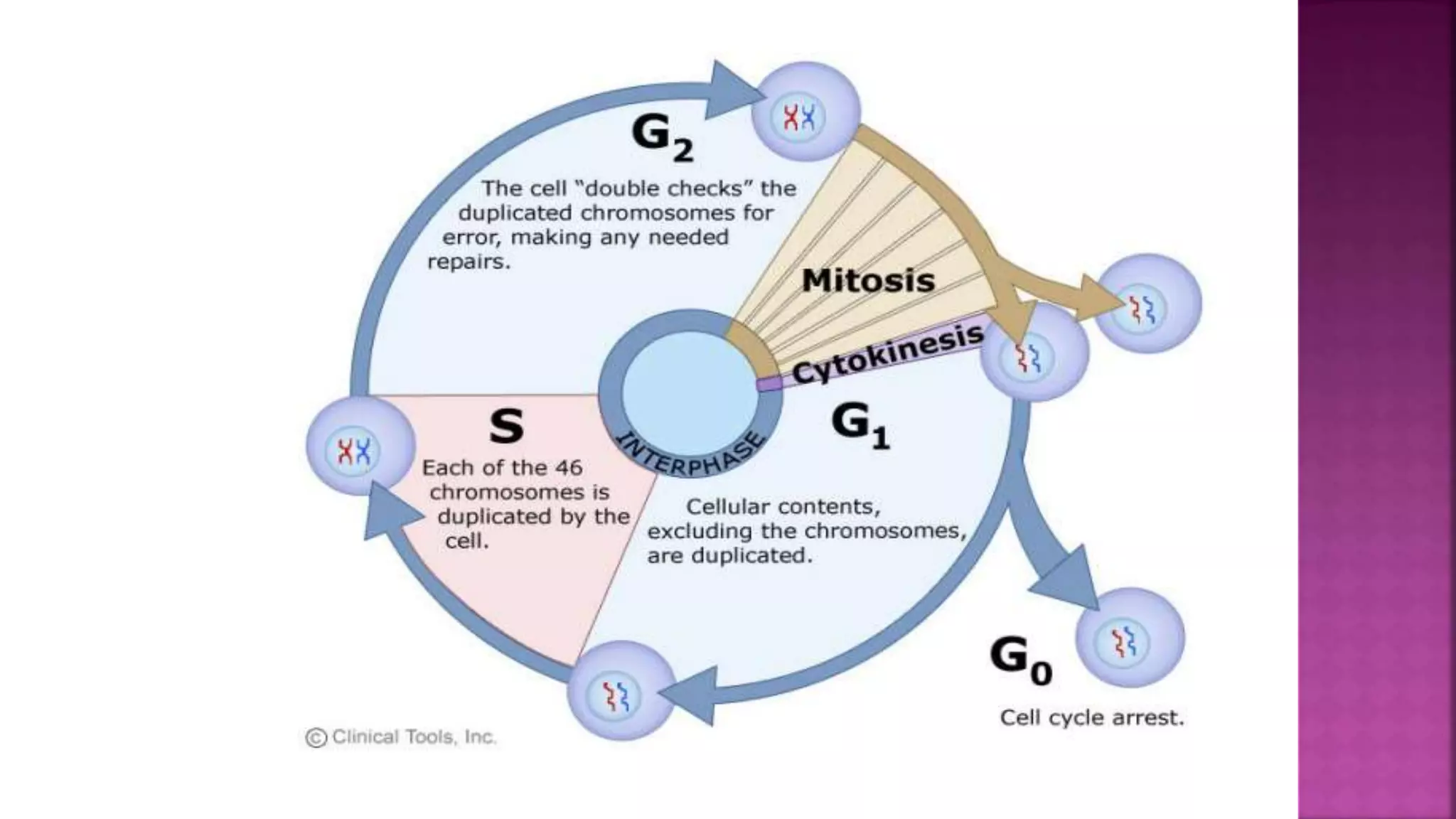
