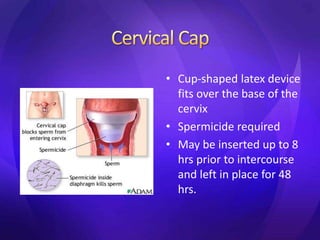
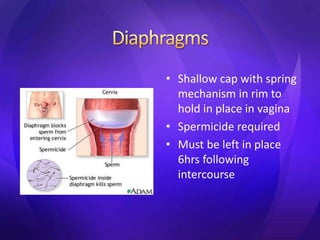
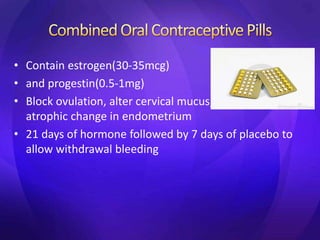
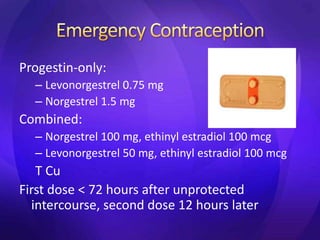
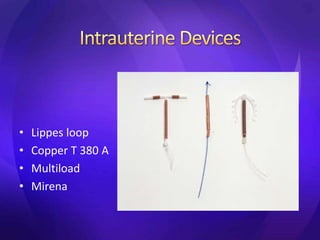
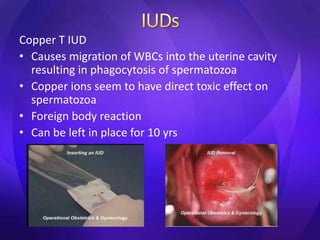
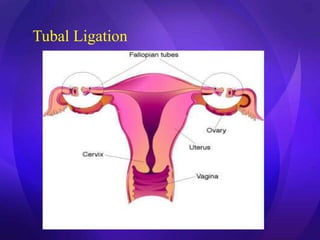
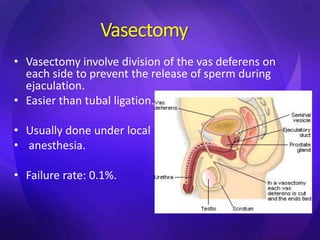
This document summarizes various contraceptive methods including barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms, hormonal methods like oral contraceptive pills and injectables, intrauterine devices, and permanent sterilization methods. It describes how each method works to prevent pregnancy and lists the advantages and disadvantages of each. Reversible long-acting methods like IUDs and implants are highly effective but have potential side effects while barrier methods are less effective but have fewer health risks. Permanent sterilization via tubal ligation or vasectomy is intended to be very effective but cannot be reversed.