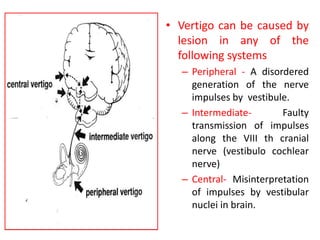
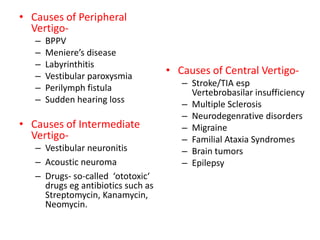
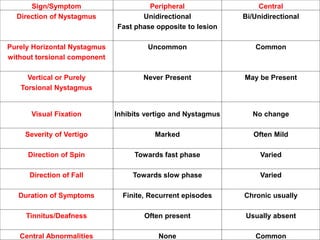
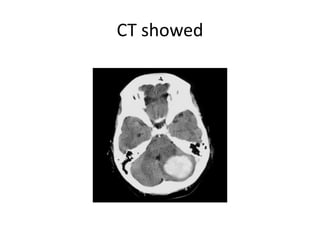
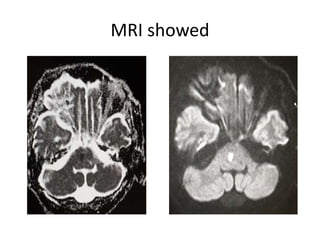
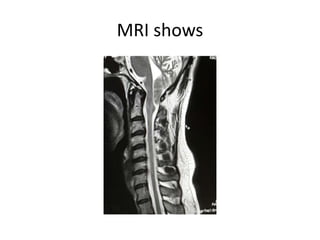
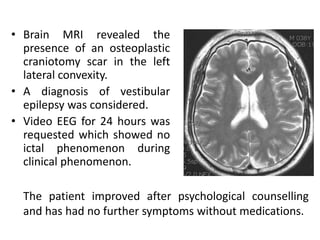
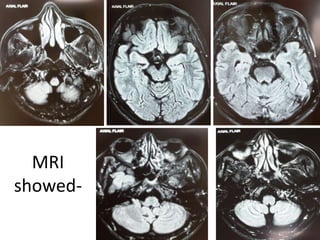
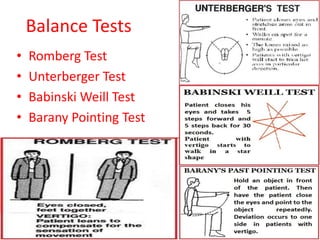
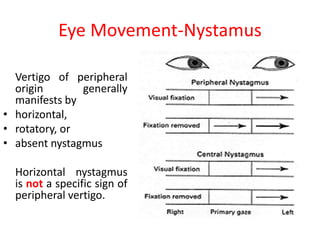
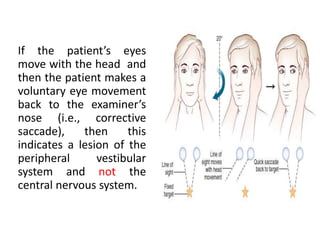
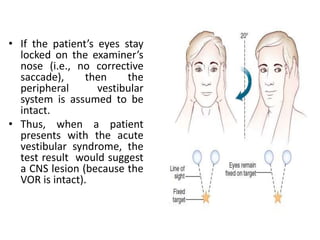
This document discusses vertigo, which refers to a hallucinatory sensation of movement caused by a mismatch of sensory information from the vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive systems. Vertigo can be caused by lesions in the peripheral, intermediate, or central nervous system. Common causes of peripheral vertigo include BPPV, Meniere's disease, and labyrinthitis. Intermediate vertigo may be caused by vestibular neuronitis or acoustic neuroma. Central causes include stroke, MS, migraines, and brain tumors. Clinical tests like nystagmus patterns and the head thrust test can help differentiate peripheral from central vertigo. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include medications, exercises