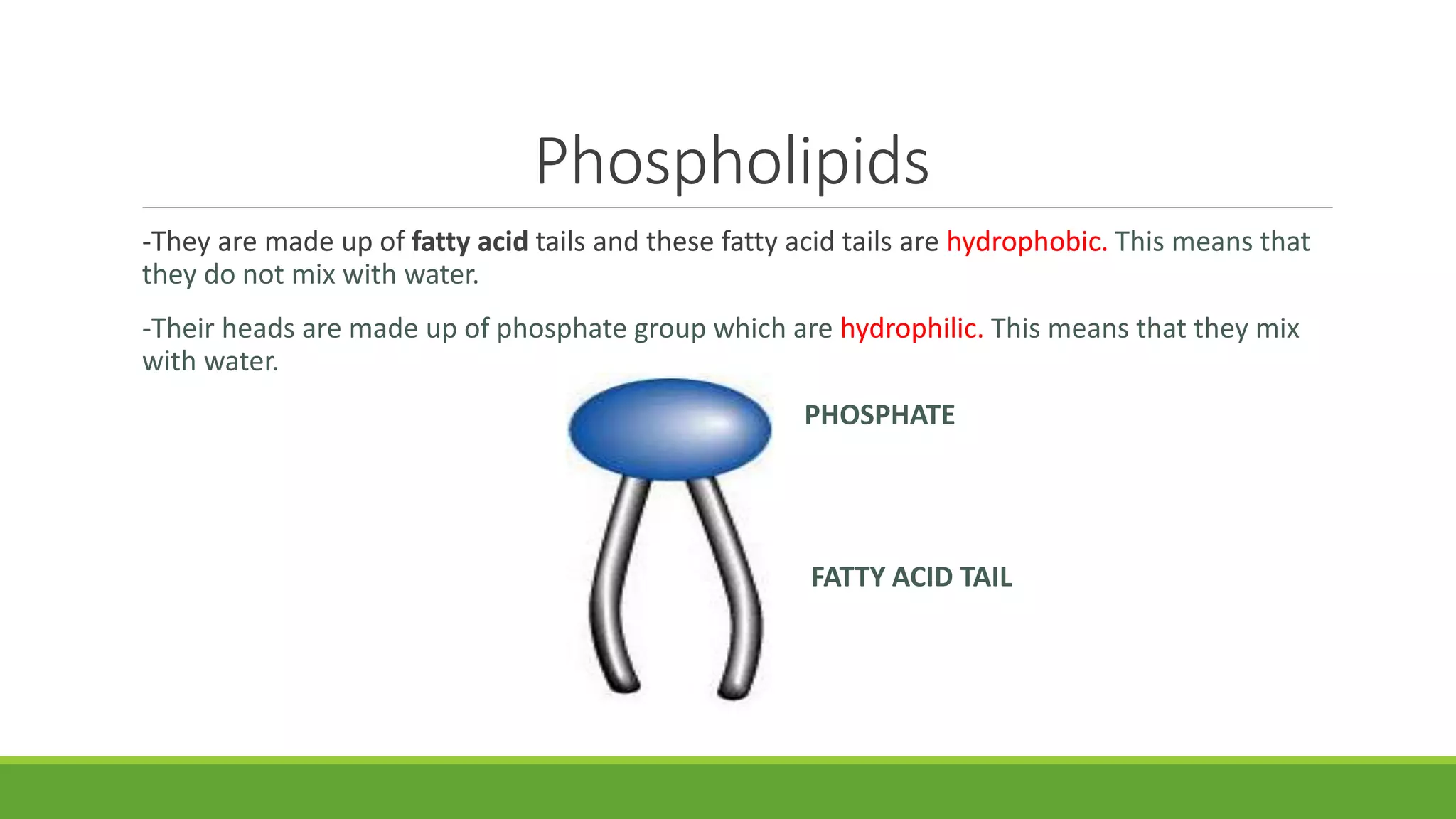
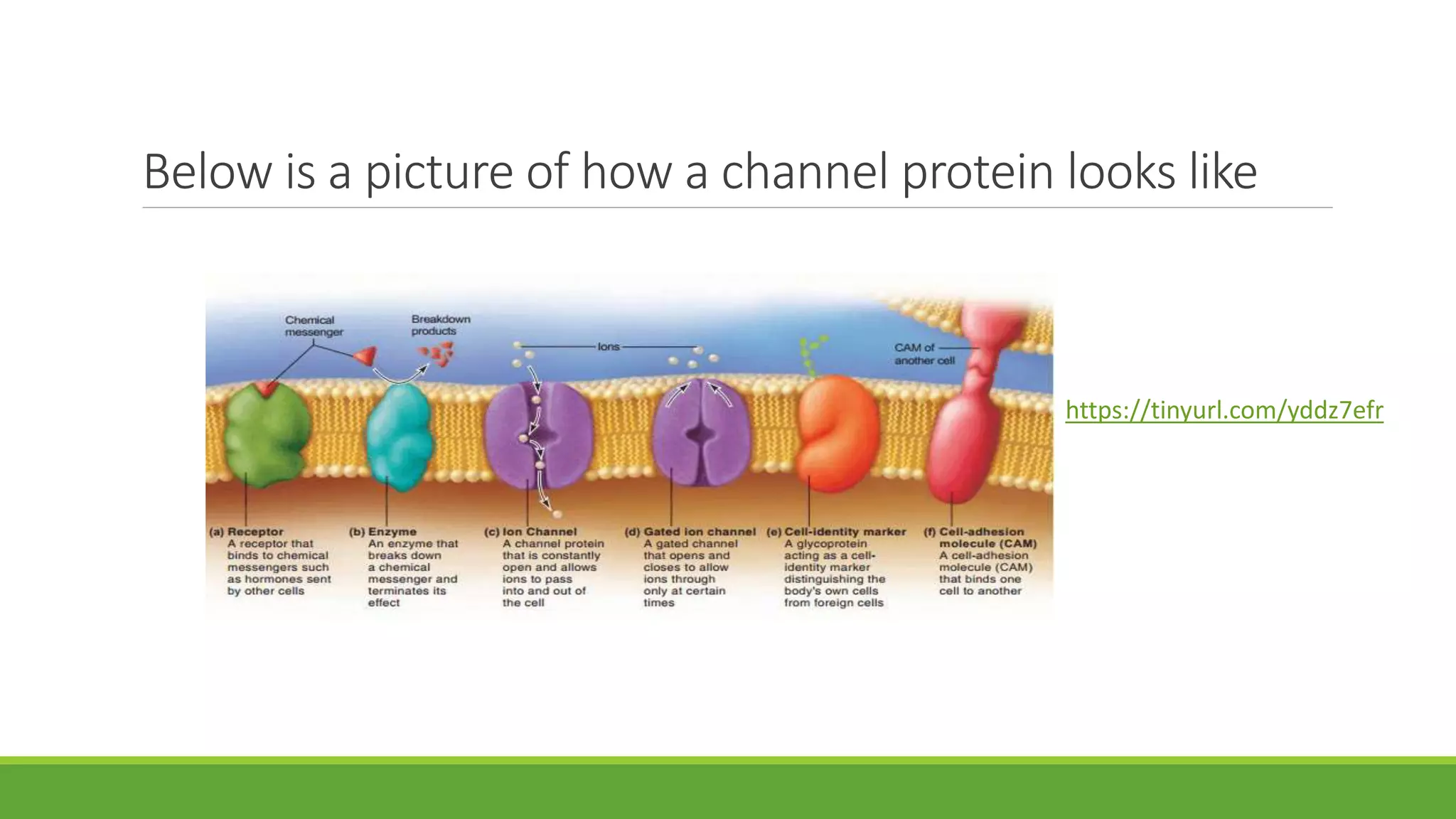
The cell membrane separates living cells from their environment and regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell through selective permeability. It is composed of lipids, primarily phospholipids, and proteins that define its specific functions, including passive and active transport mechanisms. Movement of large molecules occurs via processes like endocytosis and exocytosis.