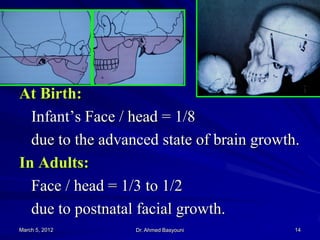
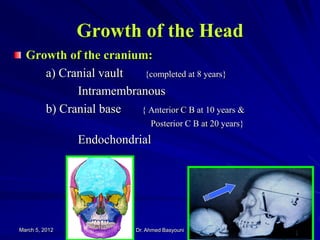
This document summarizes a lecture on craniofacial growth and development. It discusses how the cranium and face grow, defining growth and development. Growth occurs through intramembranous bone formation or endochondral bone formation at sutures and synchondroses. Factors like bone growth, soft tissues, occlusion forces, and skeletal patterns influence occlusion development. The cranial vault completes growth by age 8 while the cranial base continues growing into the 20s. The face grows rapidly in depth initially and its growth is mostly complete by ages 16-18 for the upper face and 20-25 for the mandible.