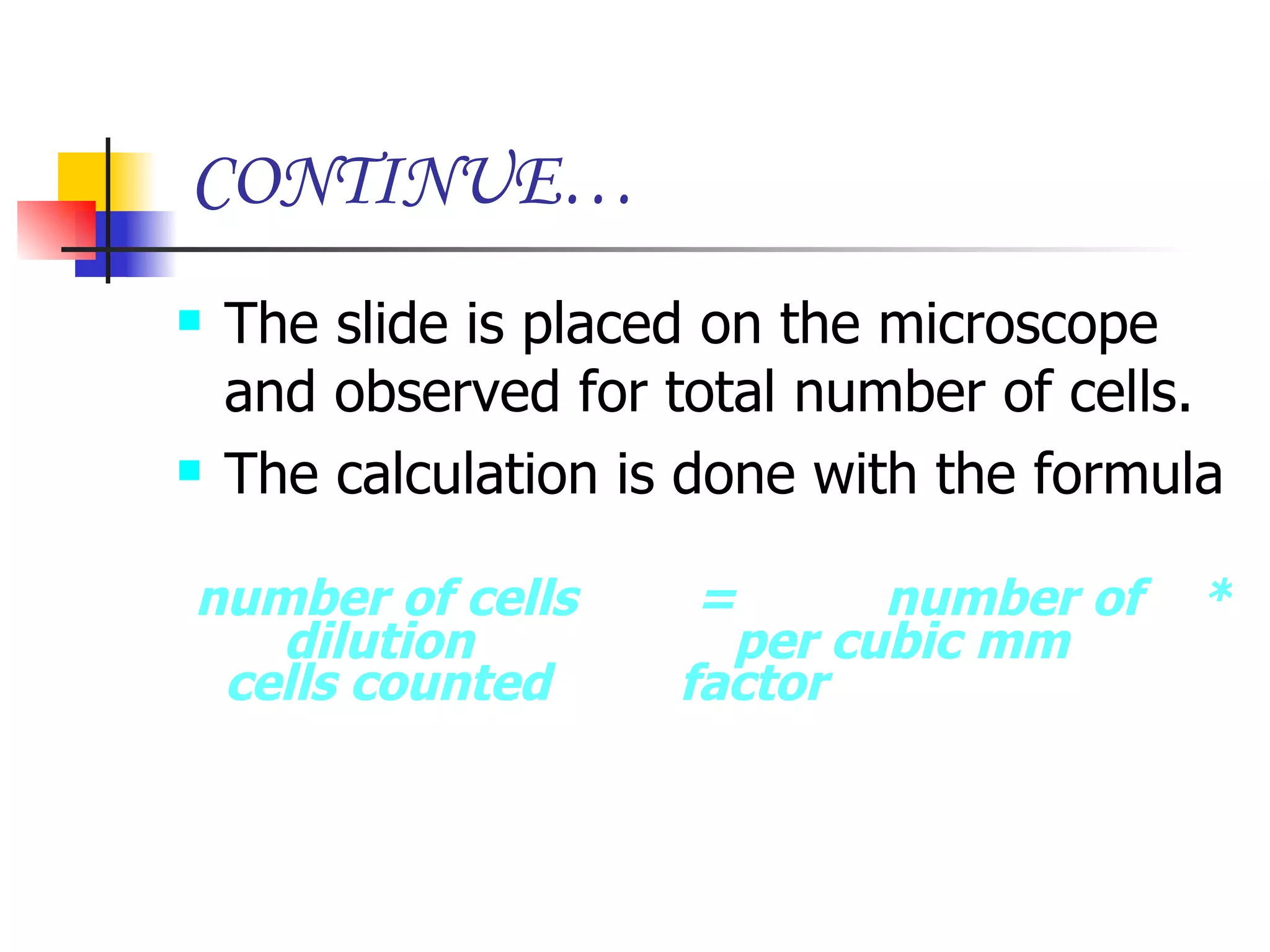
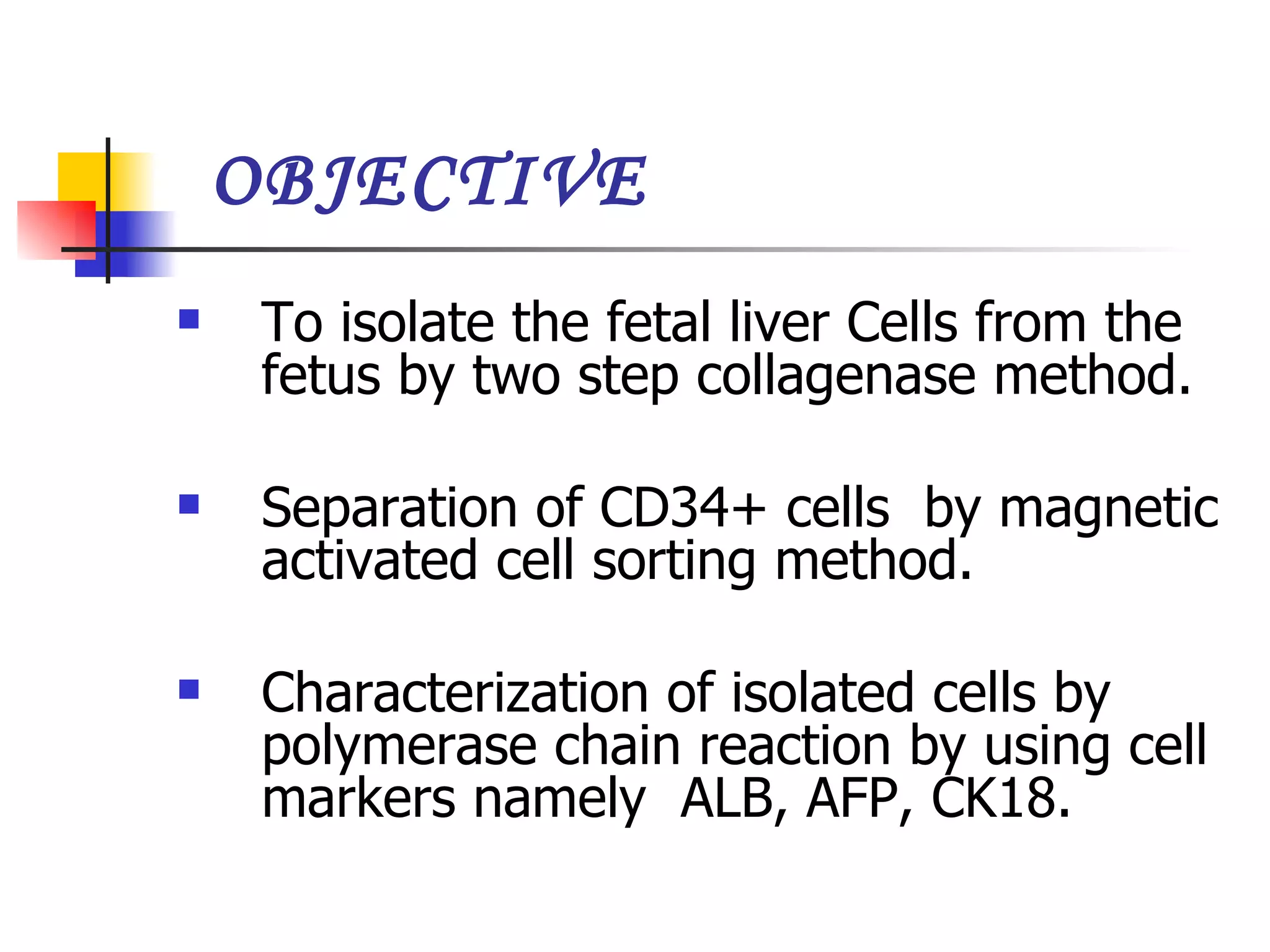
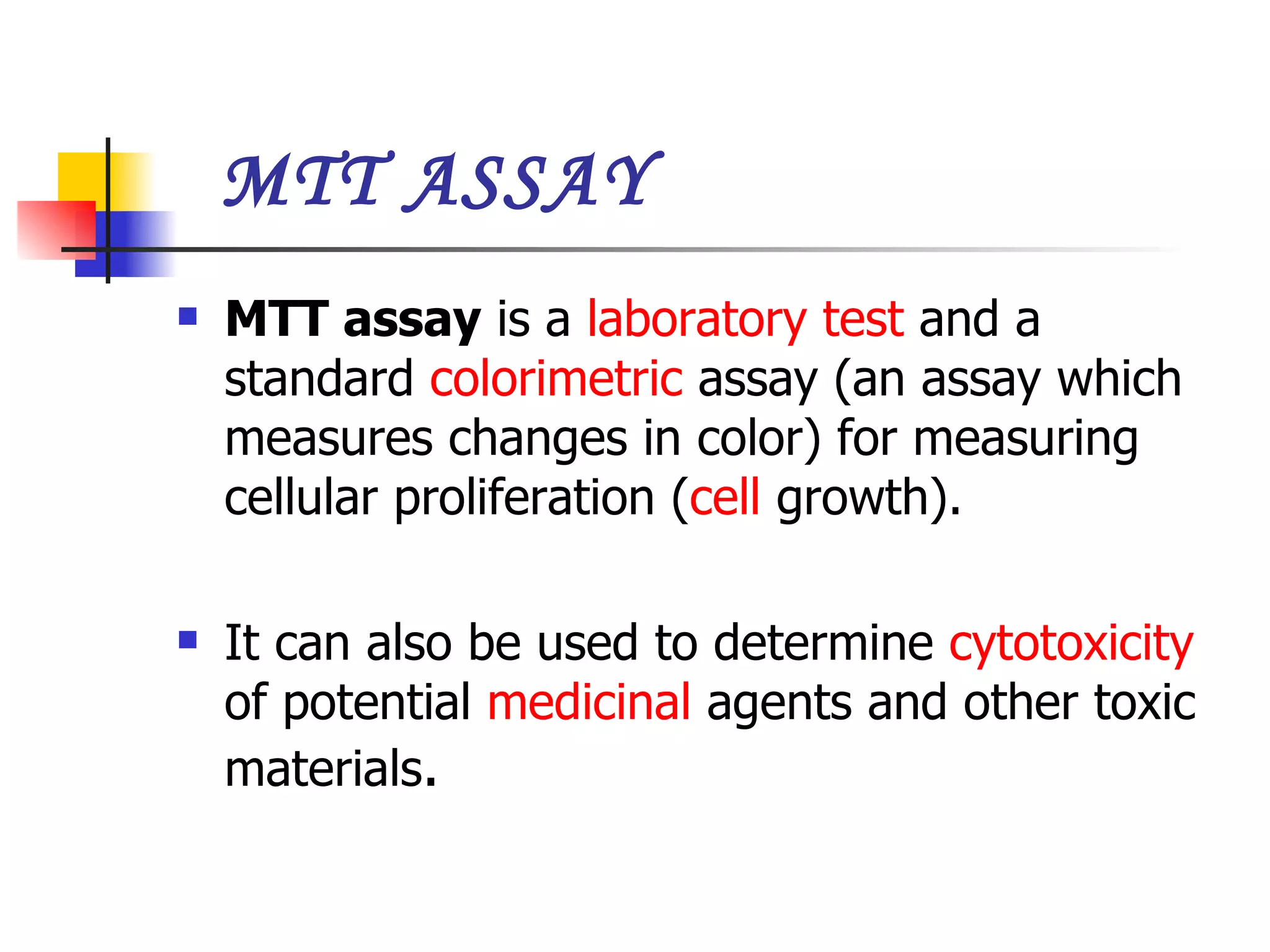
