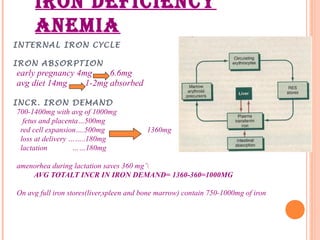
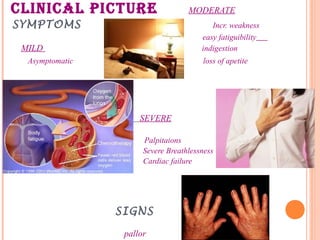
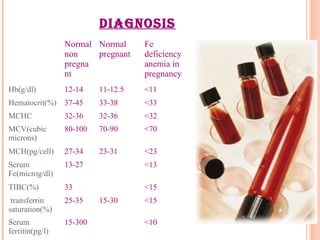
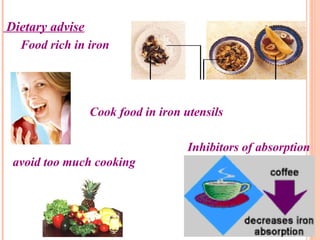
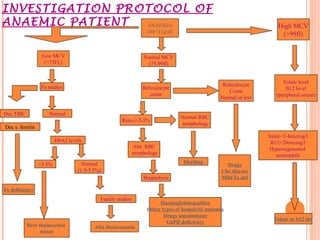
This document discusses anemia in pregnancy. It defines anemia and describes the normal physiological changes in pregnancy that can cause dilutional anemia. It then discusses the most common types of anemia in pregnancy, focusing on iron deficiency anemia. It describes the causes, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy. It notes the importance of treating anemia to prevent maternal and fetal complications.