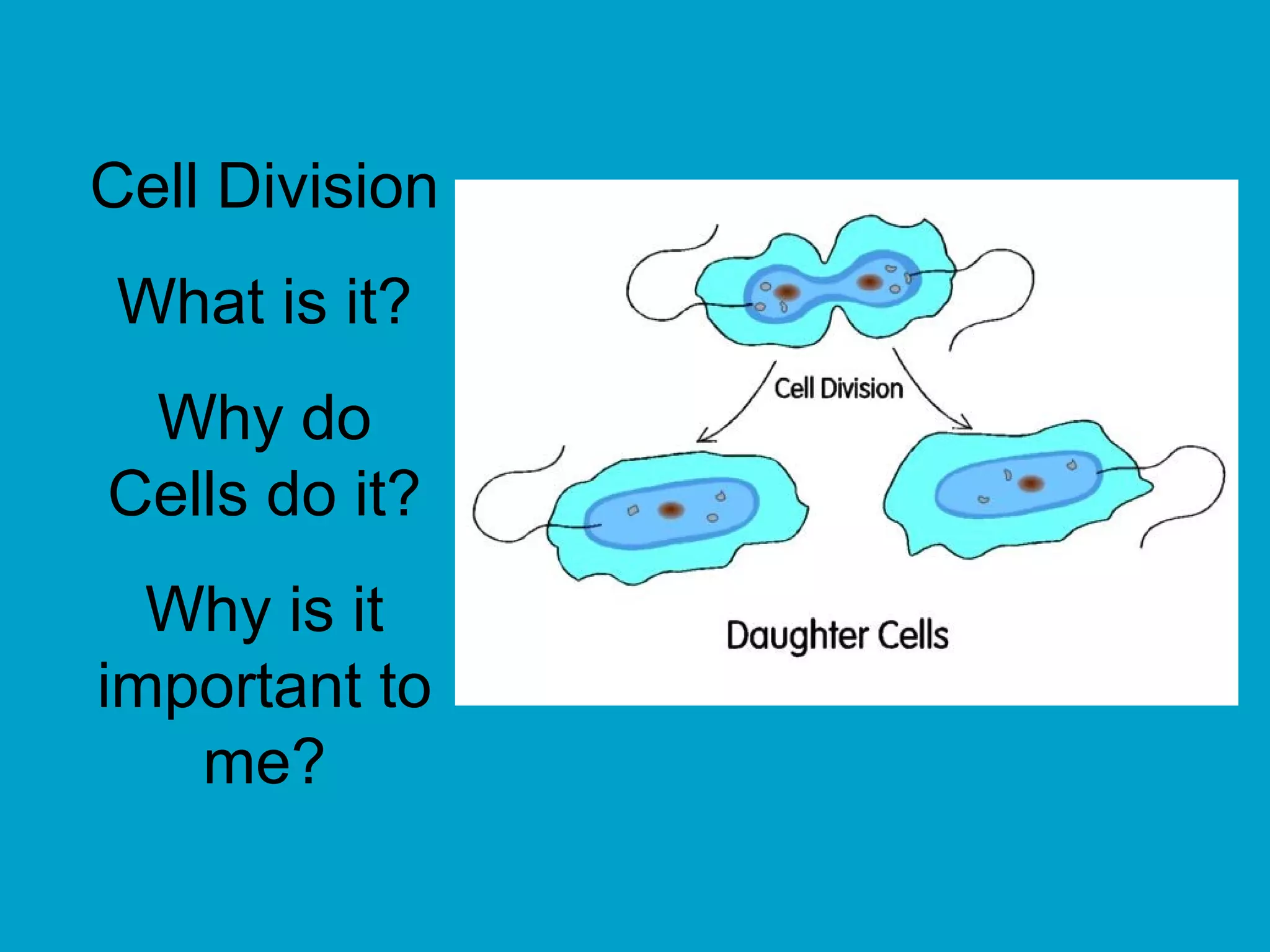
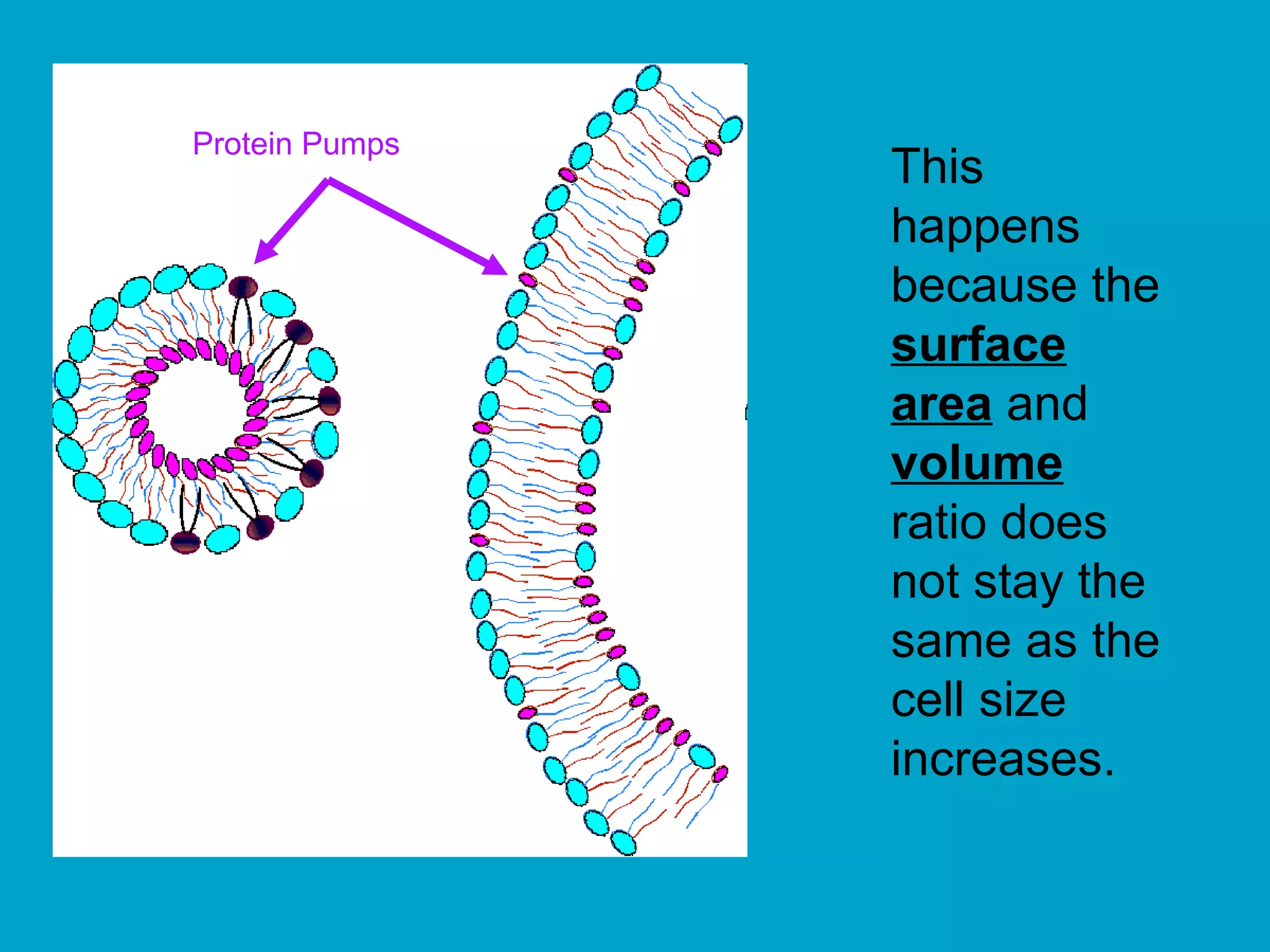
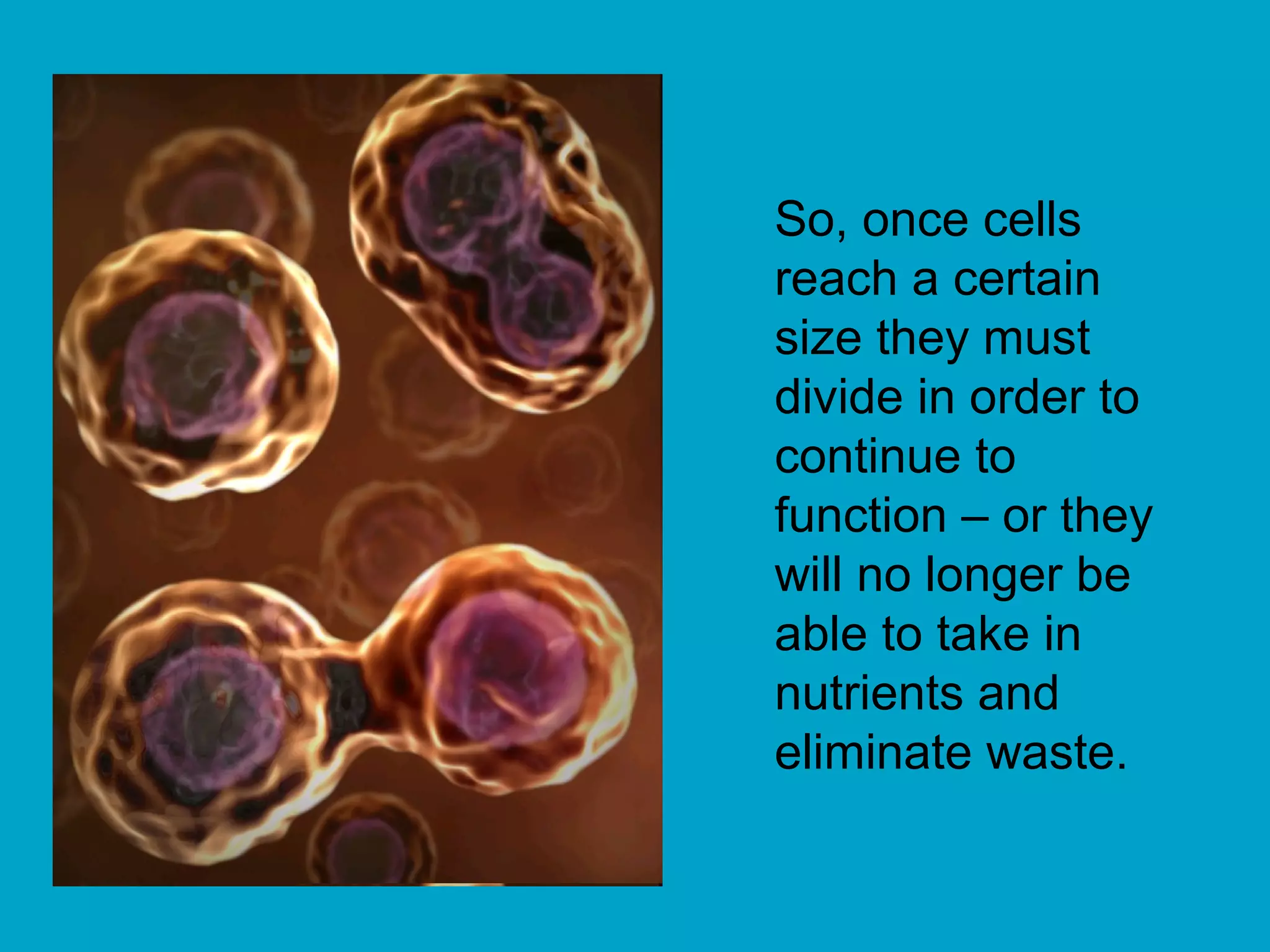
1. The document discusses the process of cell division through mitosis and meiosis.
