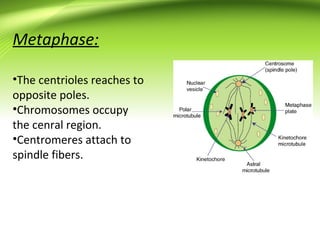
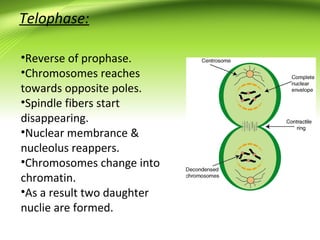
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells having identical chromosomes to the parent cell. It occurs in somatic cells and has four main phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Karyokinesis involves the division of the nucleus into two nuclei, while cytokinesis separates the cytoplasm into two daughter cells through an inward movement of the cell membrane.