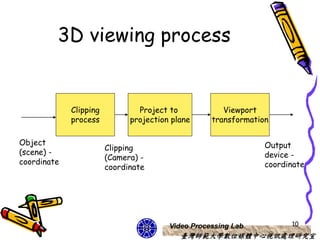
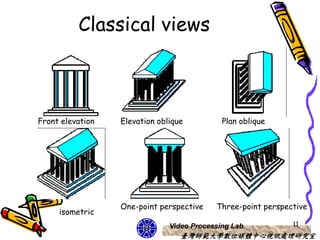
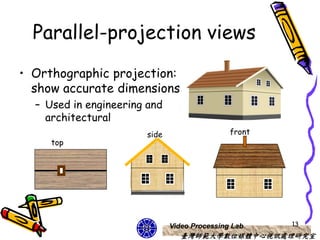
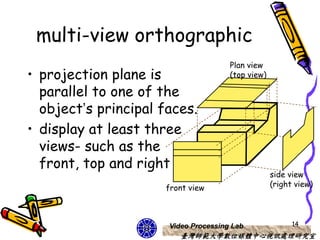
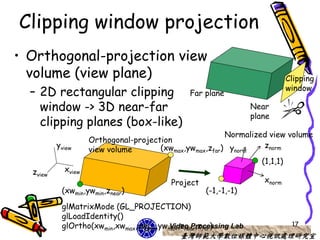
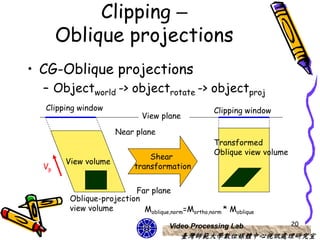
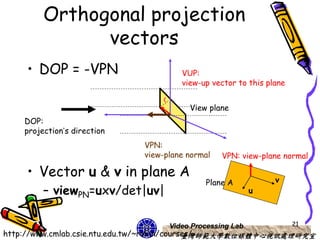
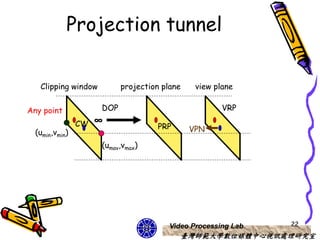
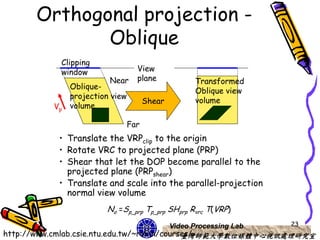
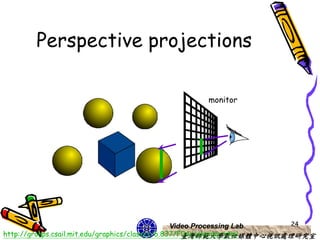
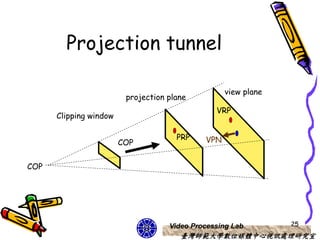
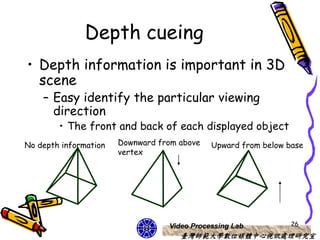
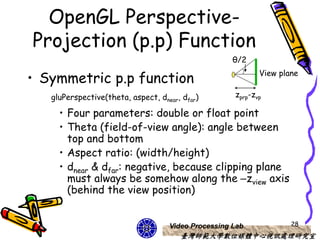
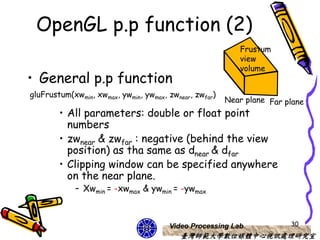
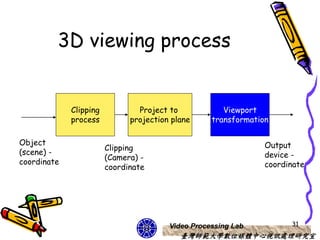
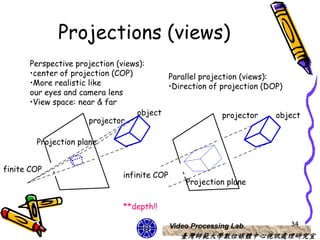
The document discusses 3D viewing frameworks and how to generate 3D views of objects and scenes by setting up a camera position and orientation, projecting object descriptions onto a view plane using different projection types like parallel, perspective, and oblique projections, and transforming the view for output. It also covers topics like depth cueing, aspect ratios, and the steps involved in the 3D viewing process using computer graphics.




















![Inquiring about values in
a matrix in OpenGL
• gluLookAt(4,4,4,0,1,0,0,1,0);
– Eye: (4,4,4), look: (0,1,0), up: (0,1,0)
n = eye-look ux uy uz dx
u = upxn
v vy vz dy
V x
v = nxu nx ny nz dz
(dx,dy,dz)=(-eye·unor, -eye·vnor, - 0 0 0 1
eye·nnor)
– To see what is stored in the modelview matrix
• Define an array GLFloat mat[16]
• Use glGetFloatv(GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX,mat)
mat: matT = V Modelview
matrix will
copy to mat[]
Video Processing Lab 44
臺灣師範大學數位媒體中心視訊處理研究室](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cg-3dviewing-course7-111015003853-phpapp01/85/CG-OpenGL-3D-viewing-course-7-44-320.jpg)