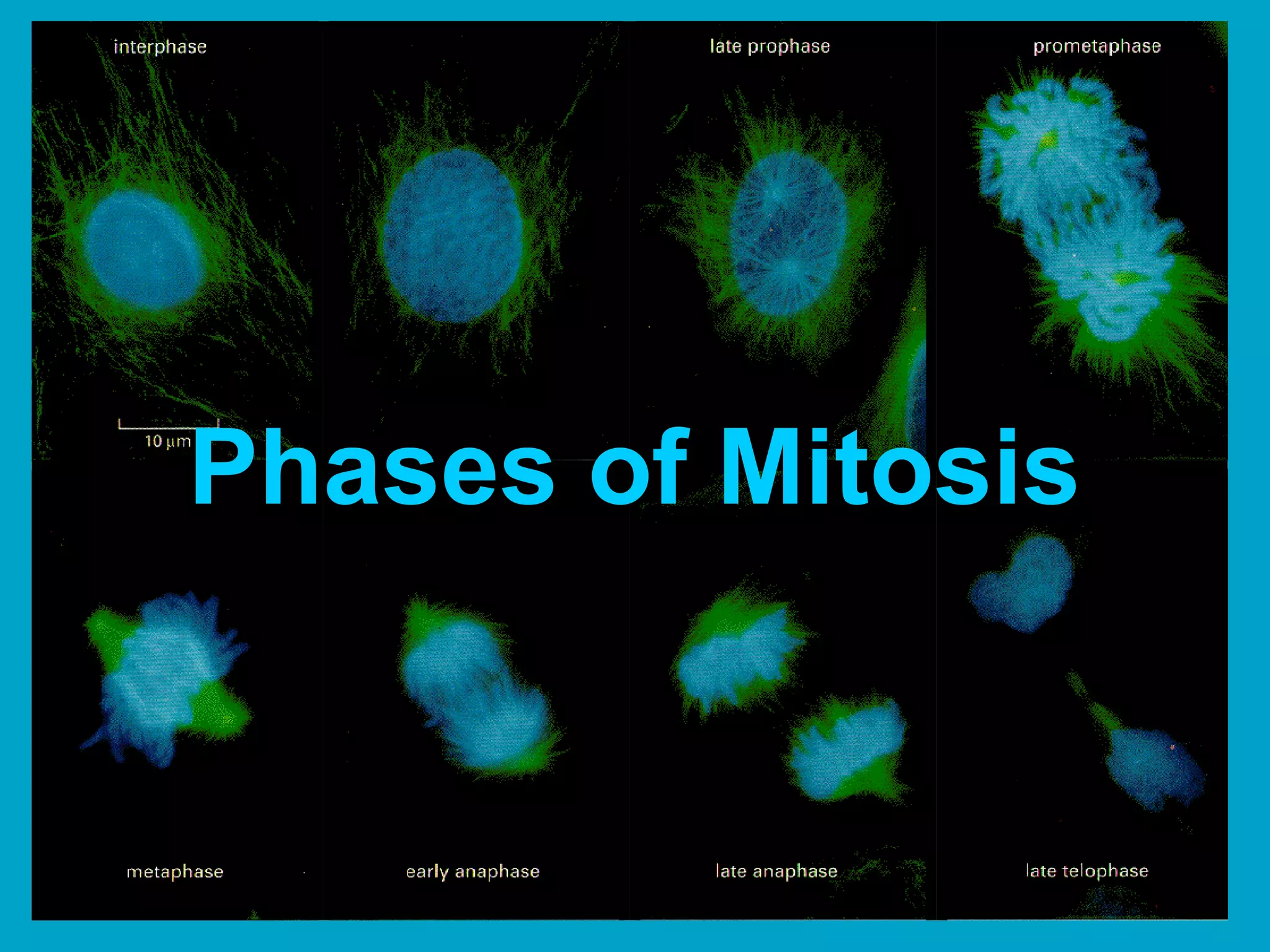
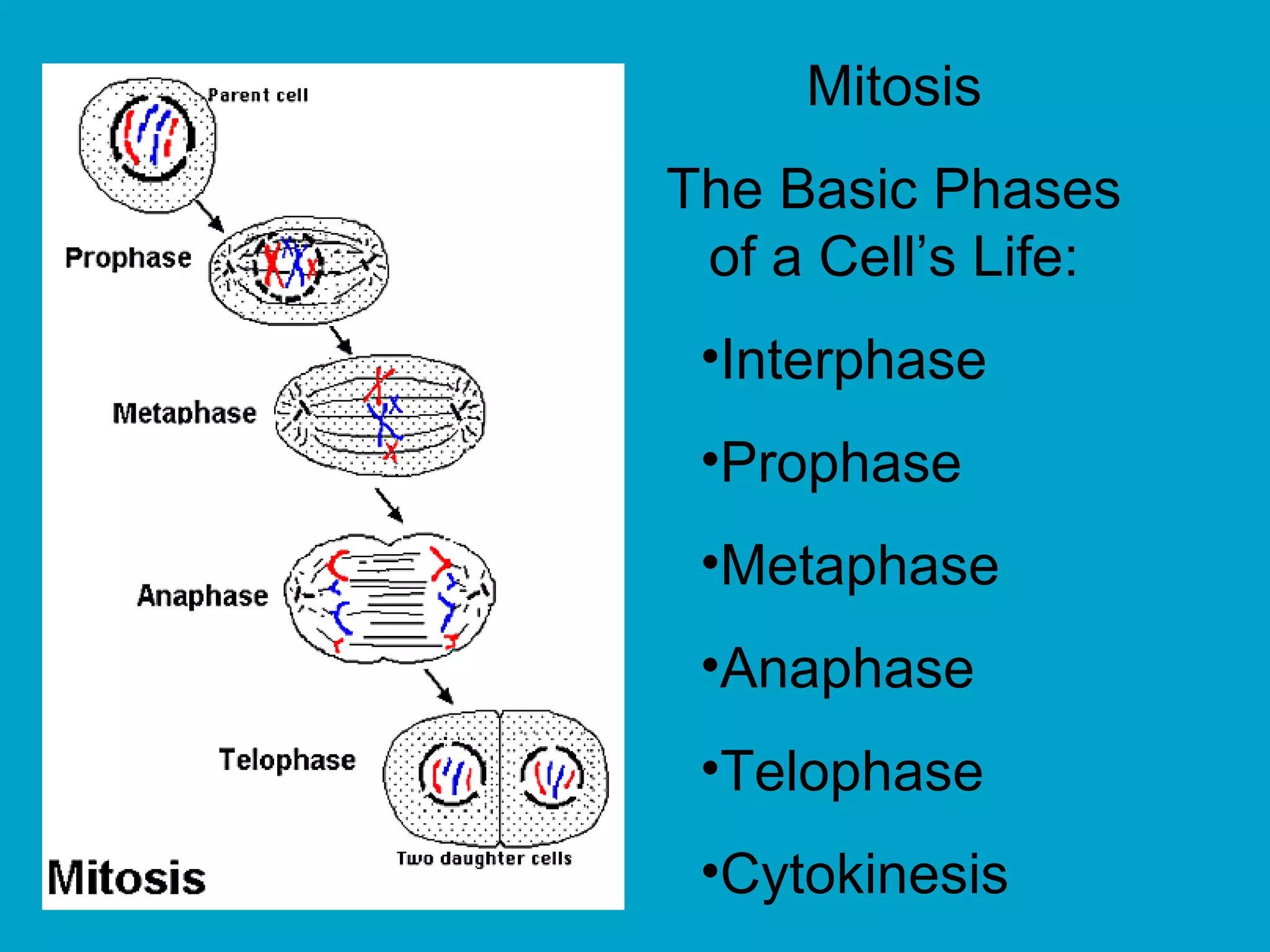
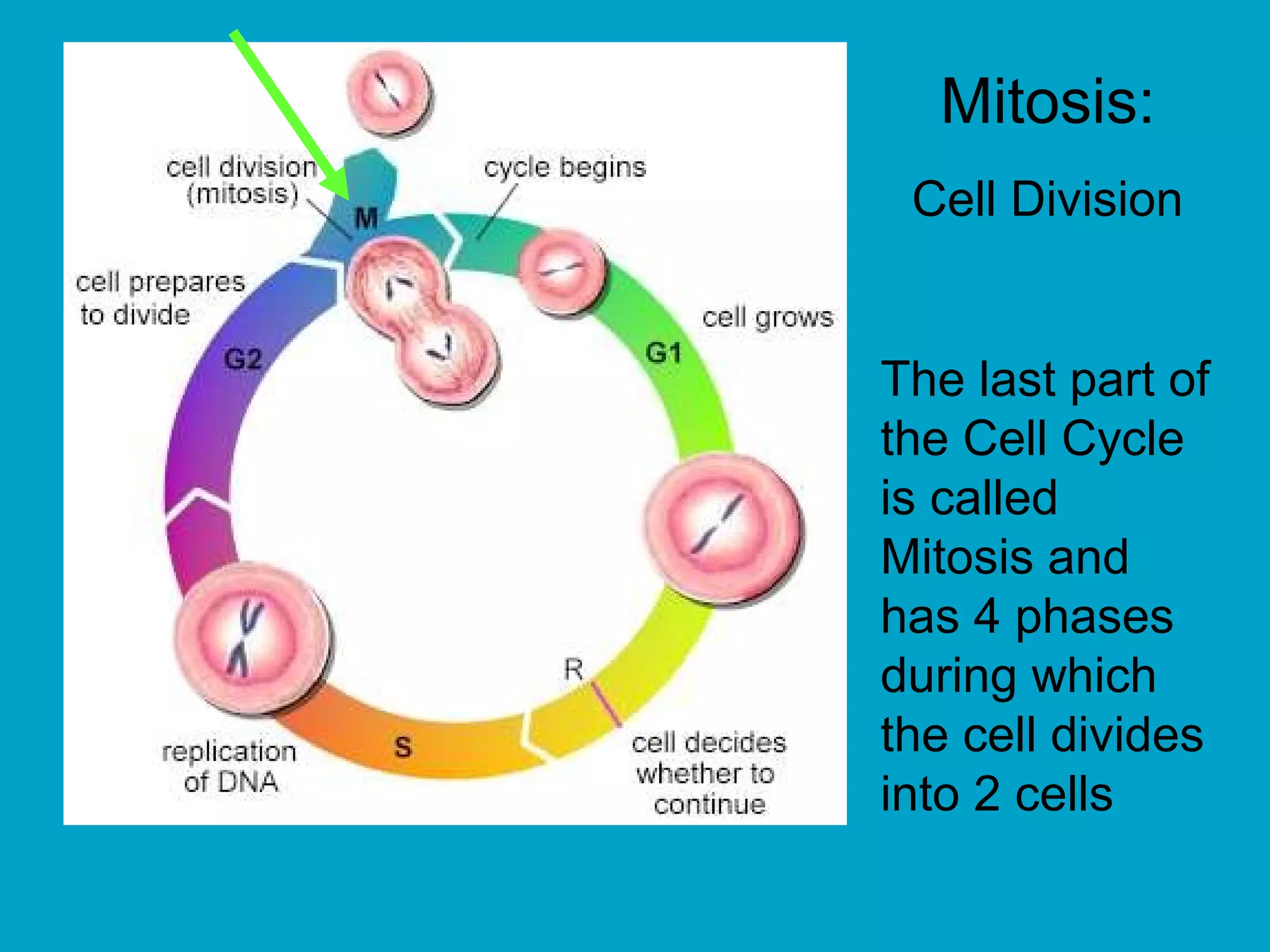
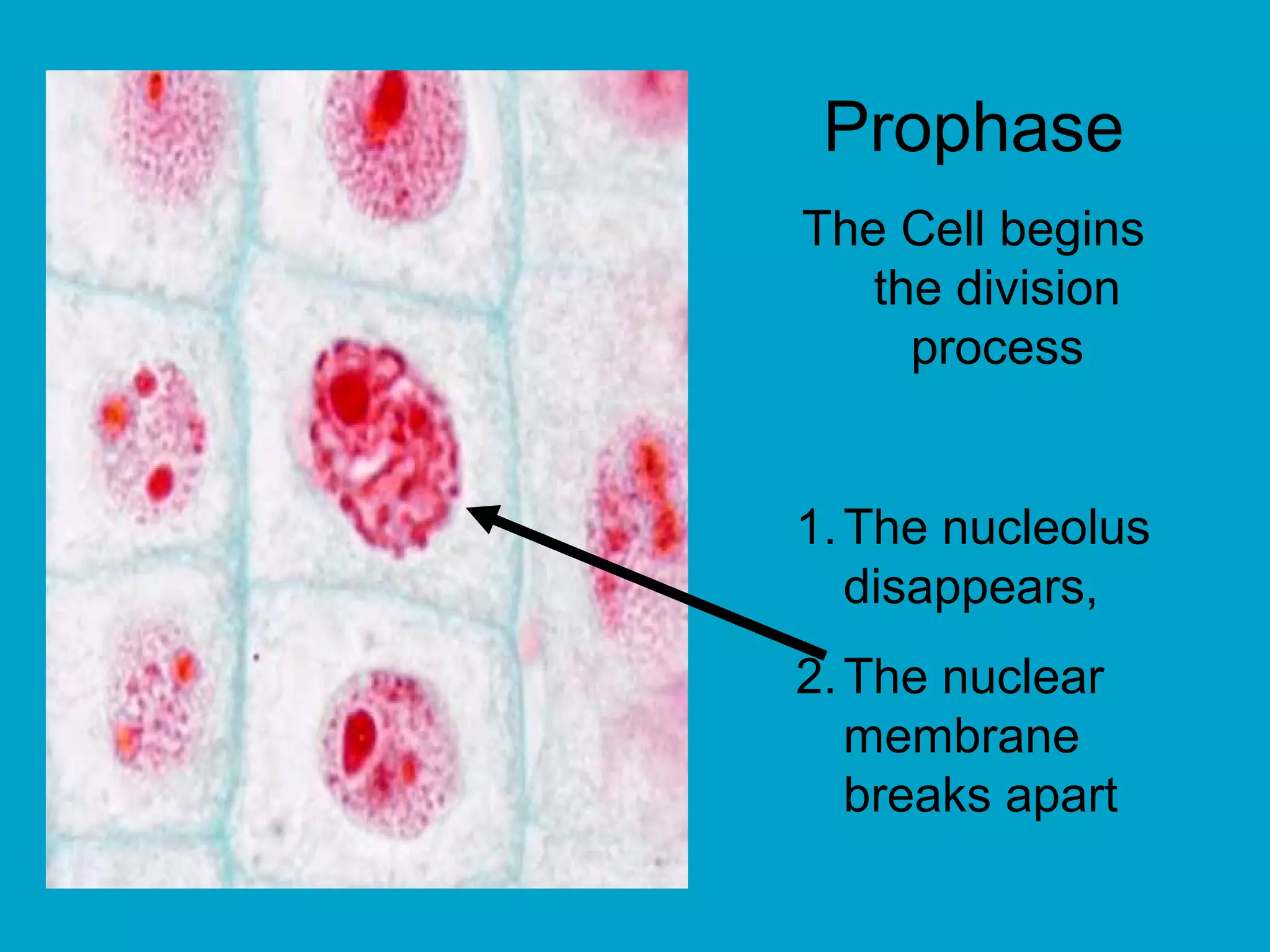
