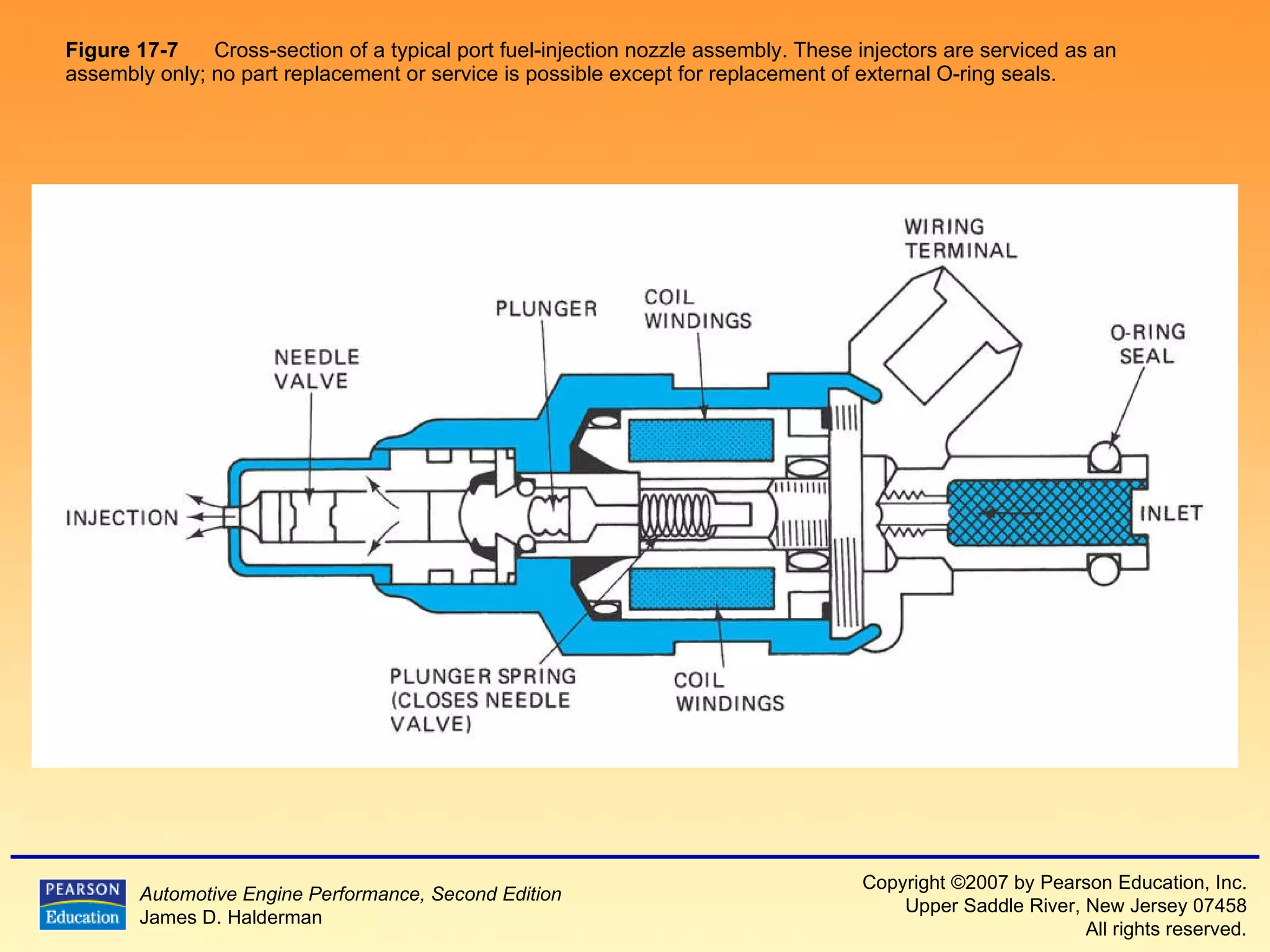
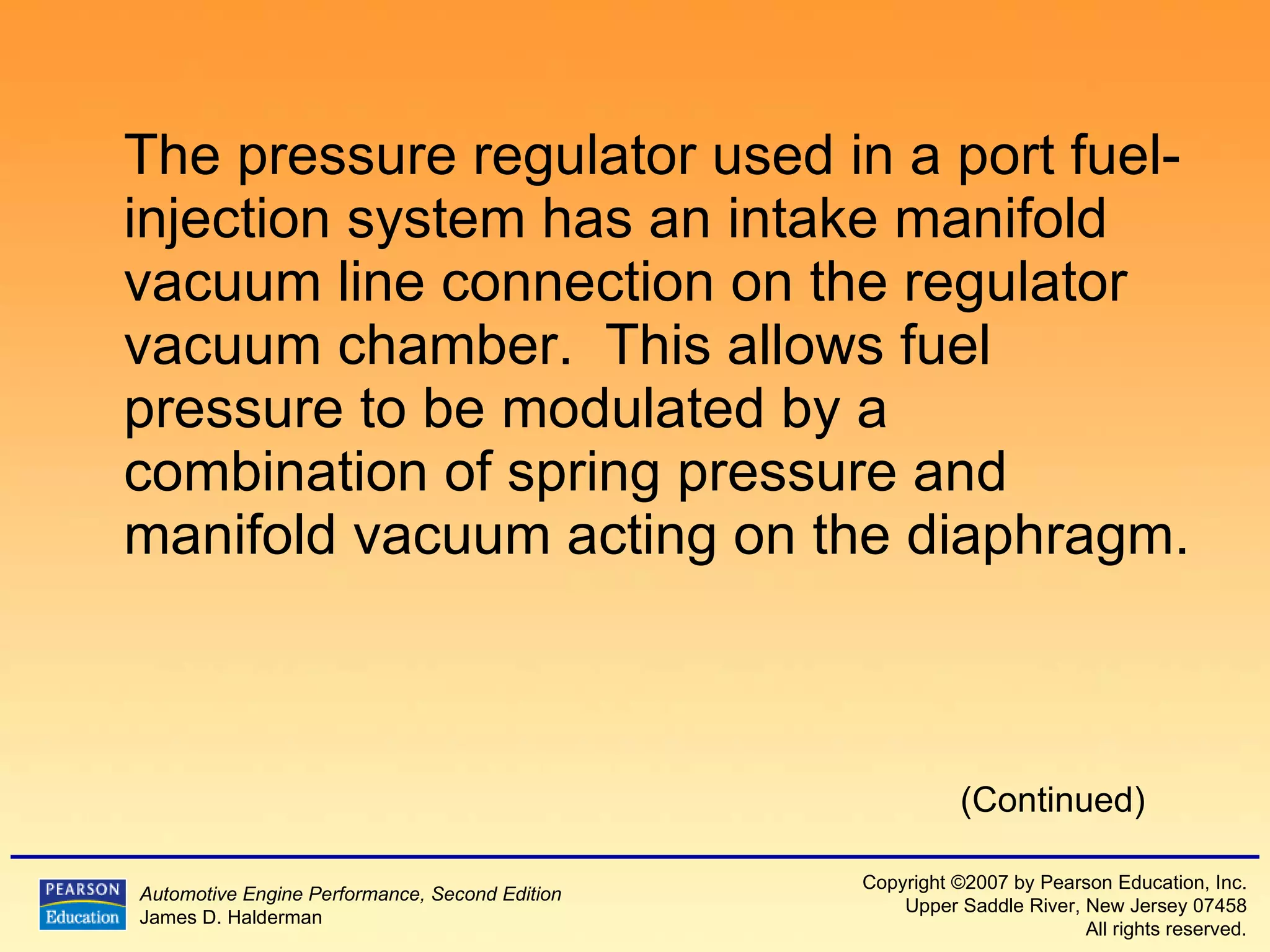