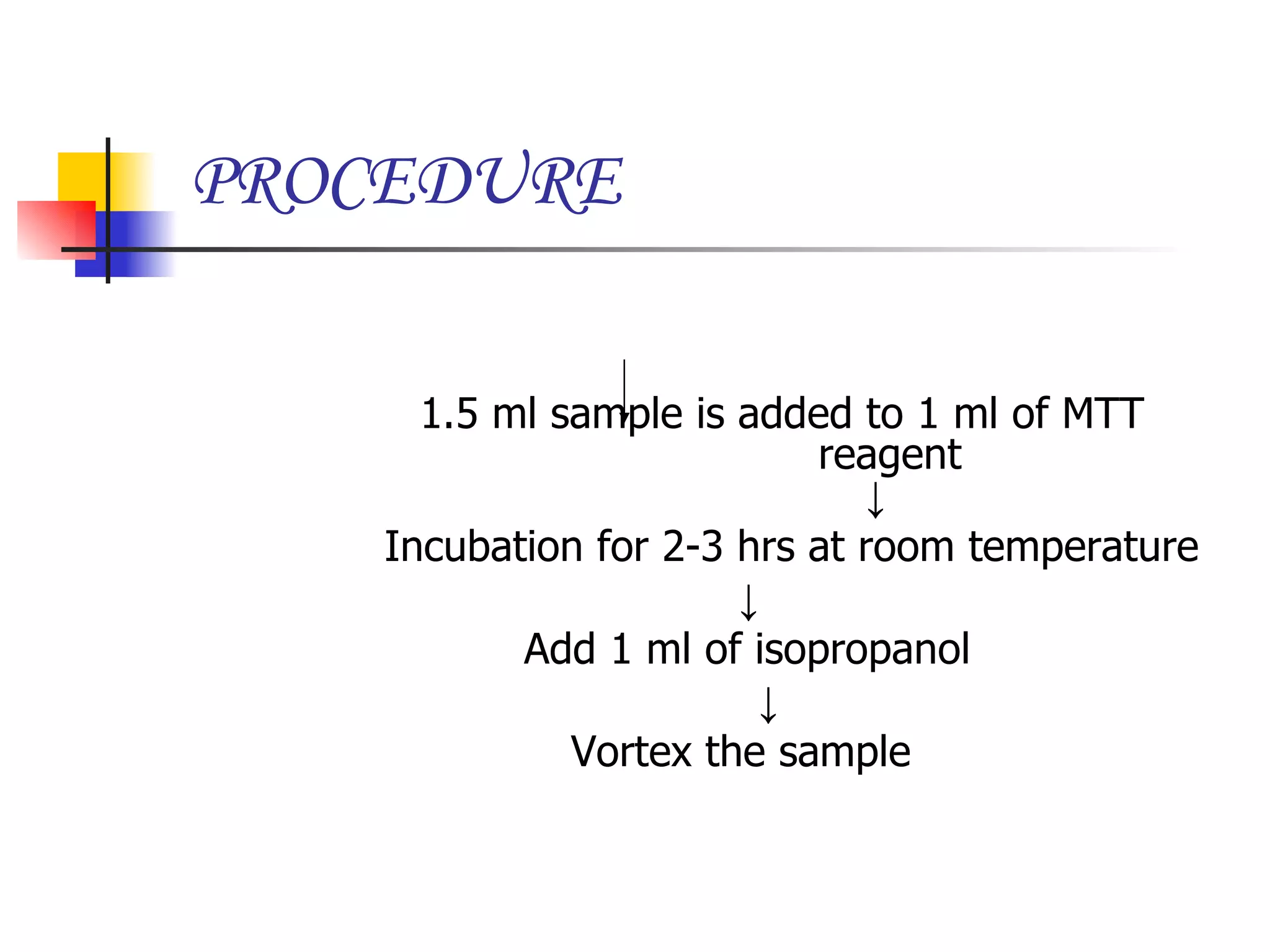
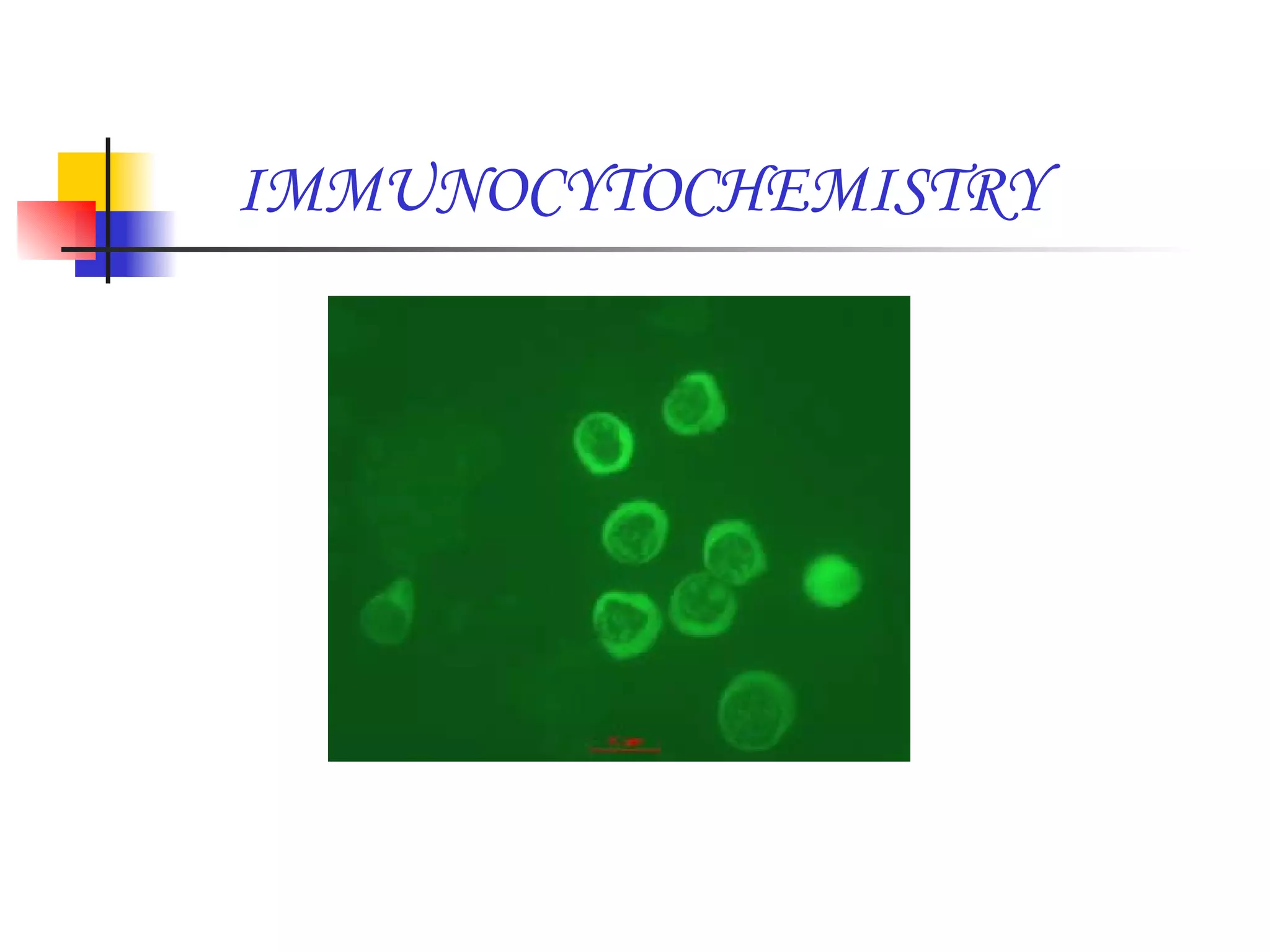
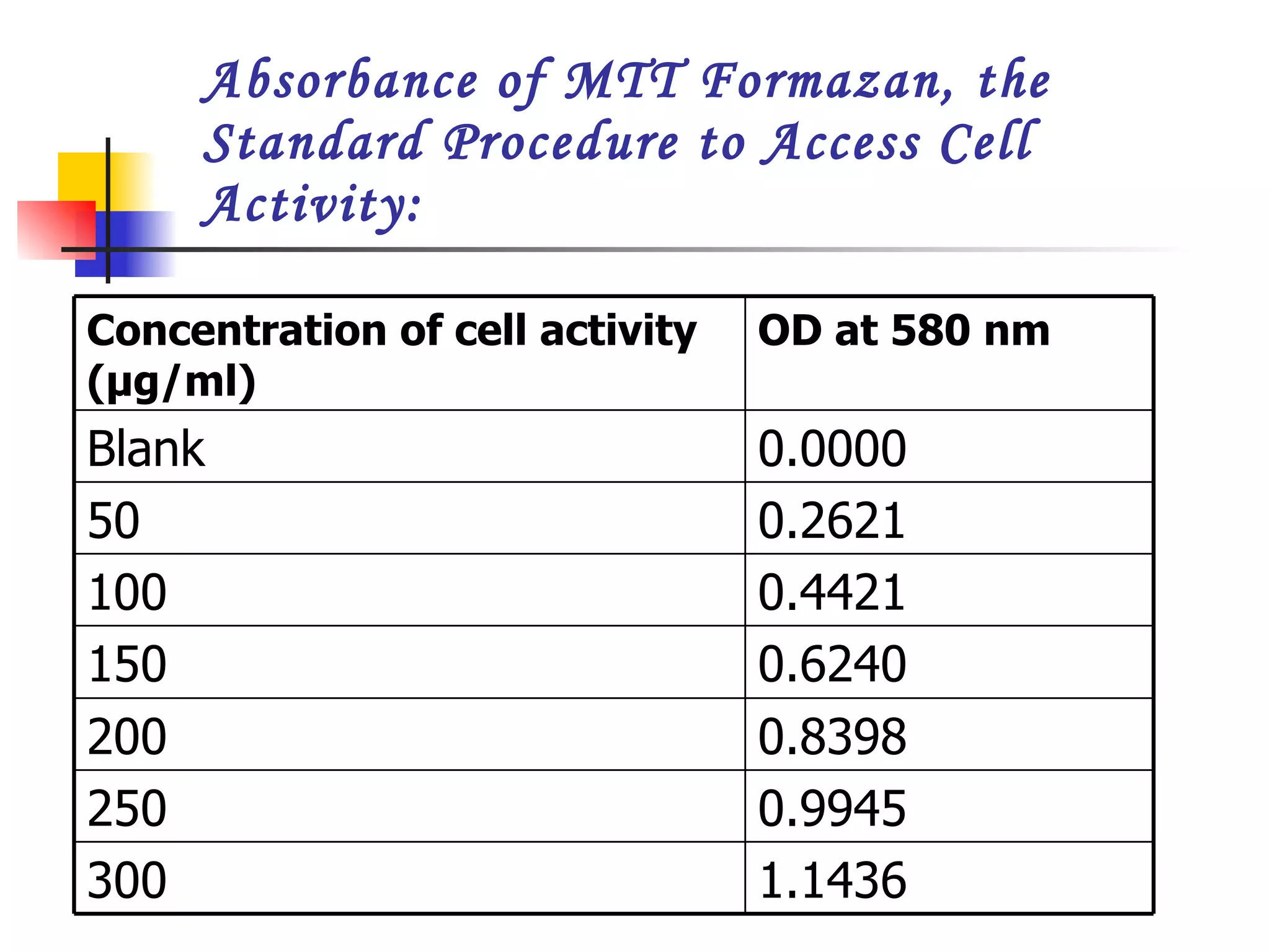