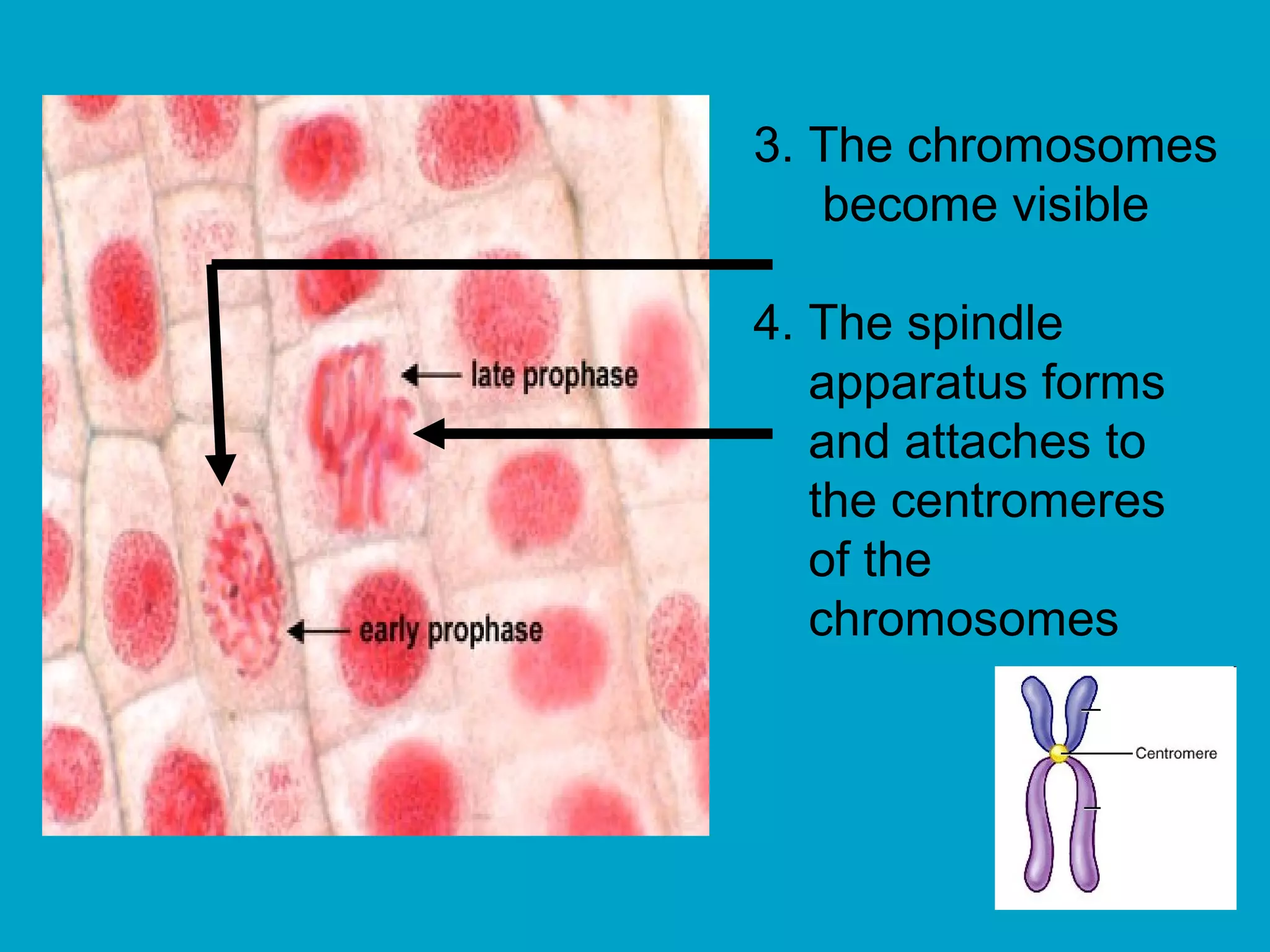
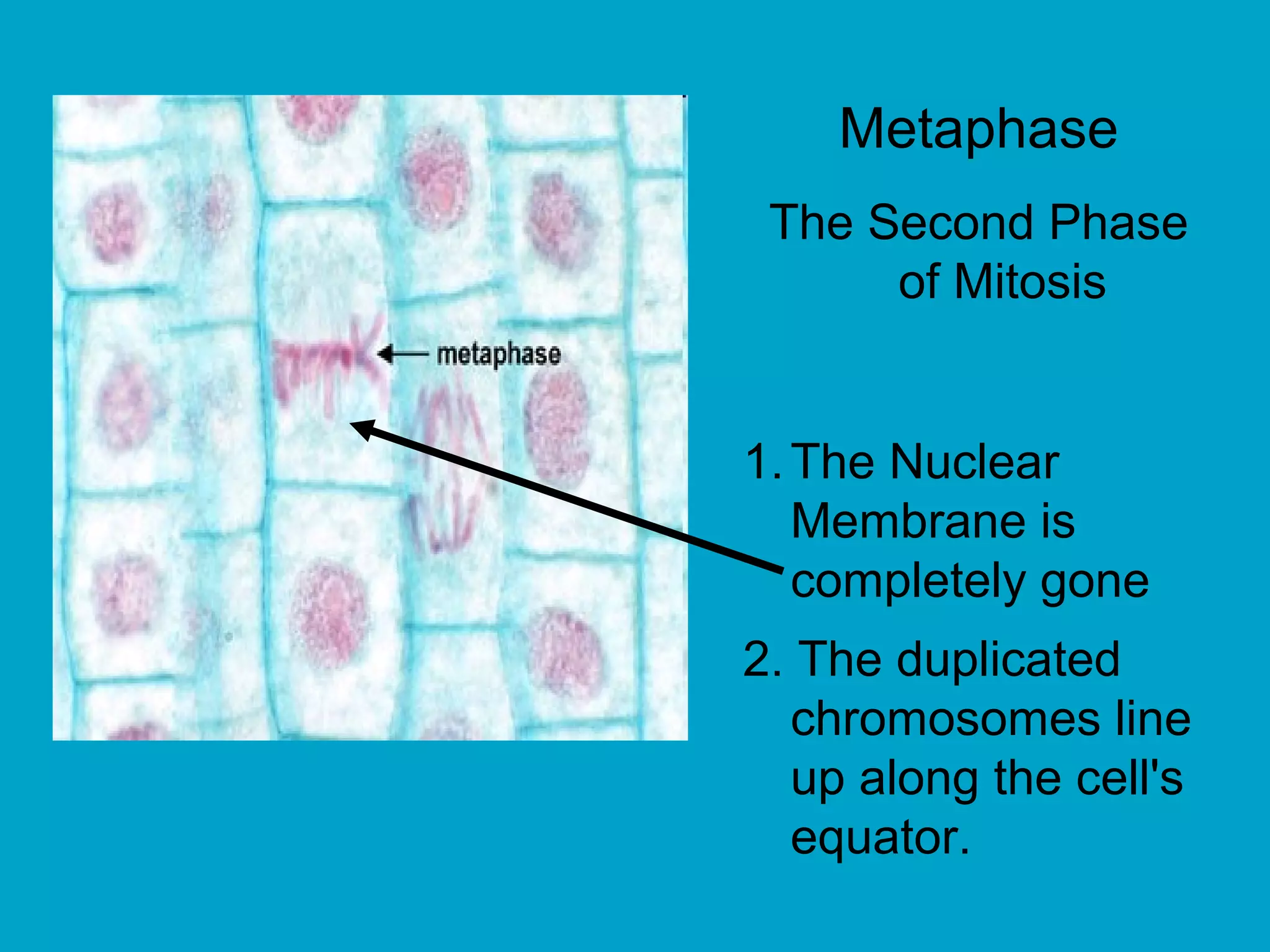
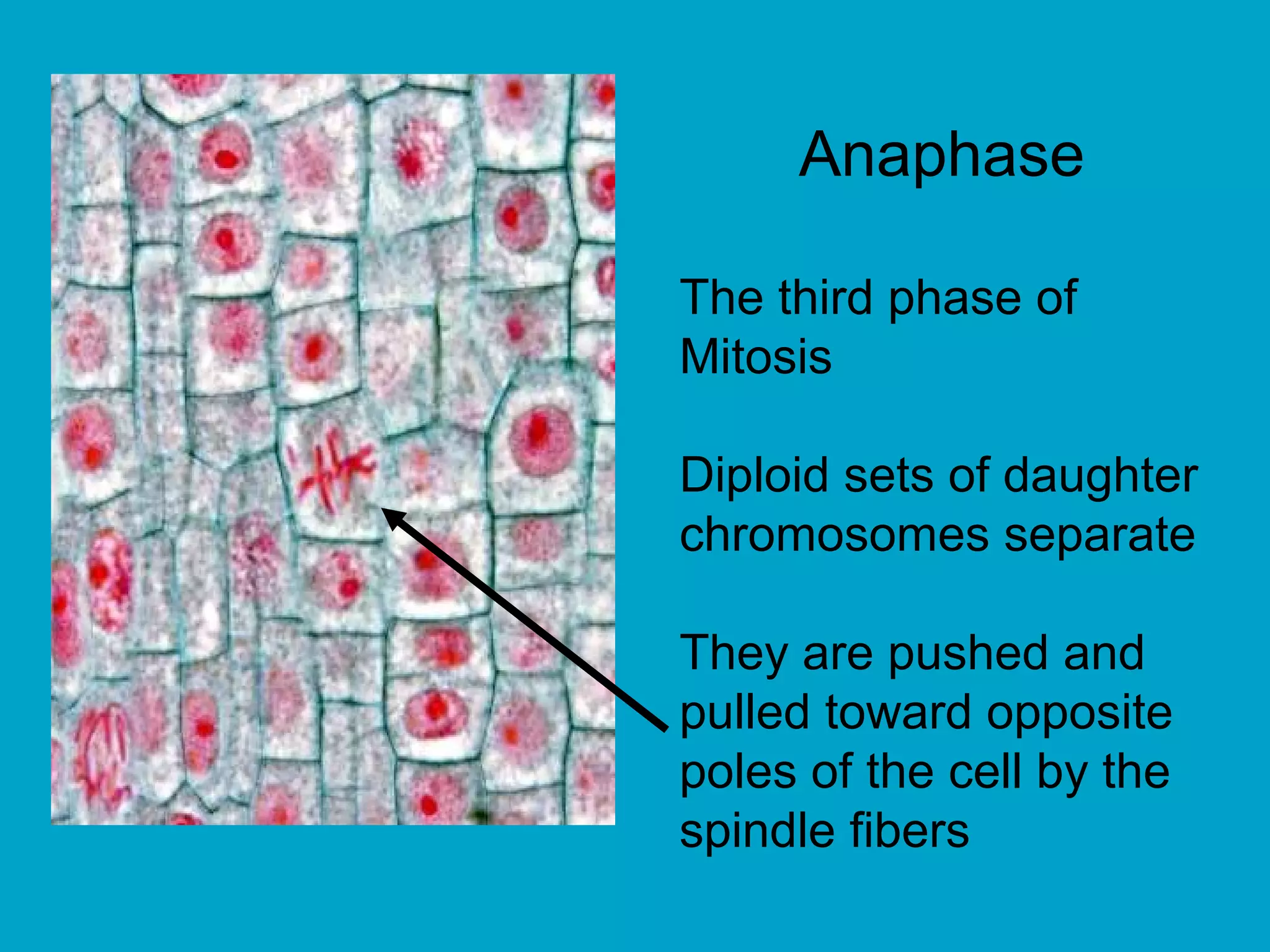
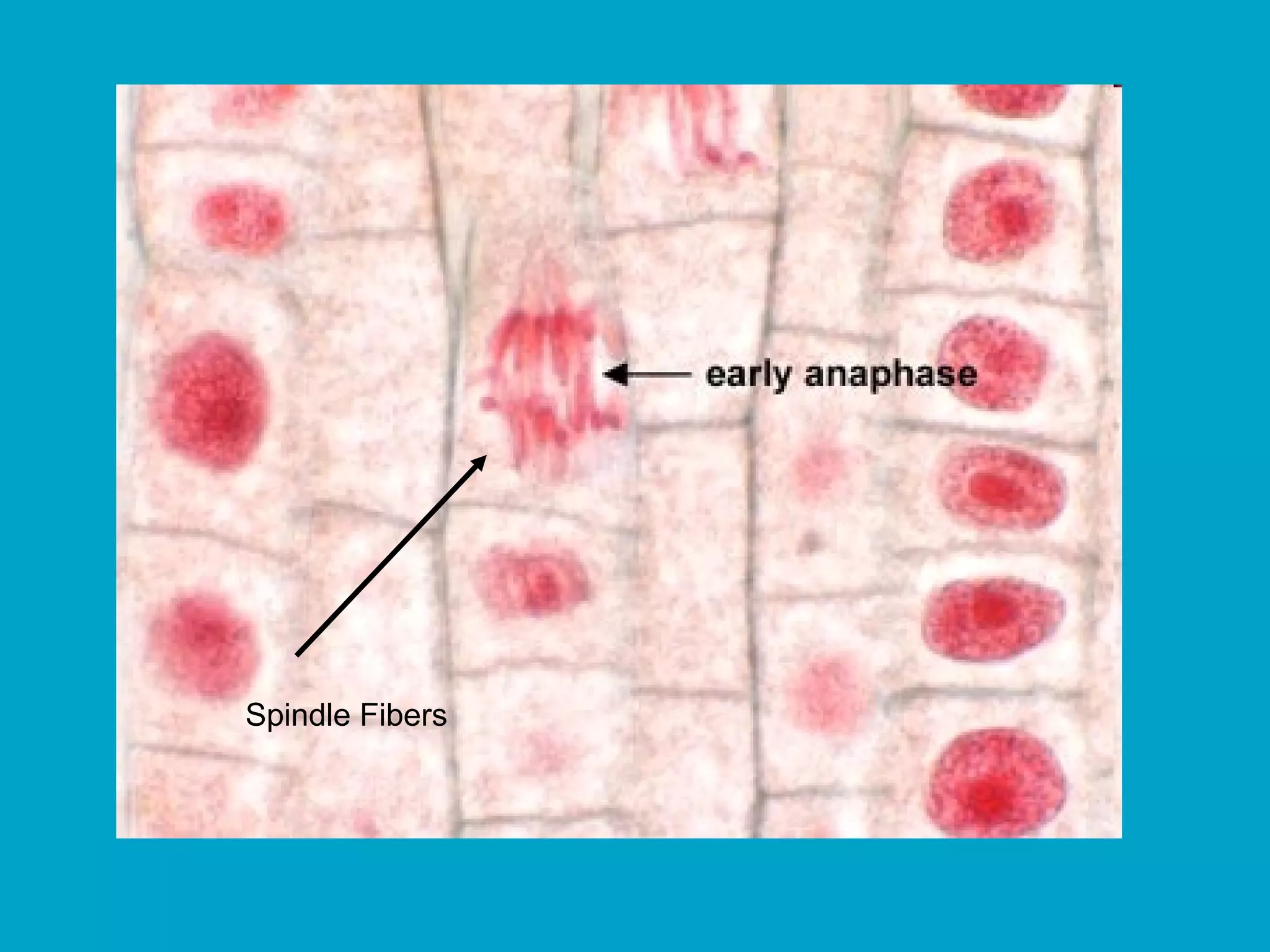
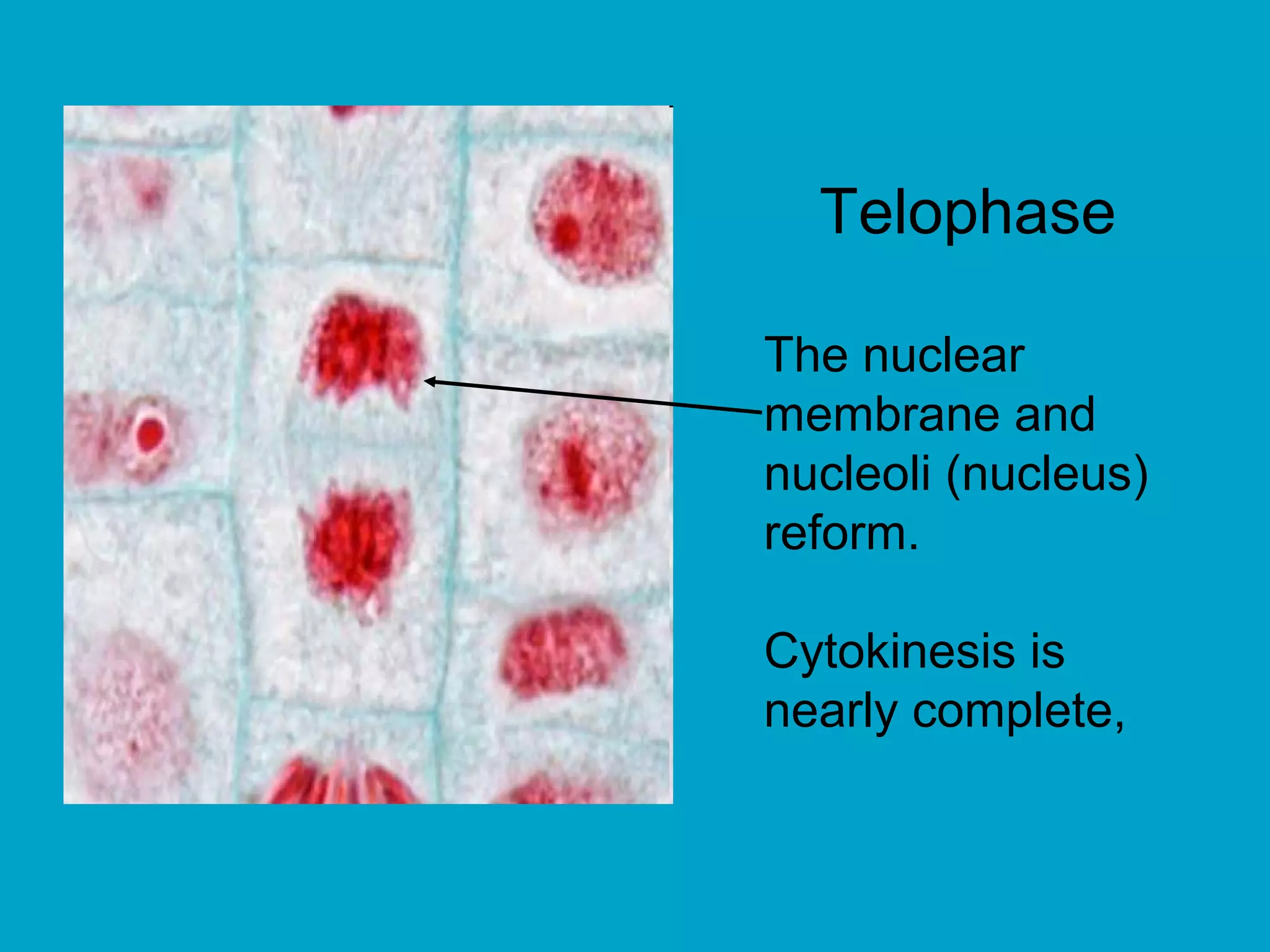