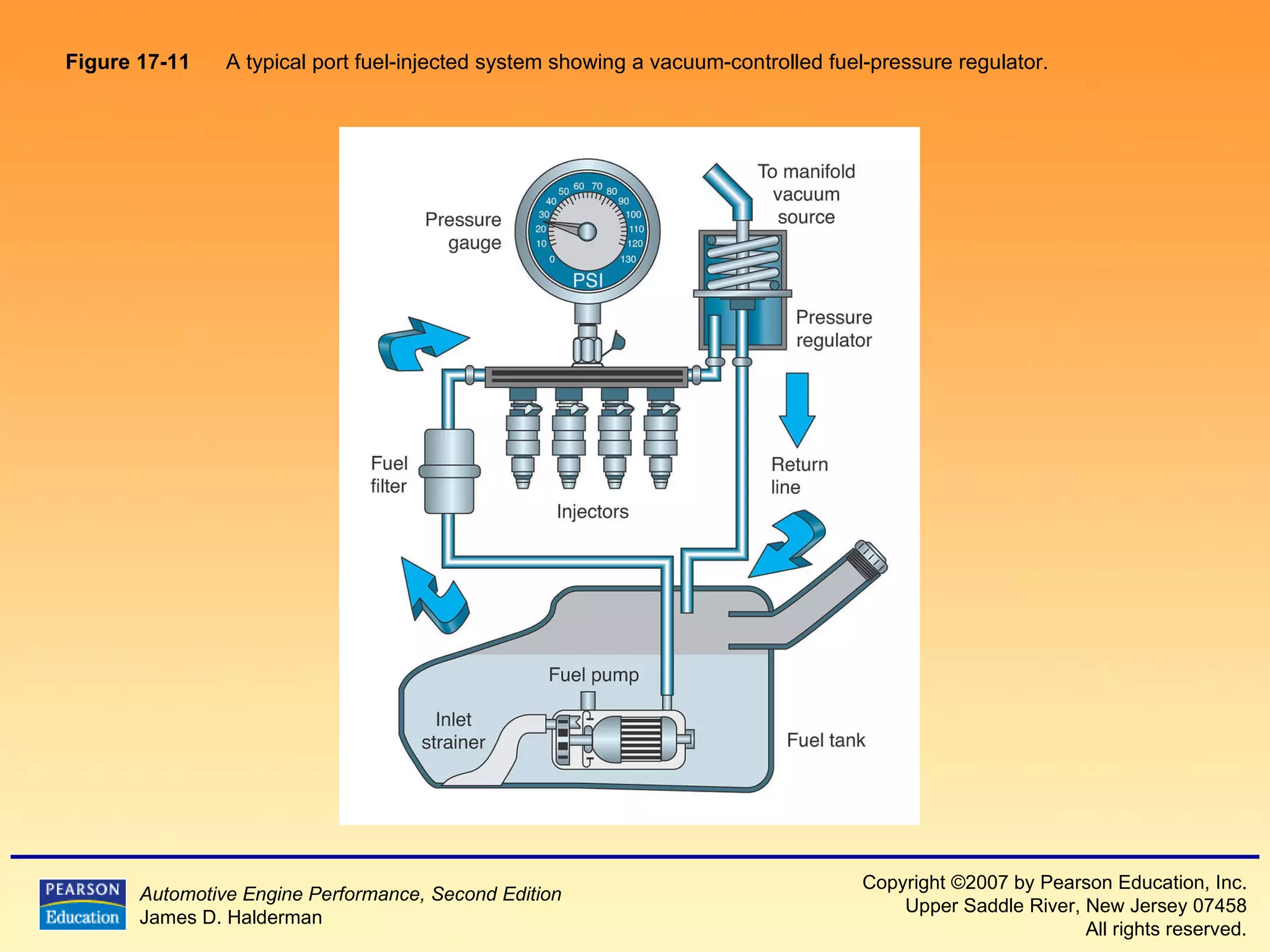
