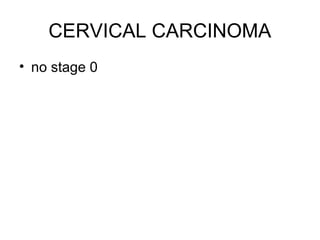
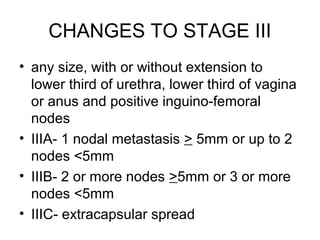
The document summarizes revised staging systems published by FIGO in 2009 for gynaecological cancers including uterine sarcomas, endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, and vulval cancer. Key changes include separating uterine sarcoma staging into different systems for leiomyosarcomas, endometrial stromal sarcomas, and adenosarcomas. The endometrial and cervical cancer staging systems were also modified, such as consolidating some stage I categories for endometrial cancer. The vulval cancer staging system saw more significant revisions, including splitting the previous stage IB into stages IA and IB. Implementation of the new staging systems may pose challenges including disseminating information and differing from TNM staging