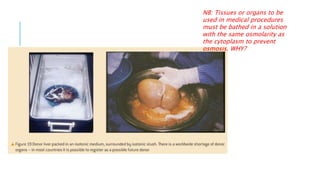
There are two main types of transport across cell membranes - passive transport which does not require energy, and active transport which does require energy in the form of ATP. Passive transport includes simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, and involves movement of substances along concentration gradients. Active transport transports substances against concentration gradients using membrane proteins and requires energy. Materials also move into and out of cells through endocytosis and exocytosis using membrane-bound vesicles.