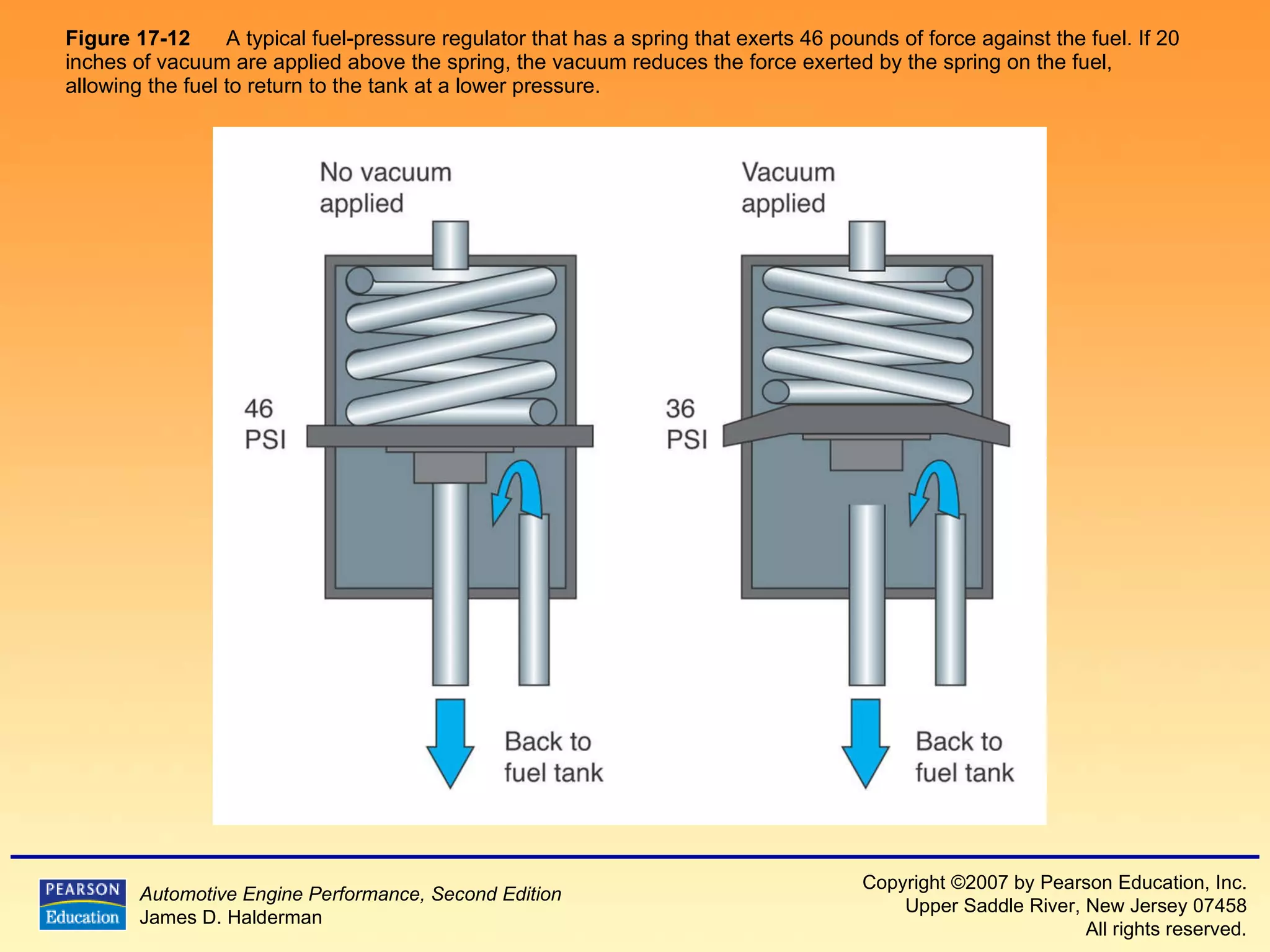
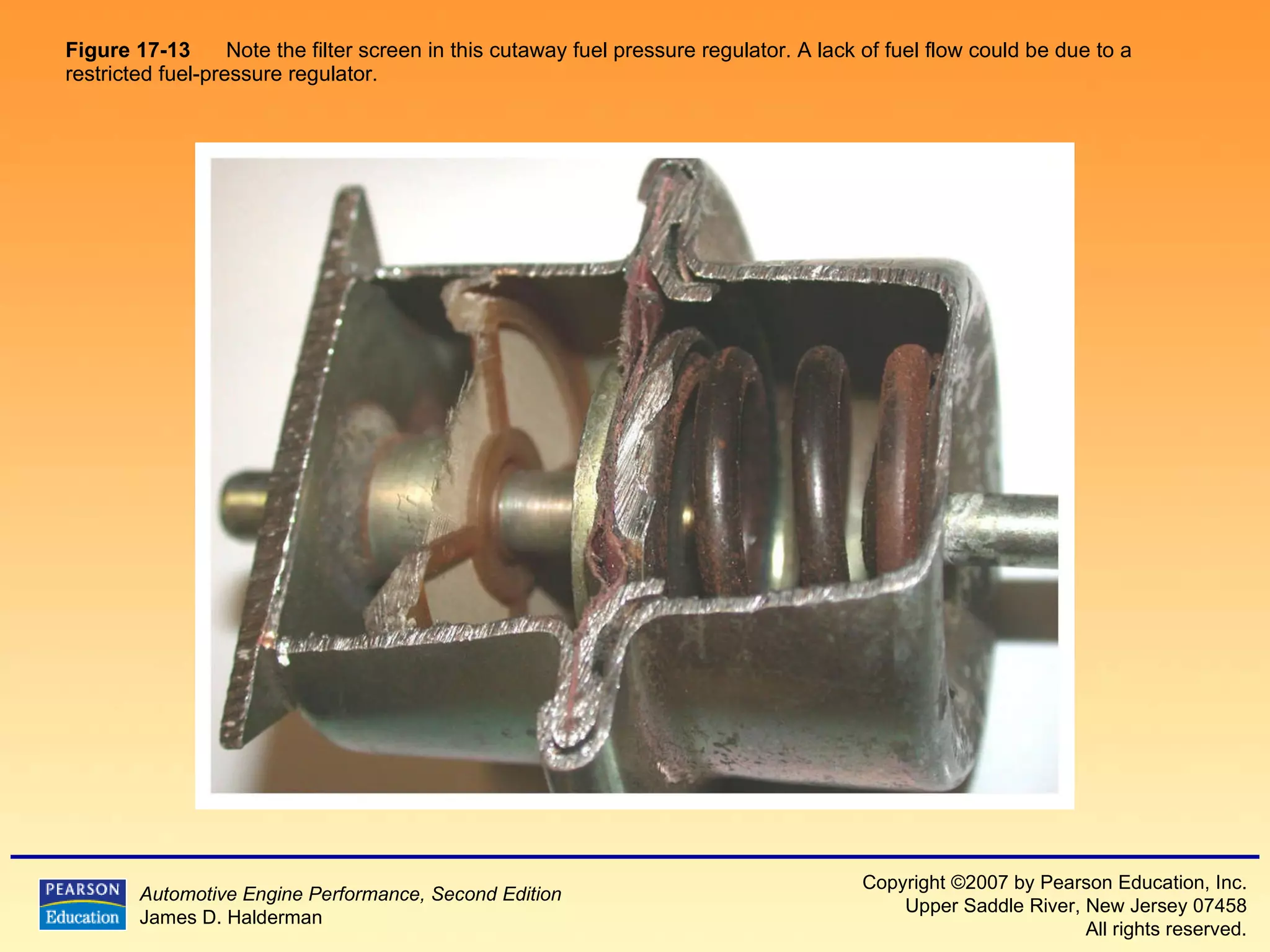
