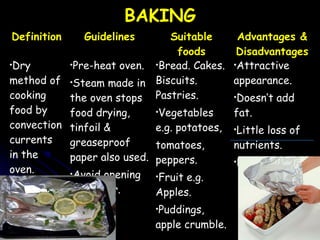
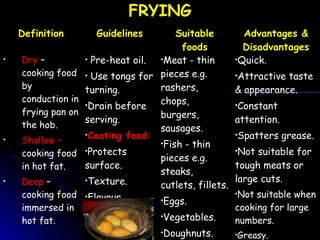
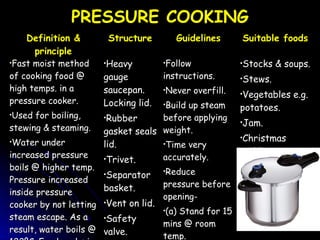
This document discusses various cooking methods and factors to consider when planning meals. It provides definitions and guidelines for different cooking techniques like boiling, simmering, poaching, braising, stewing, steaming, baking, grilling, roasting and barbecuing. For each method, it outlines suitable foods and the advantages and disadvantages. Overall, the document is a guide for selecting appropriate cooking methods based on ingredients, time available, equipment and desired results.