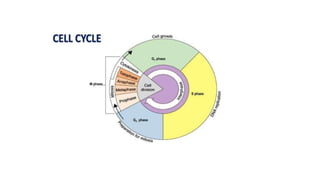
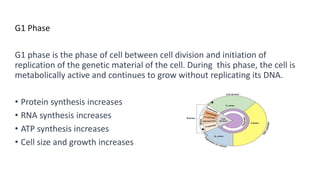
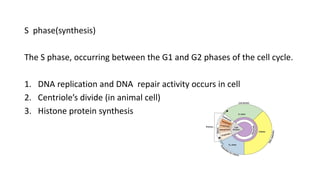
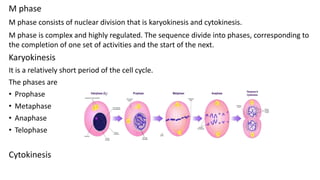
The document summarizes key aspects of the cell cycle and cell division. It begins by introducing the cell cycle, which involves the copying and distribution of a cell's genome into two daughter cells. It then describes the main phases of the cell cycle as interphase (which includes G1, S, and G2 phases) and the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). Interphase involves cell growth and DNA replication, while the M phase is when the cell undergoes nuclear and cellular division to form two daughter cells. In summary, the document provides an overview of the stages of the cell cycle, from interphase to mitosis and cytokinesis, and how cells grow and replicate their DNA before dividing.