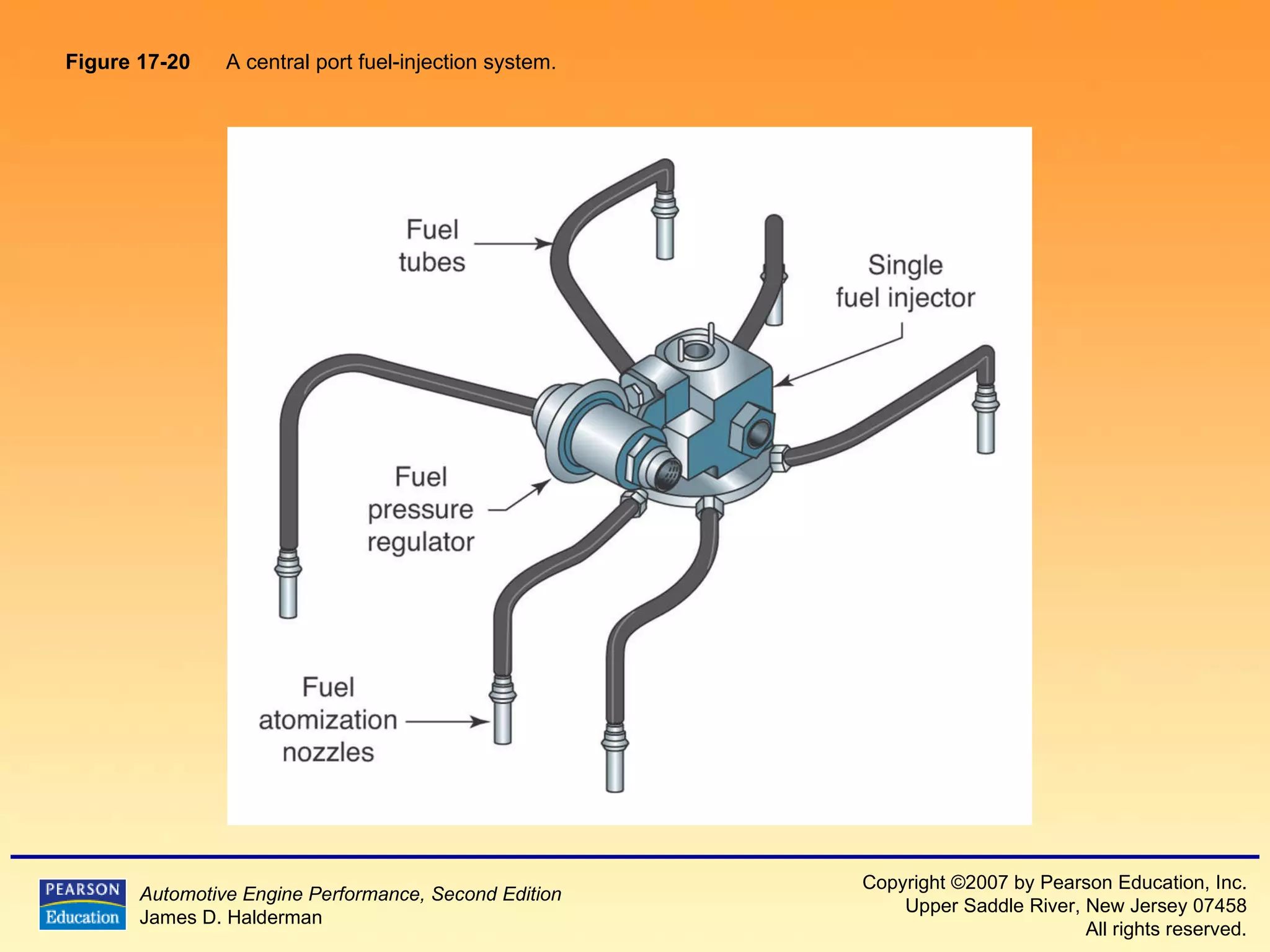
3) It provides diagrams and descriptions of the main components like the fuel rail, injectors, and pressure regulator and how they function within the fuel injection system.