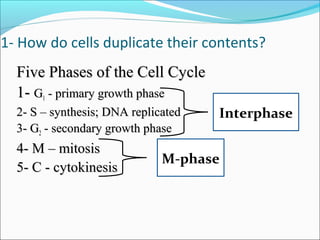
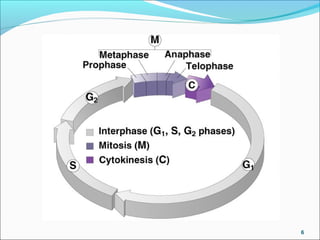
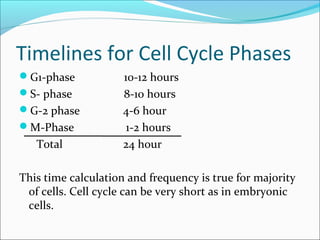
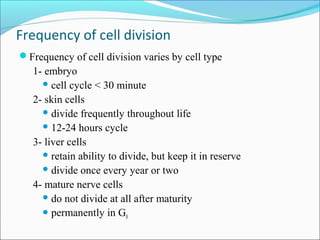
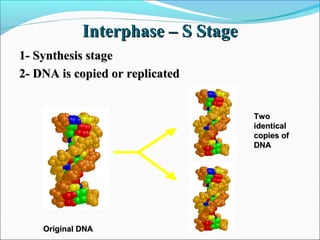
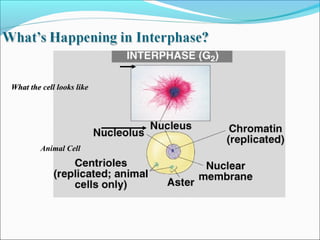
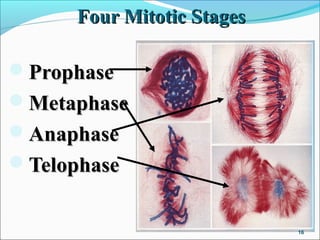
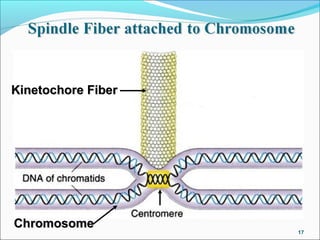
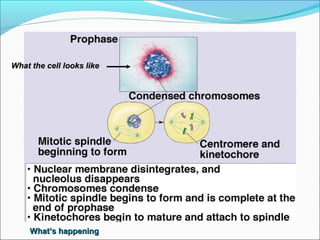
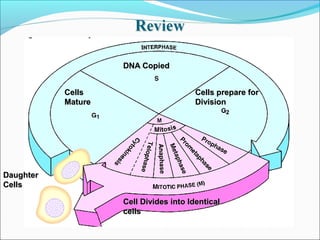
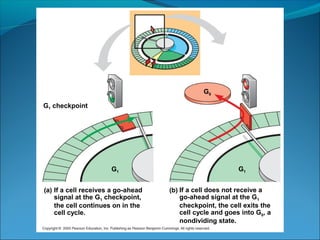
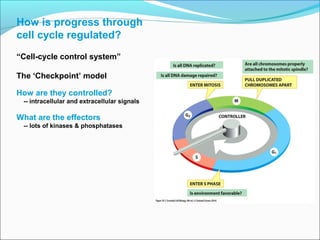
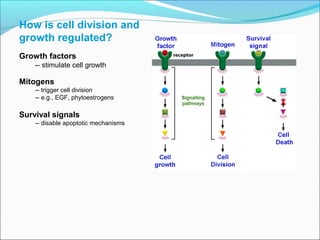
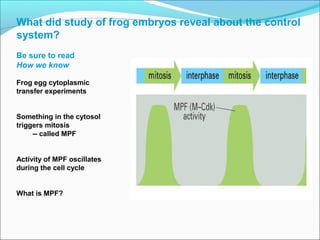
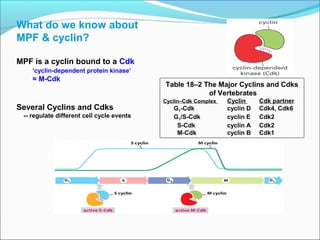
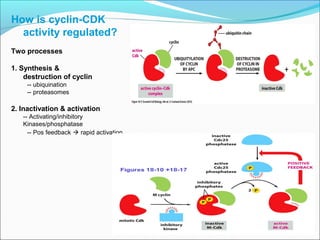
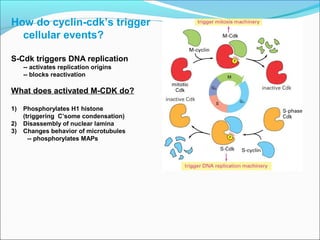
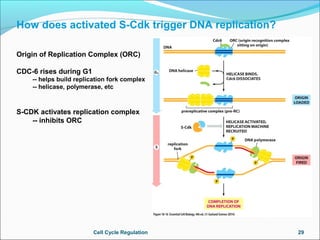
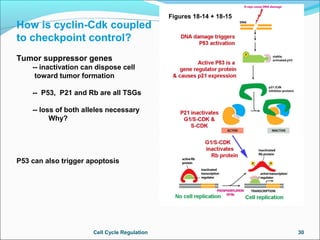
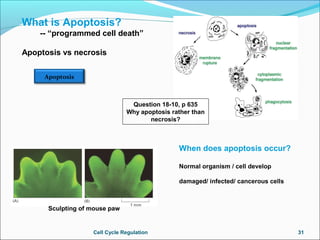
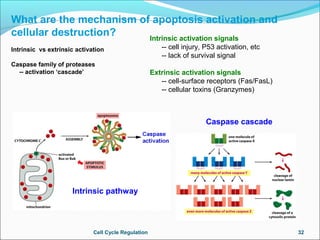
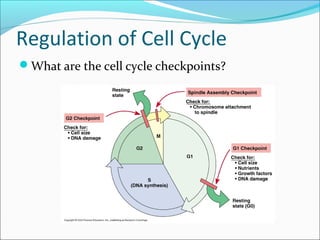
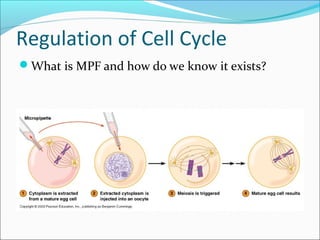
The document outlines the cell cycle, describing the orderly sequence of events through which a cell duplicates its contents and divides. It details the five phases of the cell cycle (G1, S, G2, M, C) and highlights the importance of checkpoints and regulatory mechanisms involving cyclins and kinases in coordinating cell division. Additionally, it discusses the variations in cell division frequency among different cell types and the implications for cell growth and cancer development.