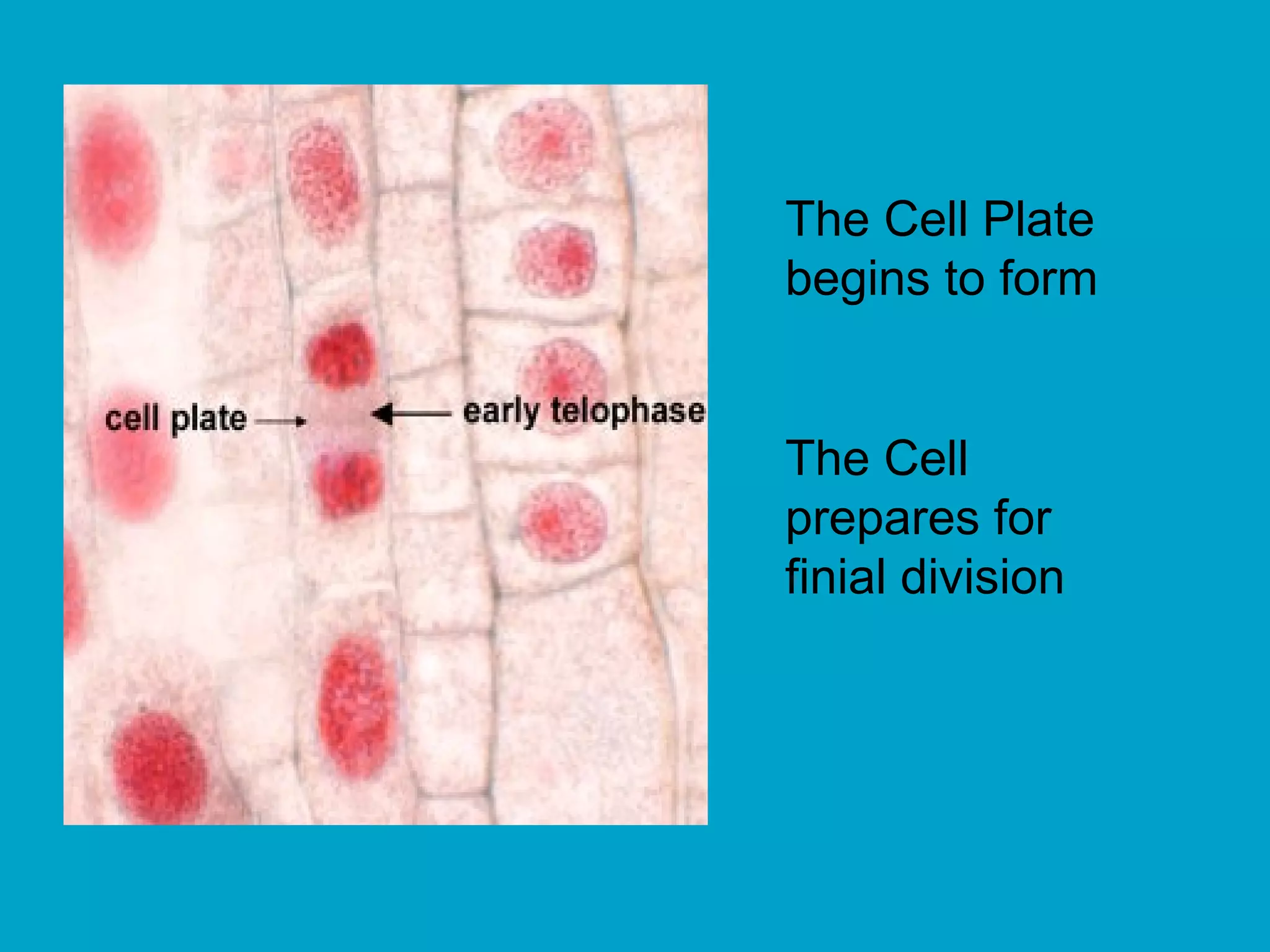
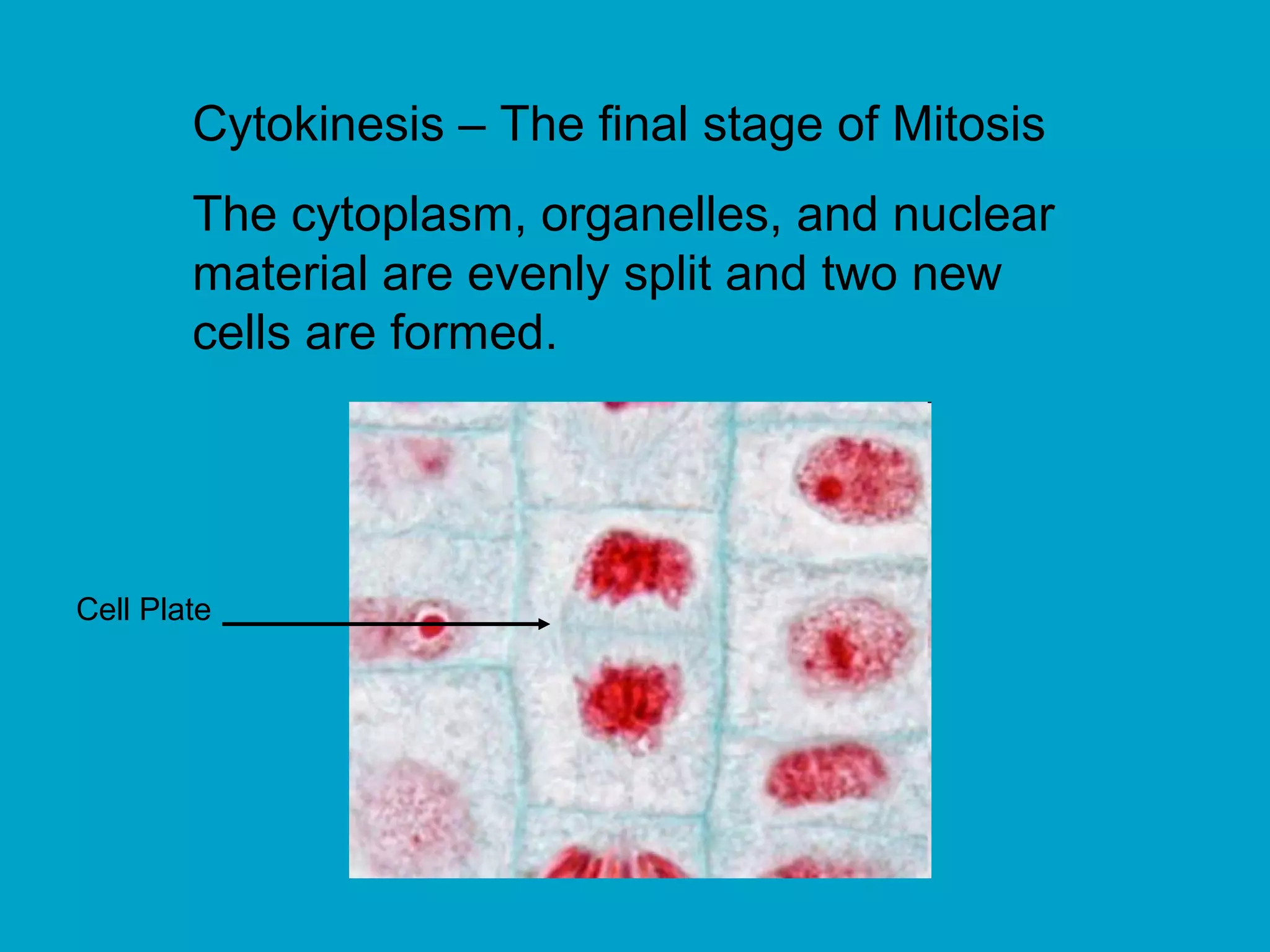
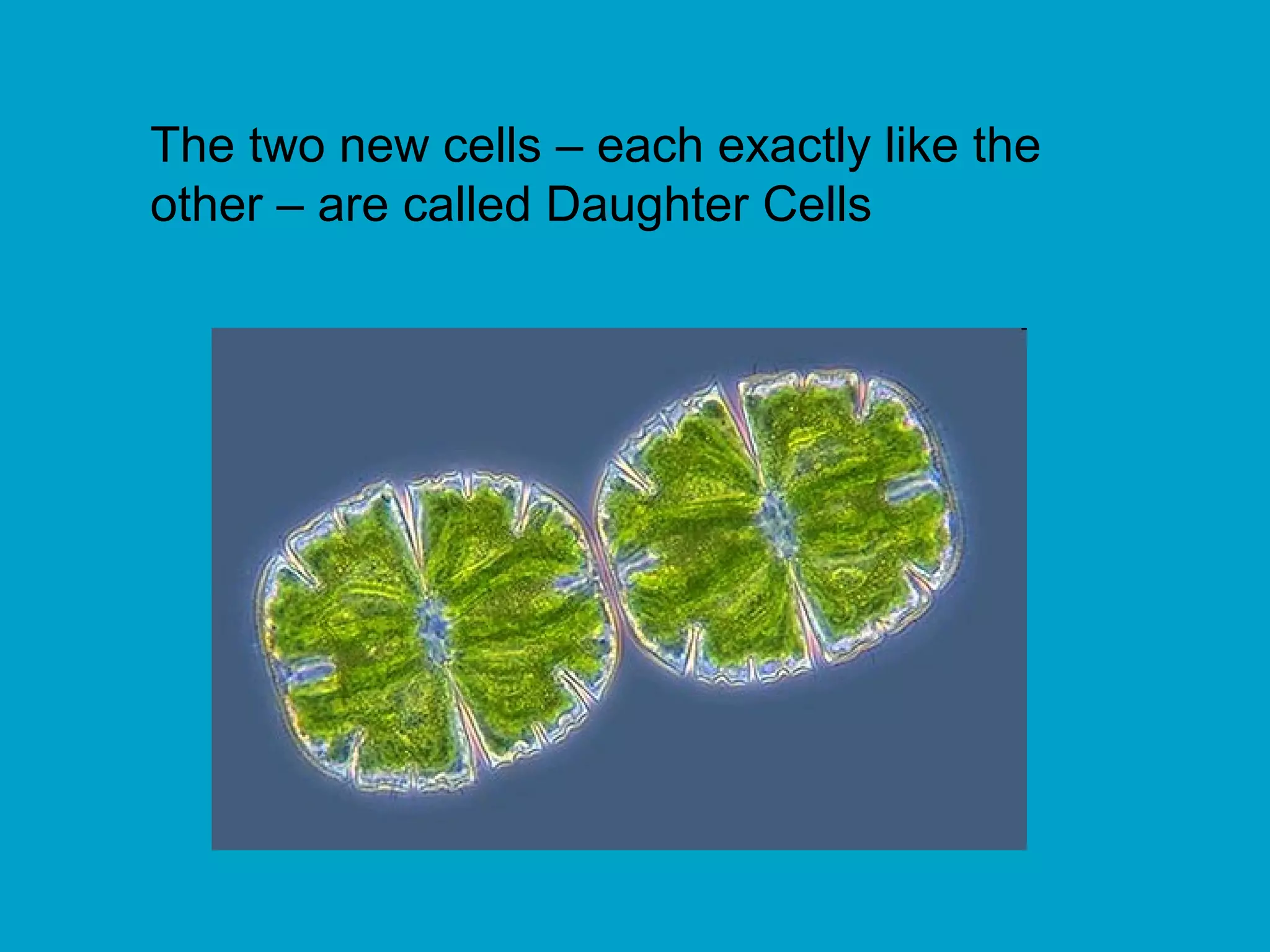
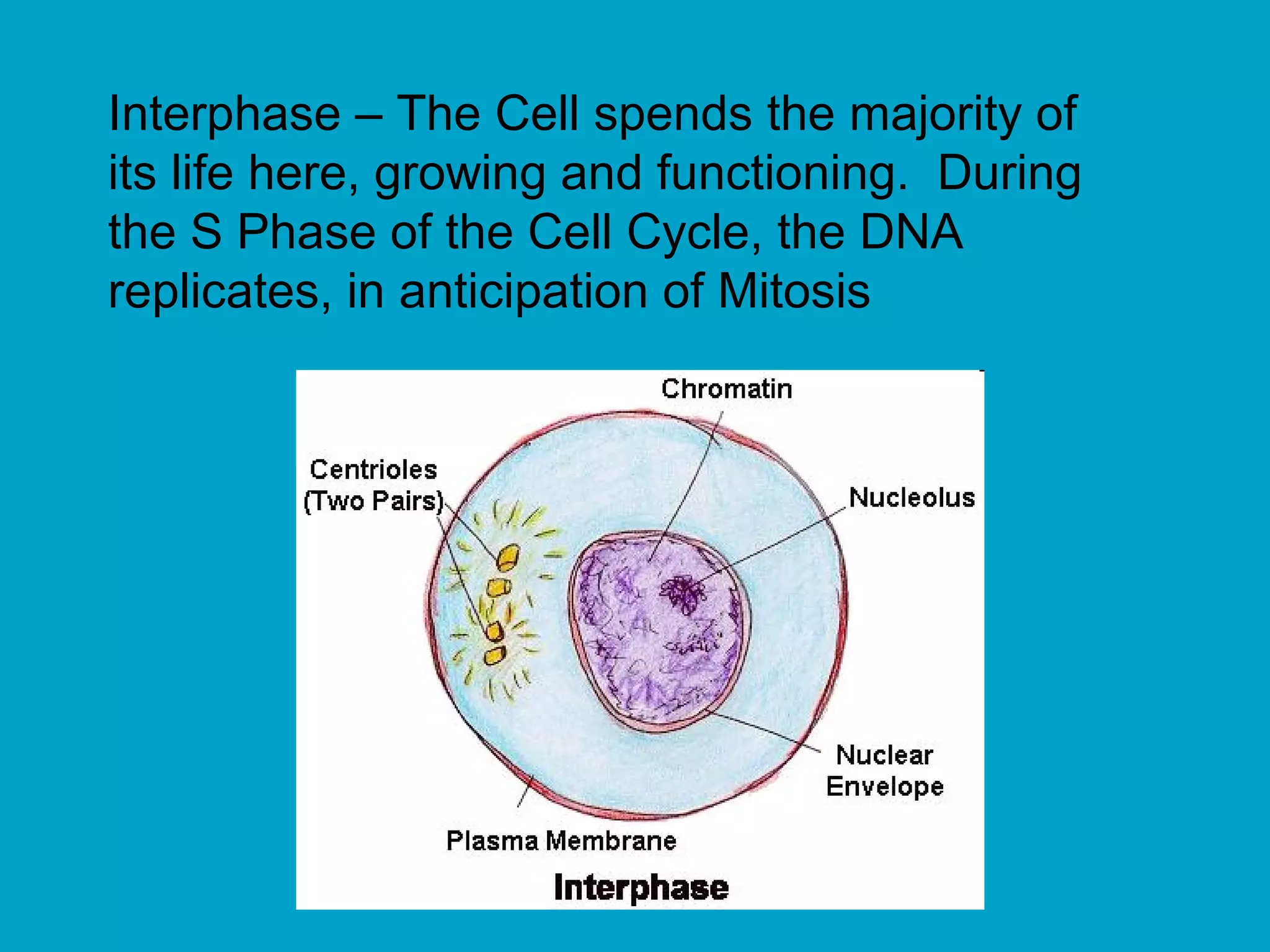
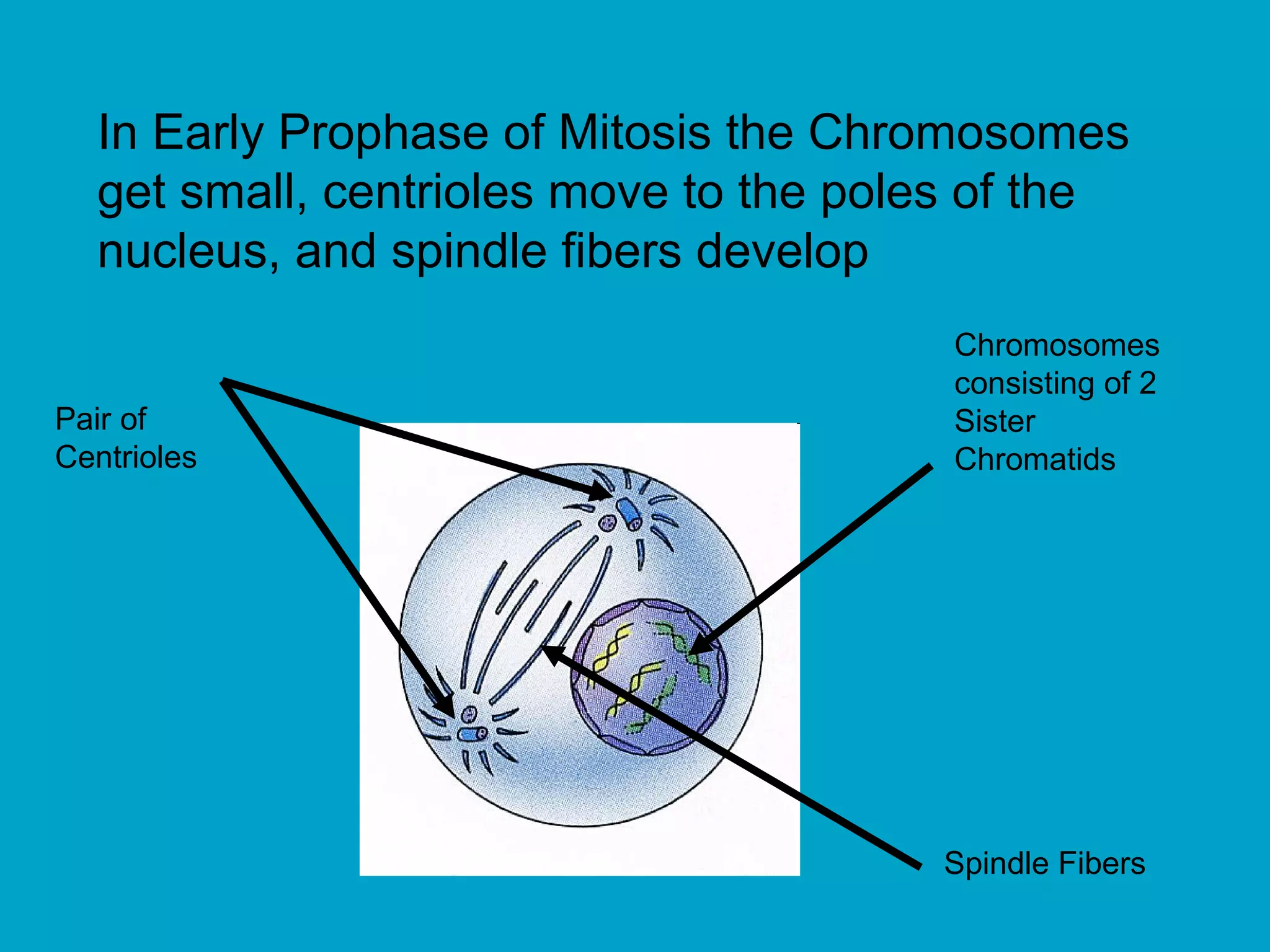
