The document provides an overview of enzymes, including their definition, models (lock and key, induced fit), chemical nature, classification, and mechanisms of action. It discusses factors affecting enzyme activity such as substrate concentration, temperature, and pH, along with inhibitors and related diseases. Additionally, it highlights the industrial applications of enzymes in various sectors including food, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals.





![Oxygenase
Dehydrogenases
Hydroperoxides
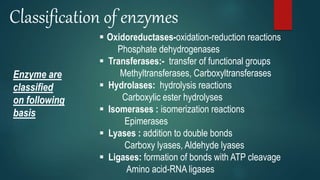
1)Oxidoreductase
Oxidases involving donation of a hydrogen
atom, oxygen is reduced to water
(H2O) or hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2)
removing hydrogen atoms
[H] instead of oxygen [O] in
its oxido-reduction
reactions
Pyruvic acid-->lactic acid
Catalyzes the
decomposition of H2O2
H2O2+ +2H+ +2e--> 2H2O
Catalyze the incorporation of
molecular oxygen into the
substrate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymesgroup-5-201009132216/85/Enzymes-ppt-12-320.jpg)