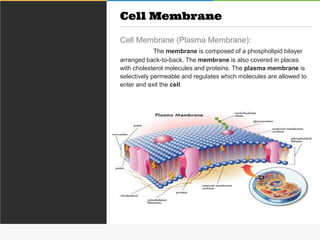
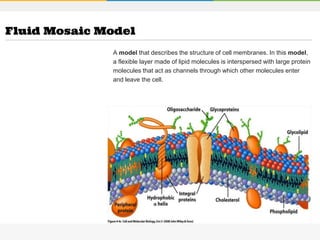
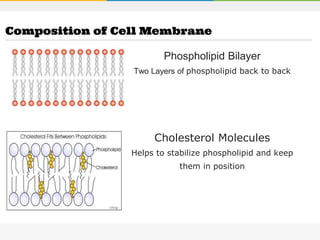
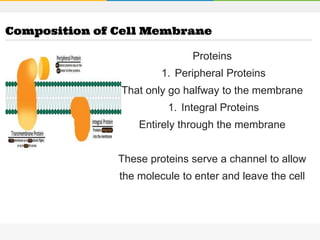
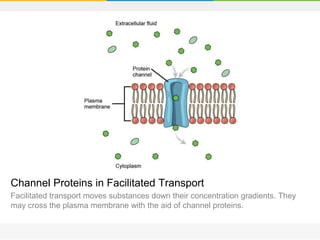
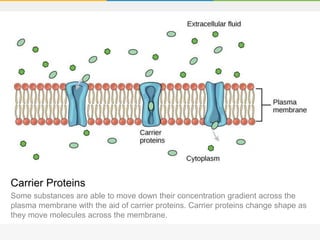
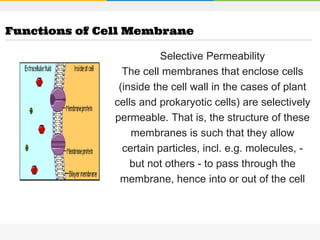
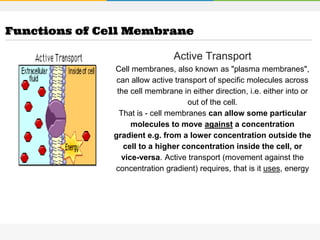
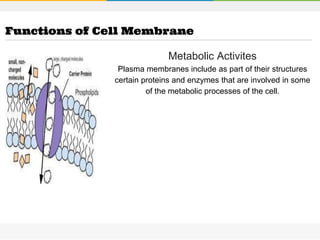
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with cholesterol molecules and integral and peripheral proteins embedded. It forms a selectively permeable barrier that regulates what enters and exits the cell according to the fluid mosaic model. Channel proteins facilitate selective transport of molecules and ions down their concentration gradients in and out of the cell, while carrier proteins assist with active transport against gradients. The main functions of the cell membrane are to enclose and protect the cell, regulate movement across it, and participate in some metabolic activities.