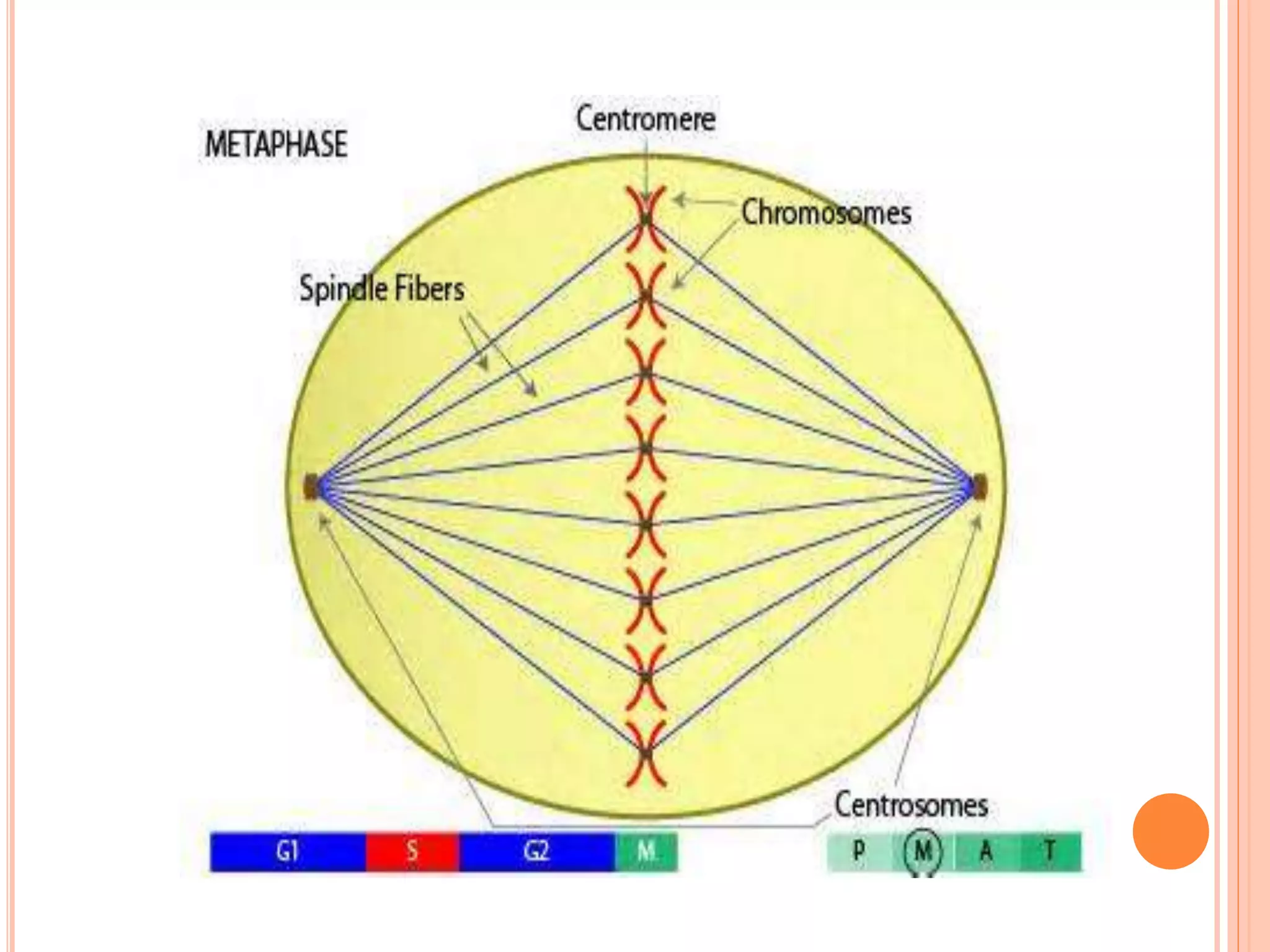
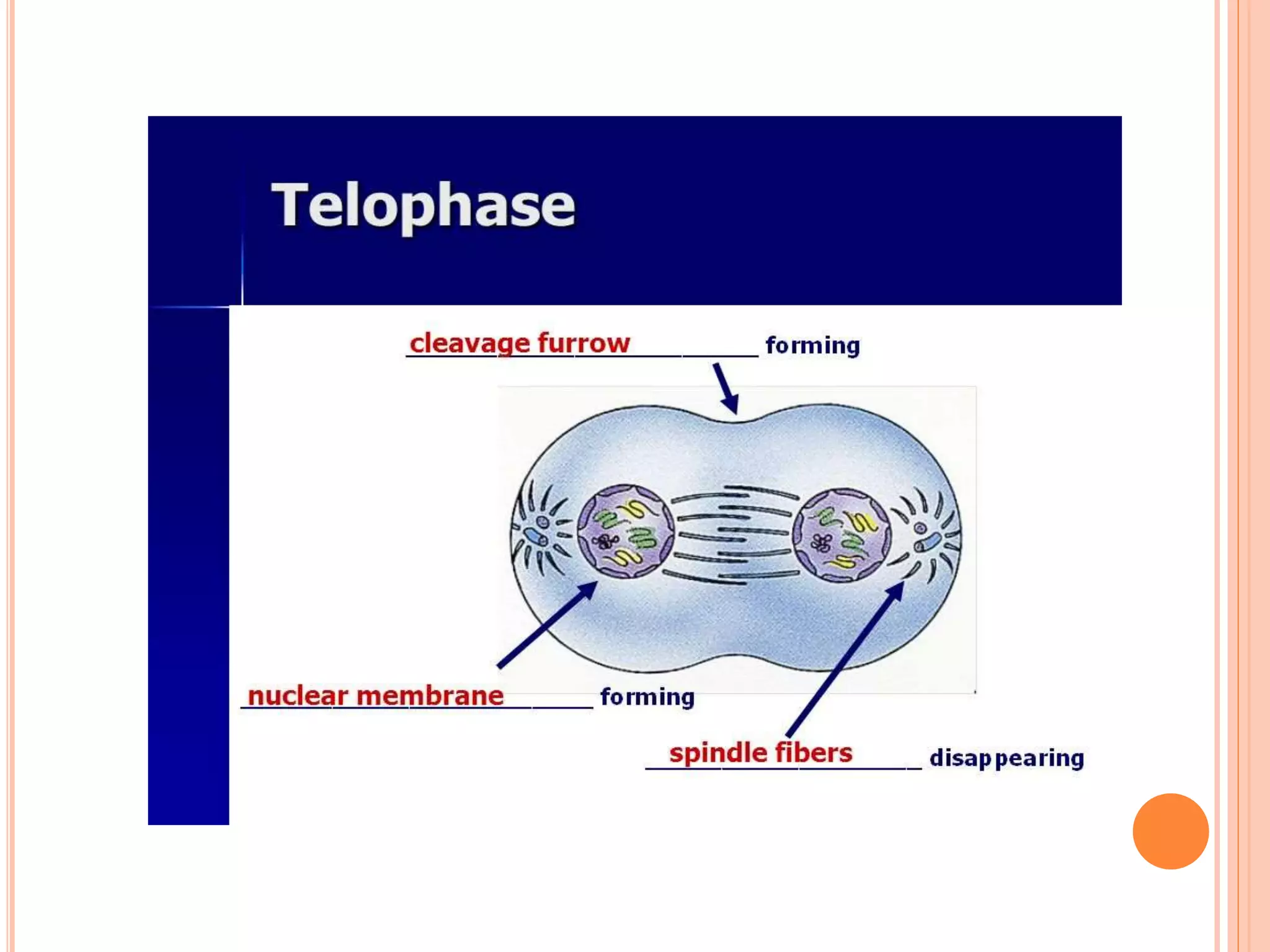
Mitosis is the process of nuclear division where a parent cell divides into two daughter cells with identical genetic material. It consists of four main phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, the chromosomes align along the center of the cell. In anaphase, the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell. Finally, in telophase, the daughter nuclei form and the cell divides through cytokinesis to complete cell division.