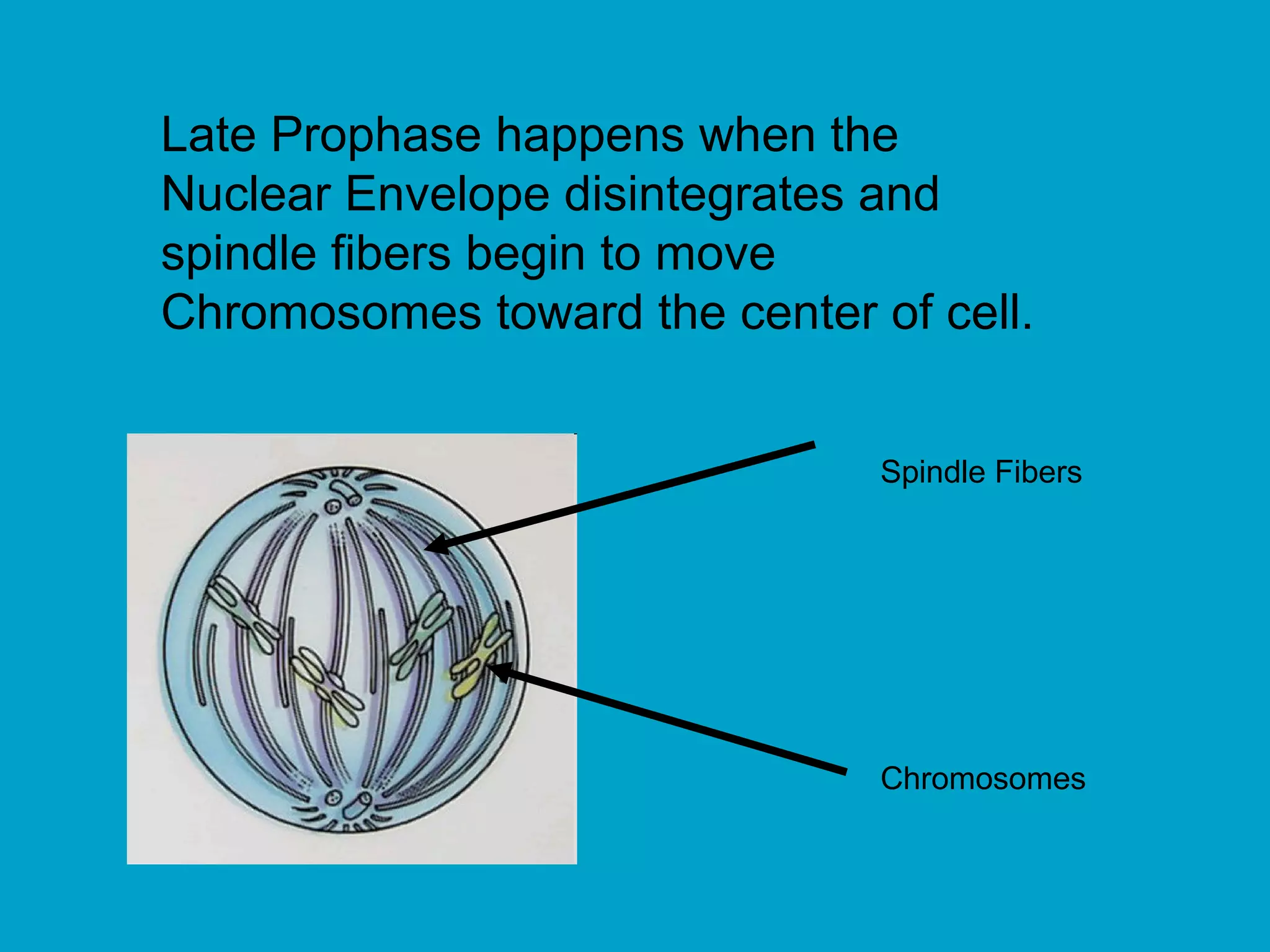
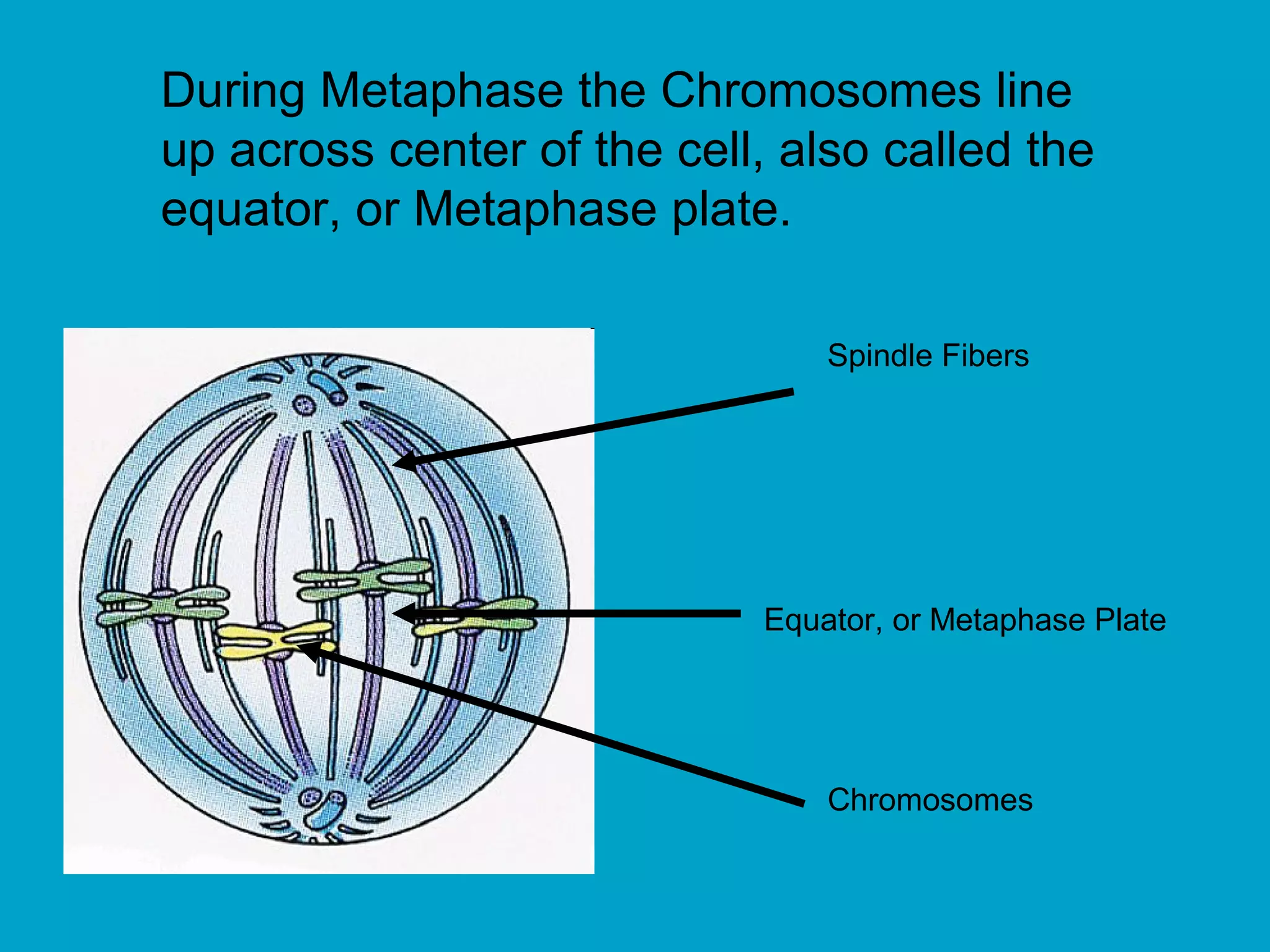
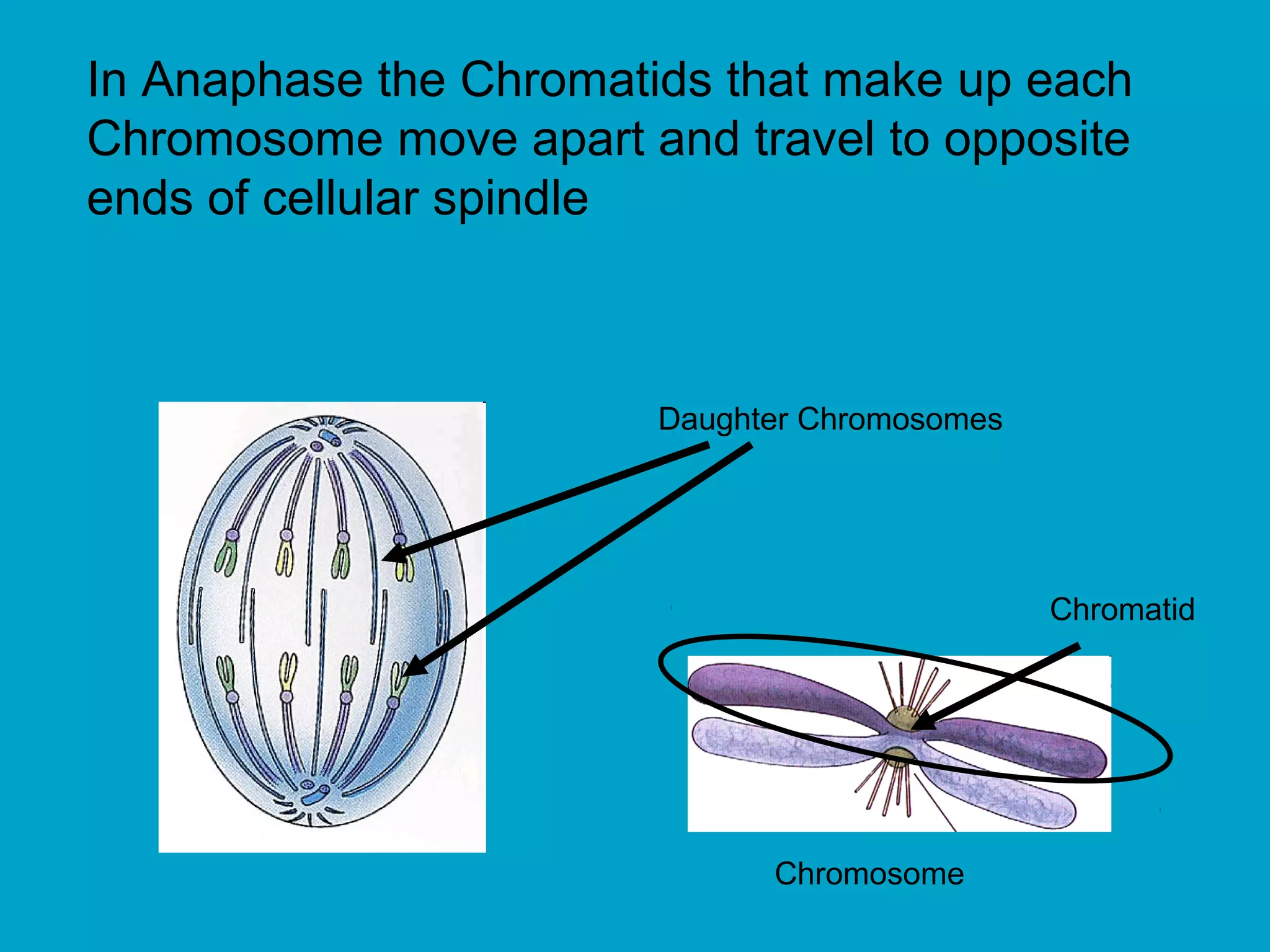
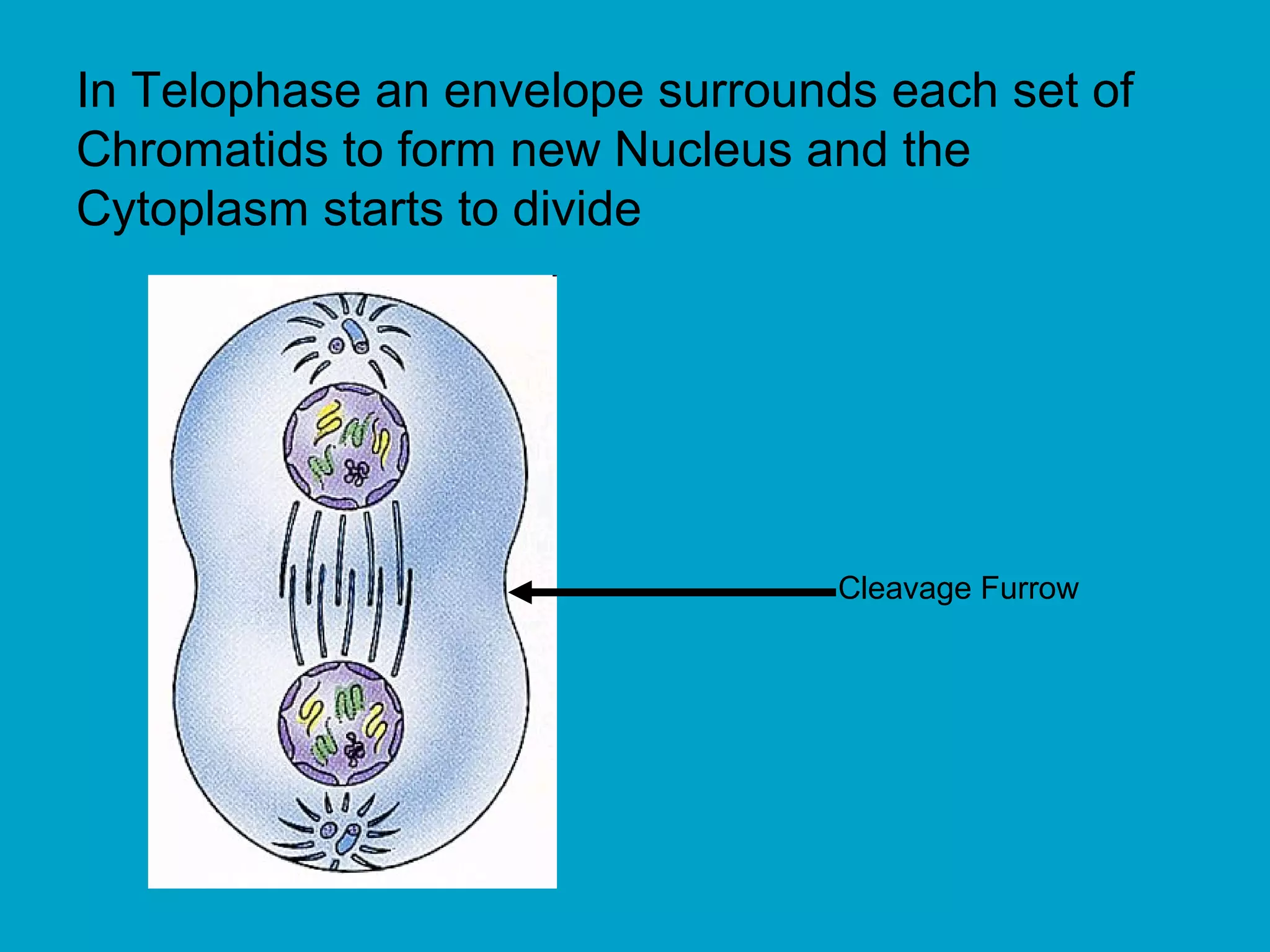
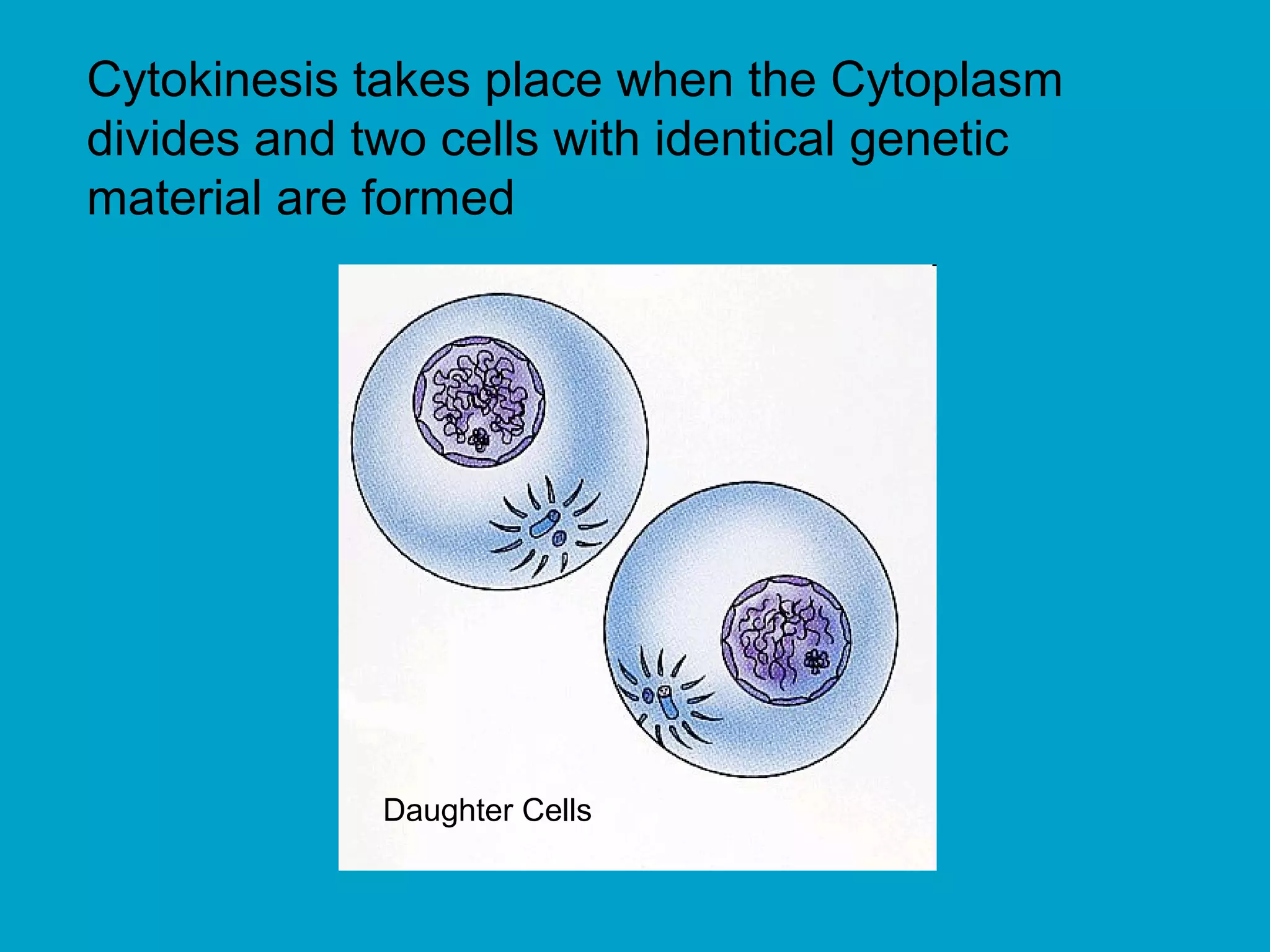
