Embed presentation
Download to read offline




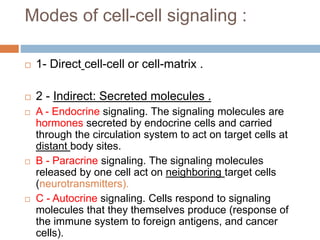
![Modes of Secretion :
Merocrine :
most abundant form of multicellular exocrine
gland .
products are secreted by exocytosis (e.g.,
pancreas, sweat, and salivary glands)
Holocrine :
products are secreted by the rupture of gland
cells [e.g., sebaceous (oil) glands of the skin]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularsecretionandcommunication-170225230707/85/Cellular-secretion-and-communication-5-320.jpg)



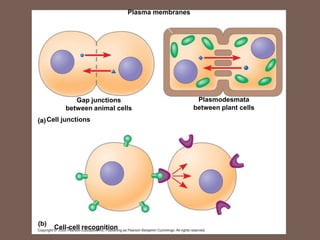

This document provides an overview of cellular secretion and communication. It defines cellular secretion as the external elimination of substances produced by cells, such as hormones and mucus. There are two main modes of secretion: merocrine secretion which involves exocytosis and holocrine secretion where gland cells rupture to release their products. The document also discusses three key processes in cellular communication - reception, transduction, and response. It outlines three main modes of indirect cell signaling: endocrine signaling through hormones, paracrine signaling between neighboring cells, and autocrine signaling where cells respond to molecules they produce.




![Modes of Secretion :
Merocrine :
most abundant form of multicellular exocrine
gland .
products are secreted by exocytosis (e.g.,
pancreas, sweat, and salivary glands)
Holocrine :
products are secreted by the rupture of gland
cells [e.g., sebaceous (oil) glands of the skin]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularsecretionandcommunication-170225230707/85/Cellular-secretion-and-communication-5-320.jpg)




