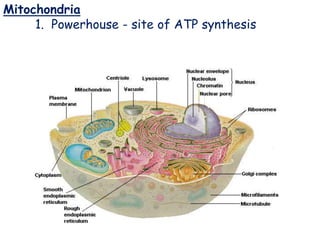
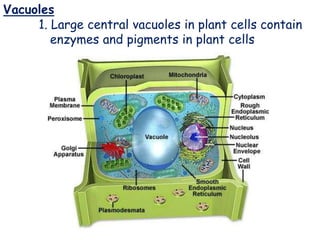
This document outlines the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as describes the main organelles found within eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells like bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles and have simpler structures, while eukaryotic cells like plant and animal cells have organelles enclosed in membranes and more complex cellular components. The document then provides details on the structures and functions of the major organelle components of eukaryotic cells, including the plasma membrane, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and more.