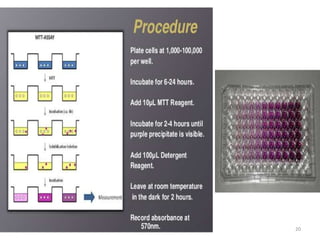
The MTT assay is a colorimetric assay that uses the yellow tetrazolium dye MTT to measure cellular metabolic activity as a proxy for cell viability. In the assay, viable cells containing NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductase enzymes reduce MTT to purple formazan crystals, which are then dissolved and quantified by spectrophotometry. The degree of color formation correlates with the number of viable cells present. The MTT assay is inexpensive, does not require cell transfer, and can be used to assess cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis for a variety of cell types.