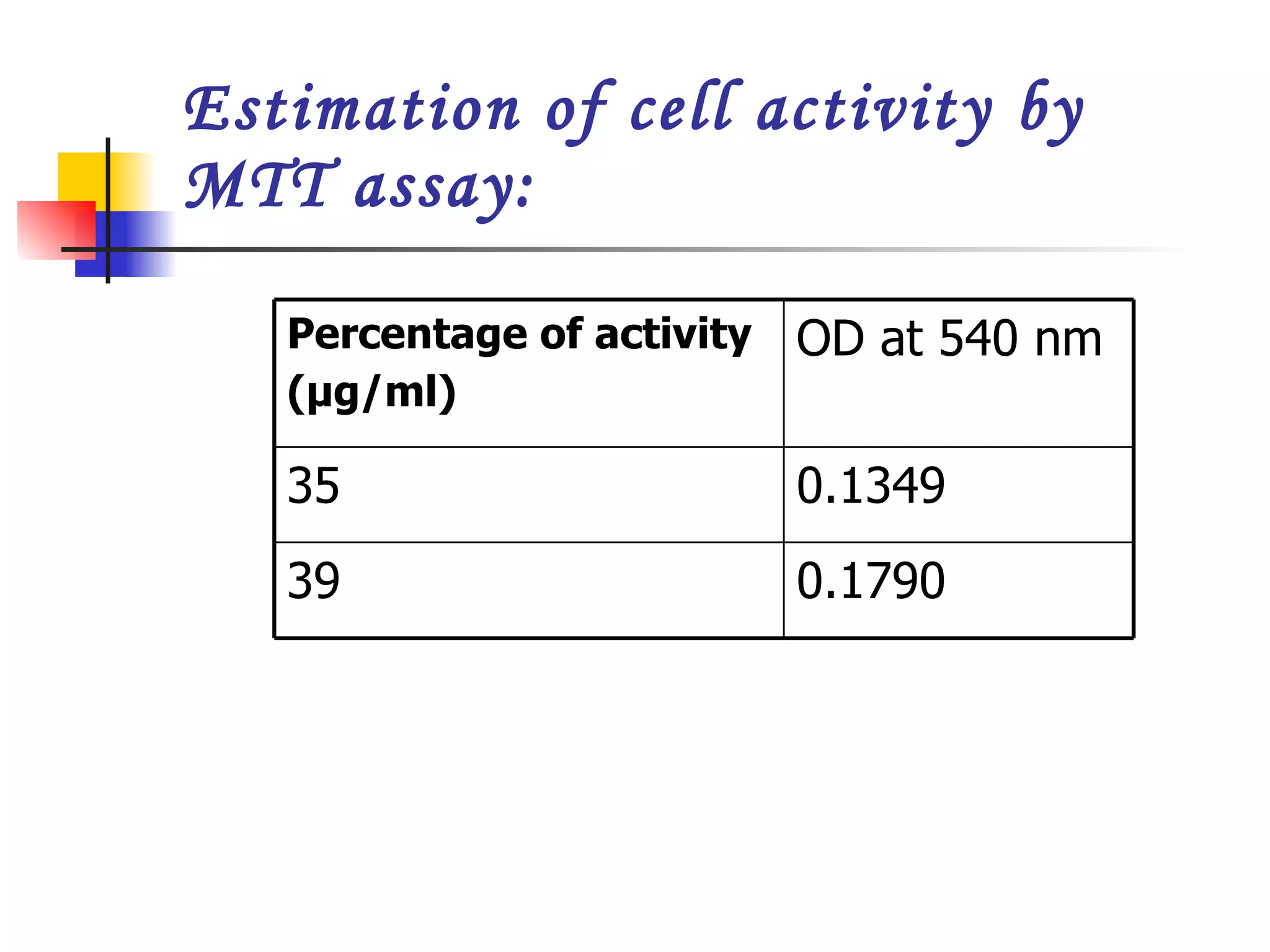
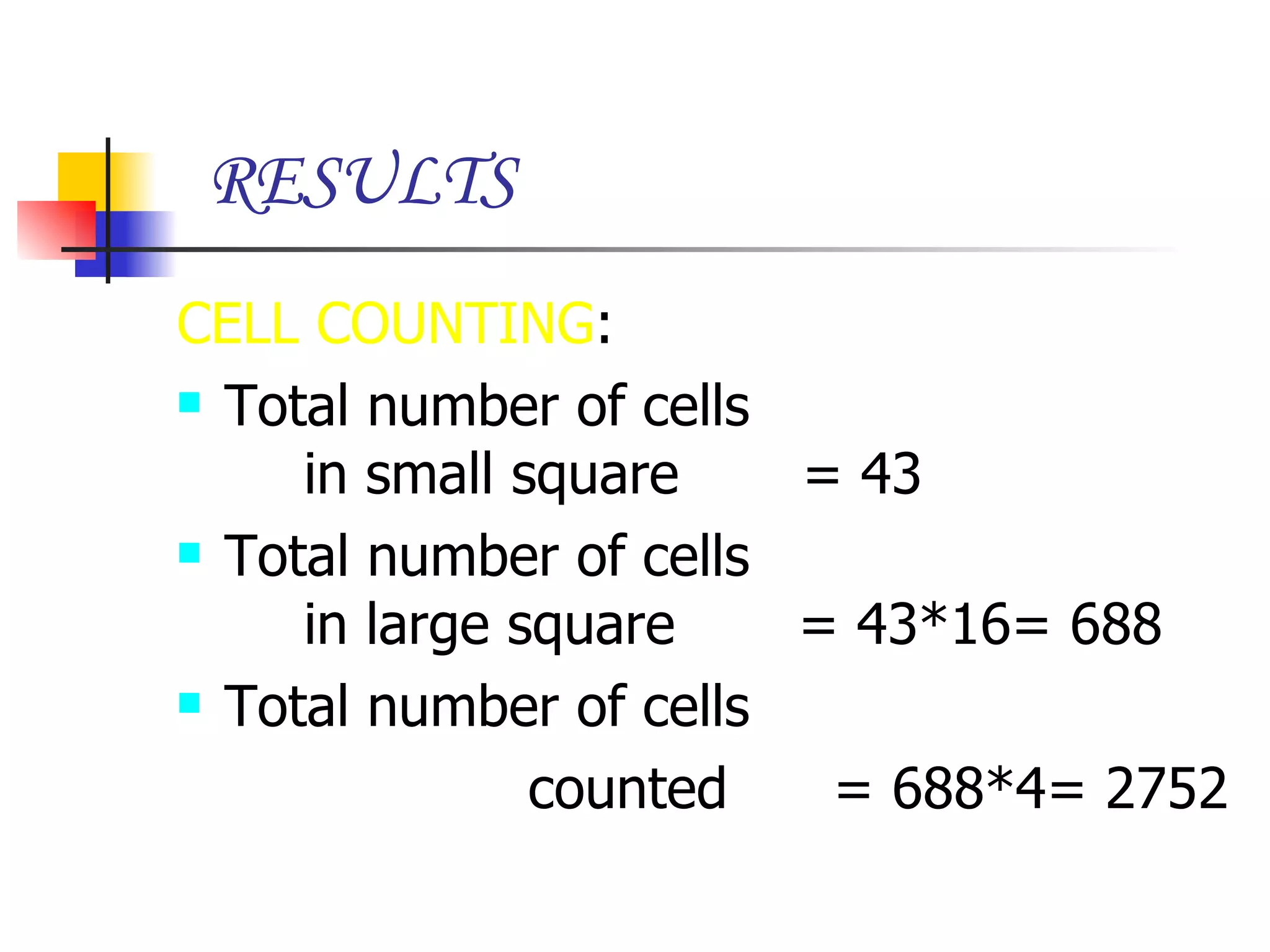This document summarizes research presented on isolating and characterizing human fetal liver stem cells. The key steps involved isolating stem cells from human fetal liver tissue using markers like AFP, CK18, and albumin. The isolated stem cells were then characterized using techniques like cell counting, viability assays, immunocytochemistry, MTT assays, and PCR to analyze RNA expression and confirm the presence of stem cell markers. The overall aim was to isolate fetal liver stem cells and characterize their properties for potential applications in areas like blood transfusions, organ transplantation, and disease research.