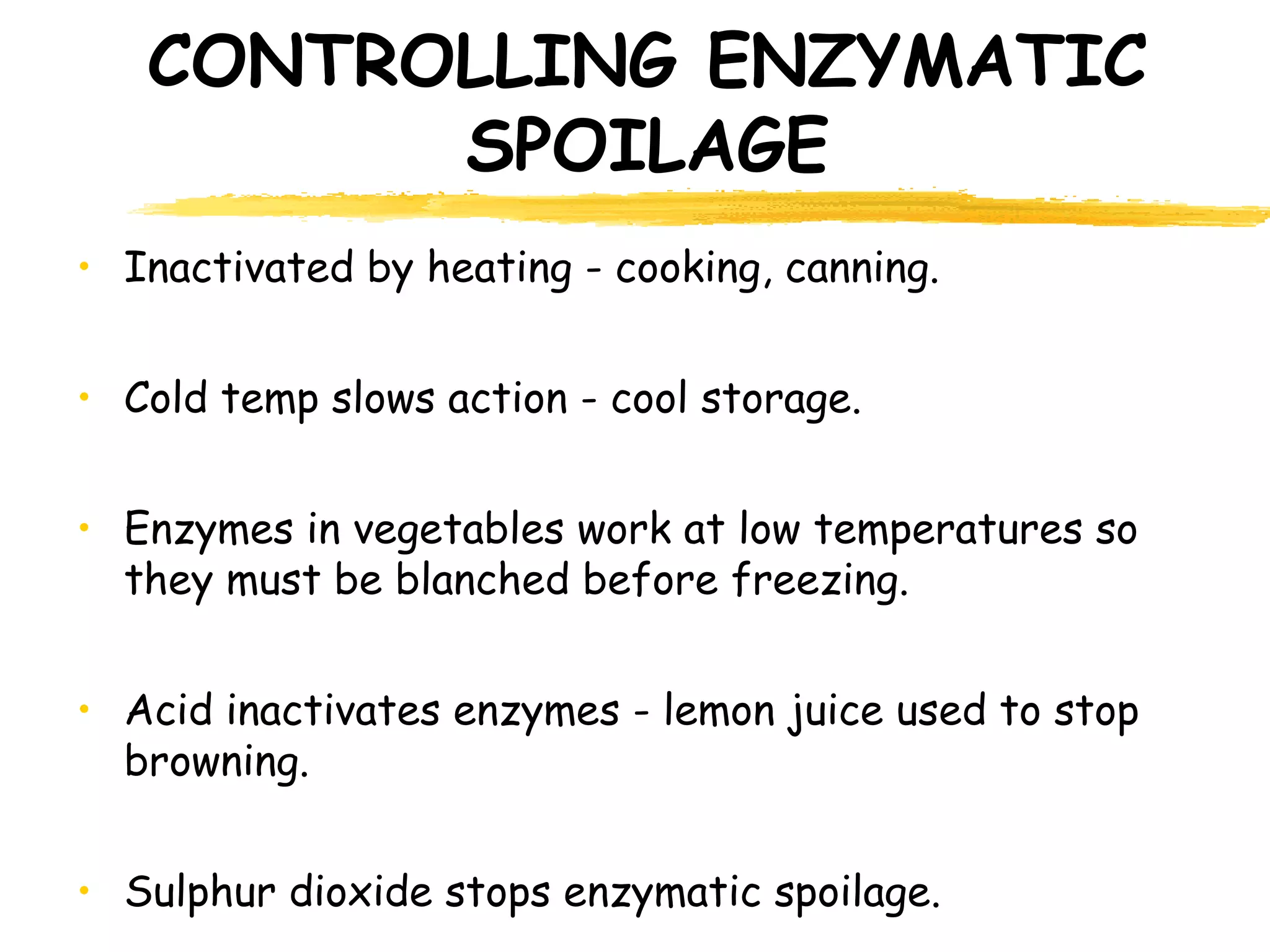
There are three main causes of food spoilage: moisture loss, enzyme action, and microbial contamination. Moisture loss mainly affects fruits and vegetables after harvesting as they lose water through their skins. Enzymes cause foods to ripen and decay over time through processes like starch changing to sugar. Microbes like yeast, mold, and bacteria grow in foods at optimal temperatures and cause spoilage both on the surface and inside foods invisibly through toxin production. Proper food handling and storage can help control spoilage from these three causes to prevent food poisoning and ensure safety.