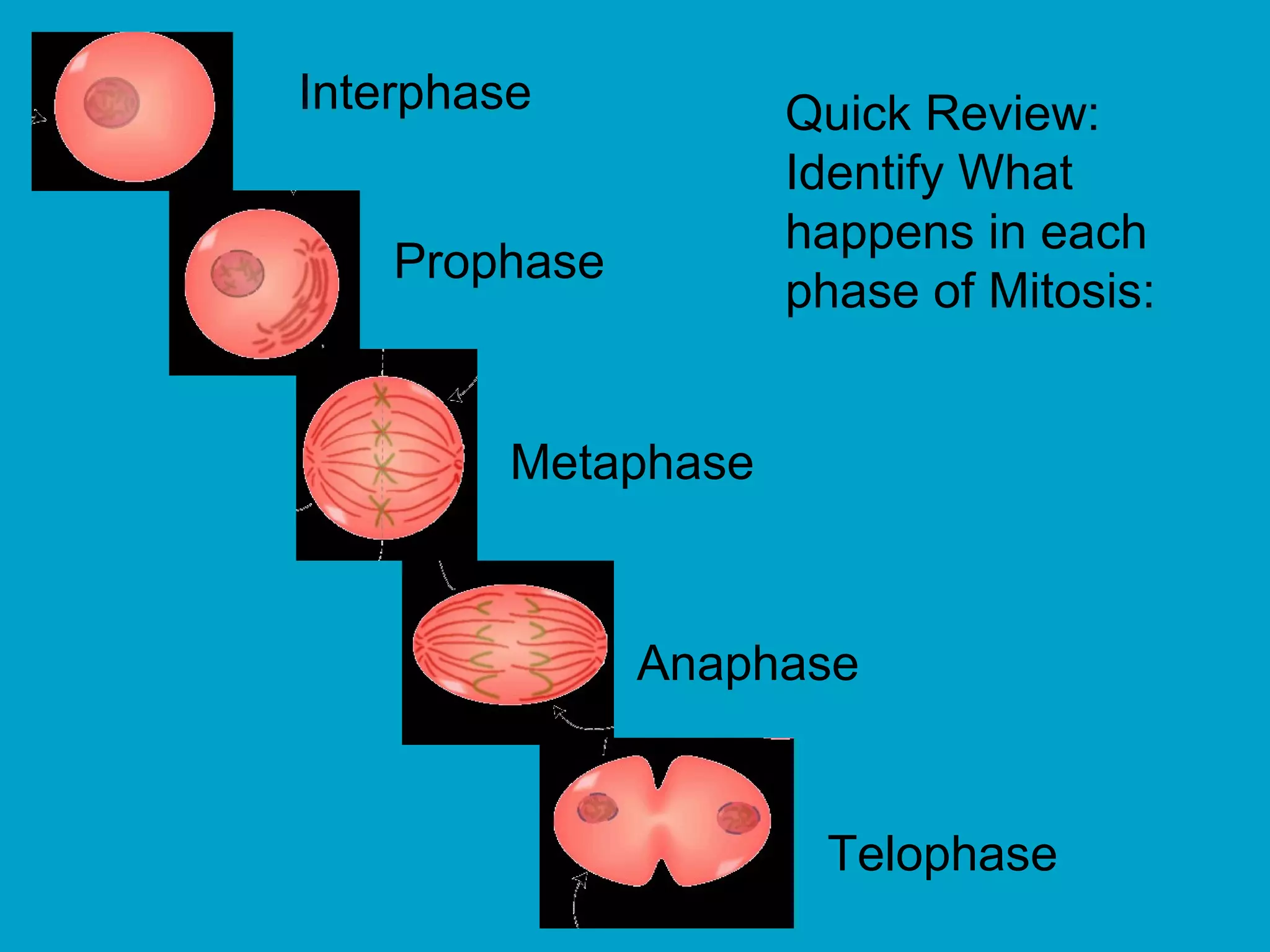
2. Mitosis is the process by which somatic body cells divide. It occurs in several phases: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
