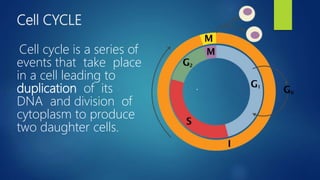
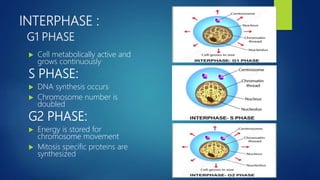
Group 5's members are listed as Nimra khan, Kashmala, Laiba, Iqra, Shiasta, and Taqdees. The document then defines the cell cycle as a series of events leading to DNA duplication and cell division into two daughter cells. It describes the two main phases as interphase and mitotic phase. Interphase is further broken down into G1, S, and G2 phases for cell growth and DNA replication. The mitotic phase is described in detail, outlining the specific processes of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase leading to cytokinesis and two daughter cells. Meiosis is also summarized as reducing chromosome number by half in daughter cells compared