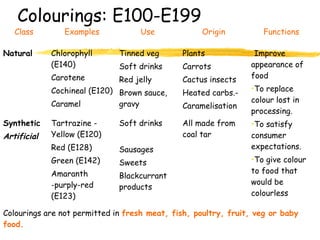
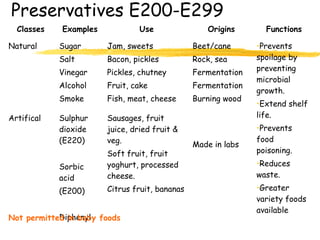
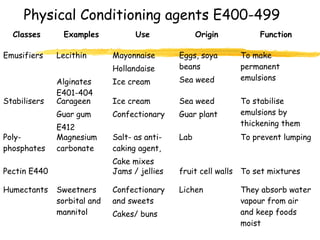
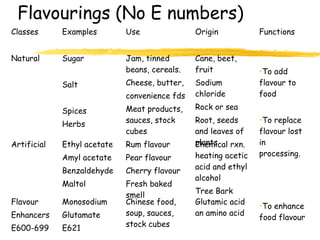
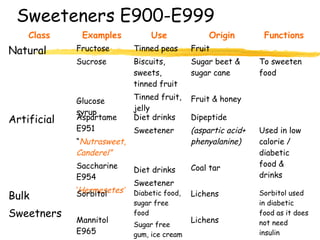
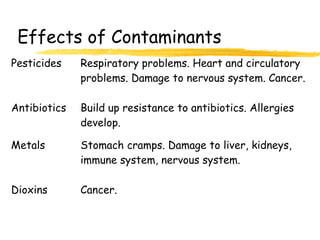
This document discusses food additives and contaminants. It defines food additives as substances intentionally added to food to improve properties like color, flavor or preservation. Additives are classified and regulated in the EU with E numbers. They provide benefits but also risks if overused. Contaminants unintentionally enter food through means like pesticides, packaging chemicals or microbes and can harm health if levels exceed regulations. The EU and FSAI work to test foods and enforce safe additive and contaminant levels.