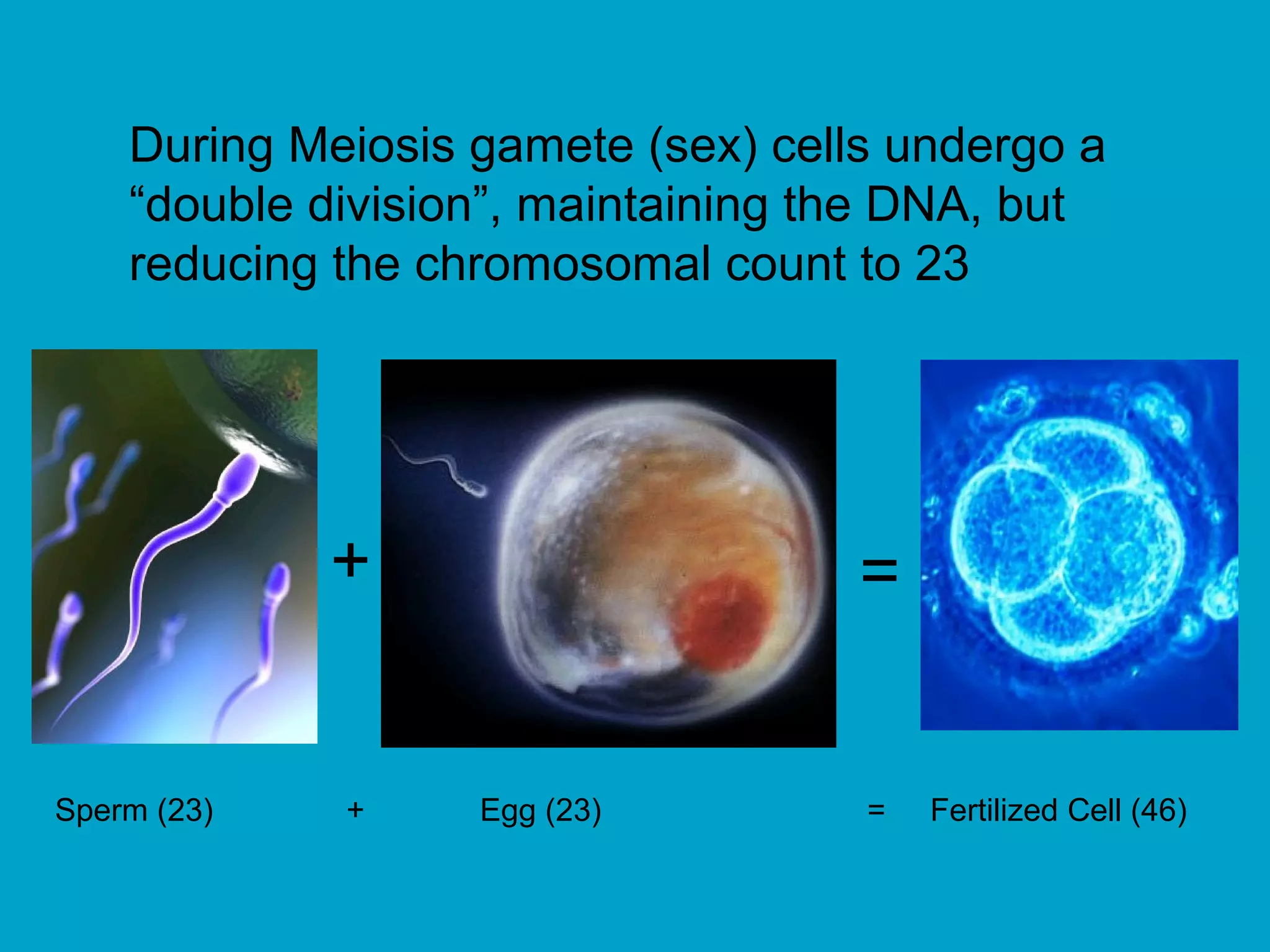
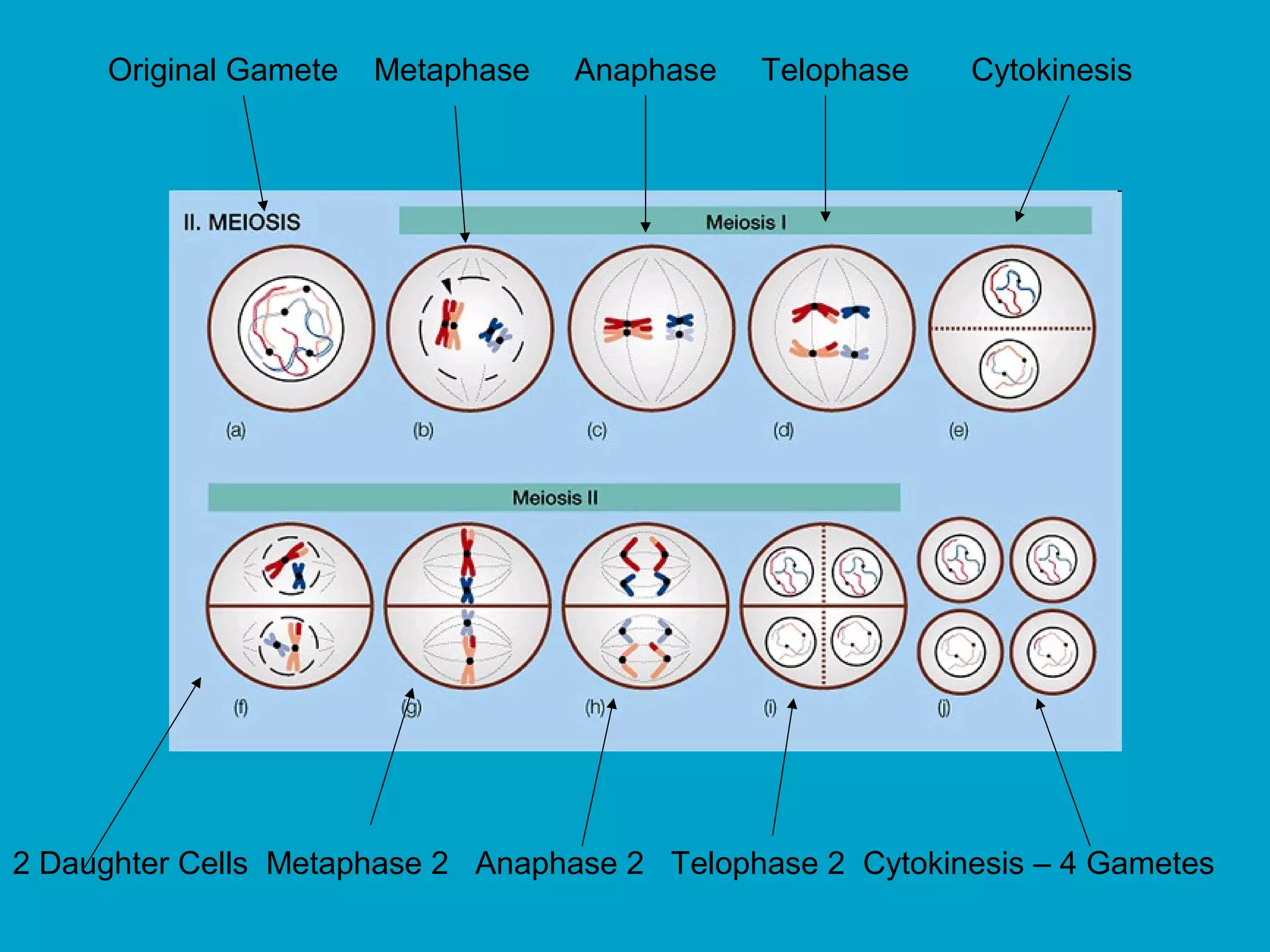
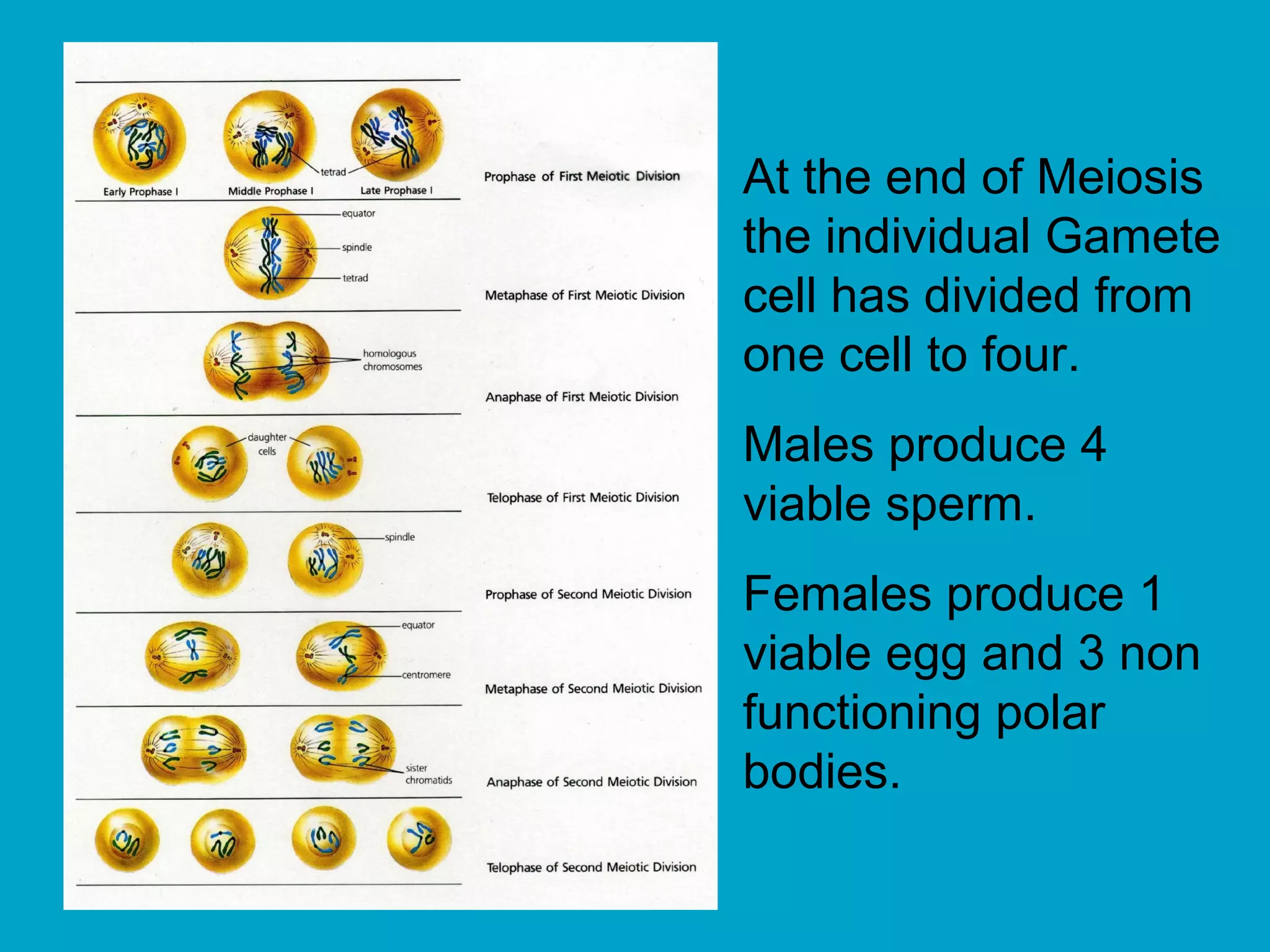
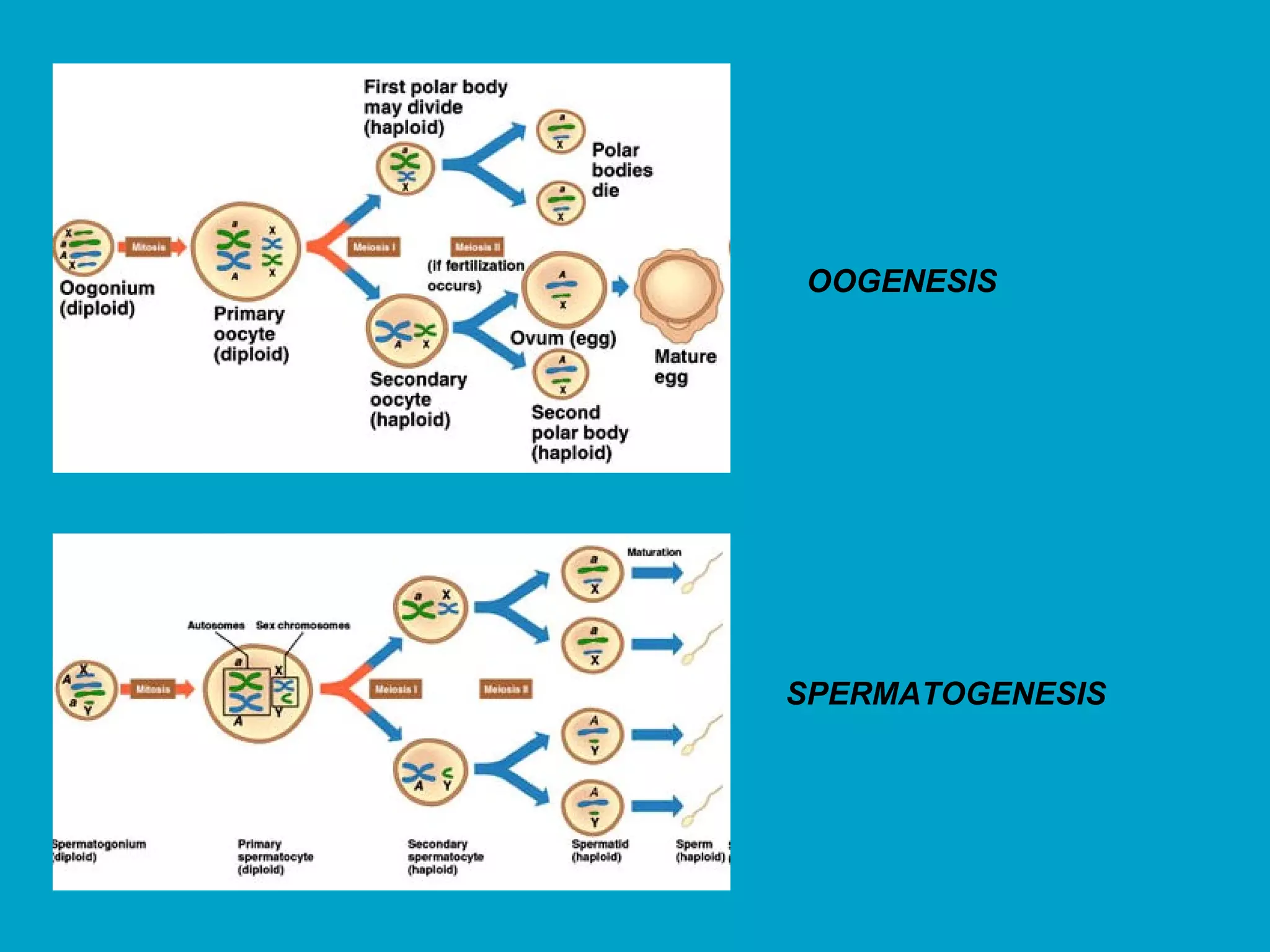
3. Meiosis produces gametes like eggs and sperm, which have half the number of chromosomes as body cells. It involves two cell divisions and results in four daughter cells with unique combinations of chromosomes from each parent.