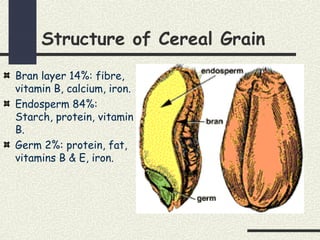
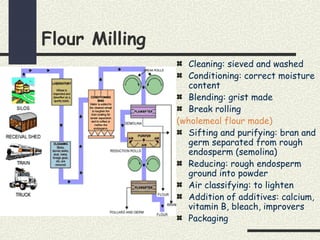
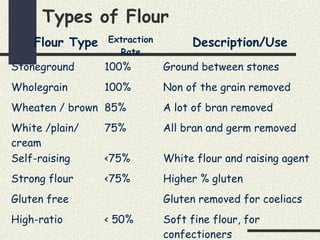
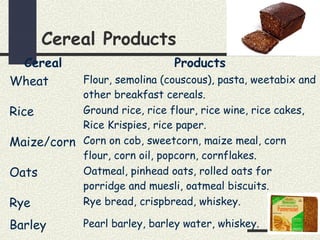
Cereals are grains from cultivated grasses and include wheat, rice, maize, oats, rye, and barley. The cereal grain has three main parts - the bran layer, endosperm, and germ. Cereals provide protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. They are a good source of energy, fiber, vitamin B, calcium, and iron. Cooking cereals through various heating methods makes them more digestible while reducing some vitamins. Milling and processing cereals removes bran and germ, lowering fiber and nutrients in white flours compared to whole grains. Common cereal products include breads, pastas, breakfast cereals, and more made from different types of