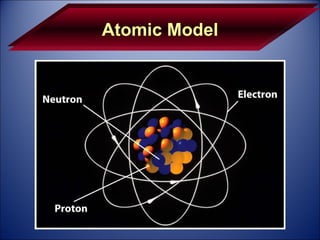
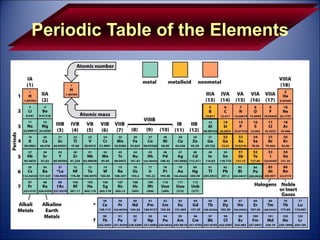
The document discusses the history and development of atomic theory from Democritus' idea that matter is made of indivisible particles called atoms, to modern atomic structure and the periodic table of elements. It covers key contributors like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr and their experiments that provided evidence for atoms and determined atomic structure, including the discovery of subatomic particles like electrons and the nuclear model of the atom. It also discusses applications of atomic and molecular spectroscopy.