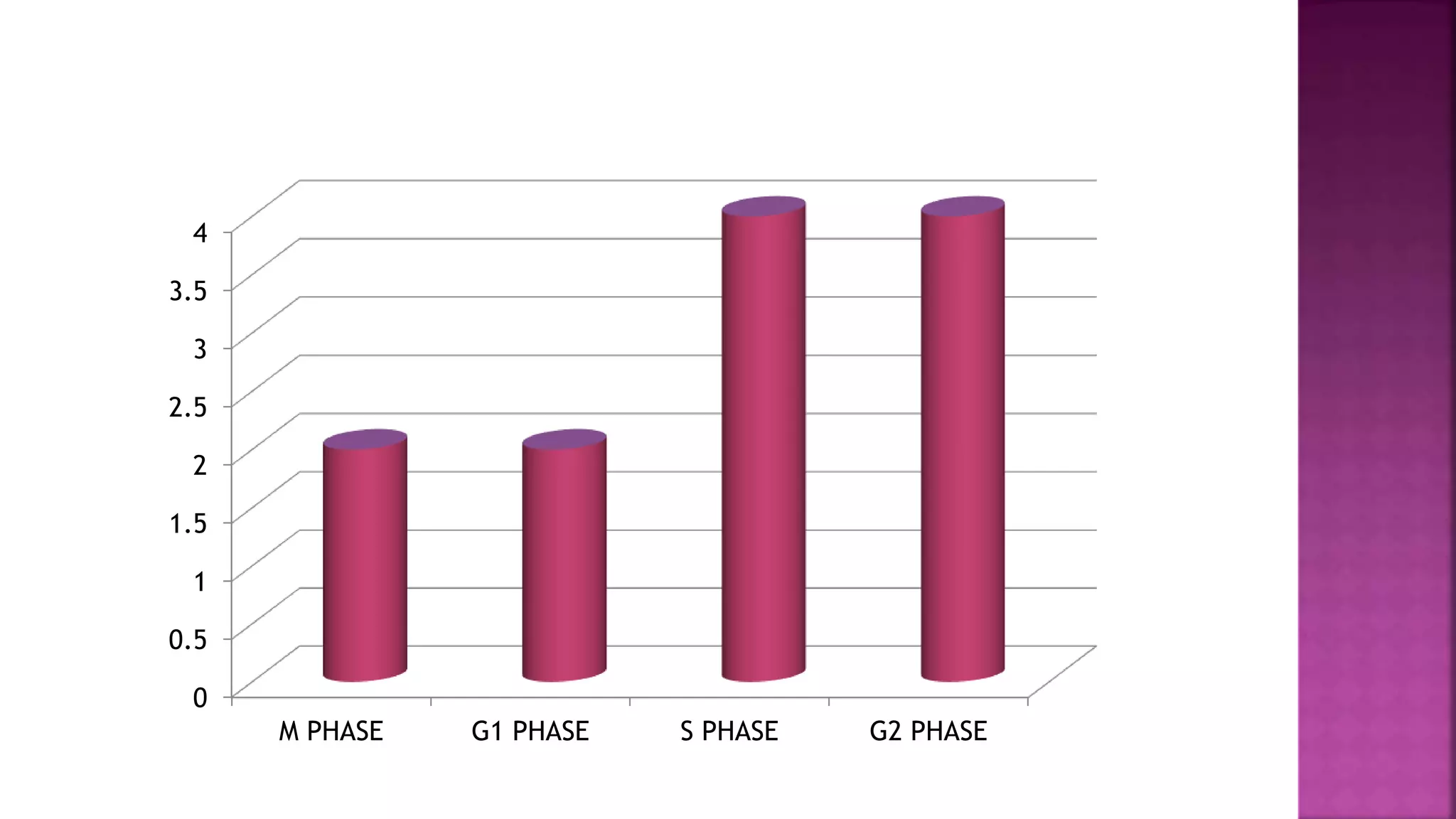
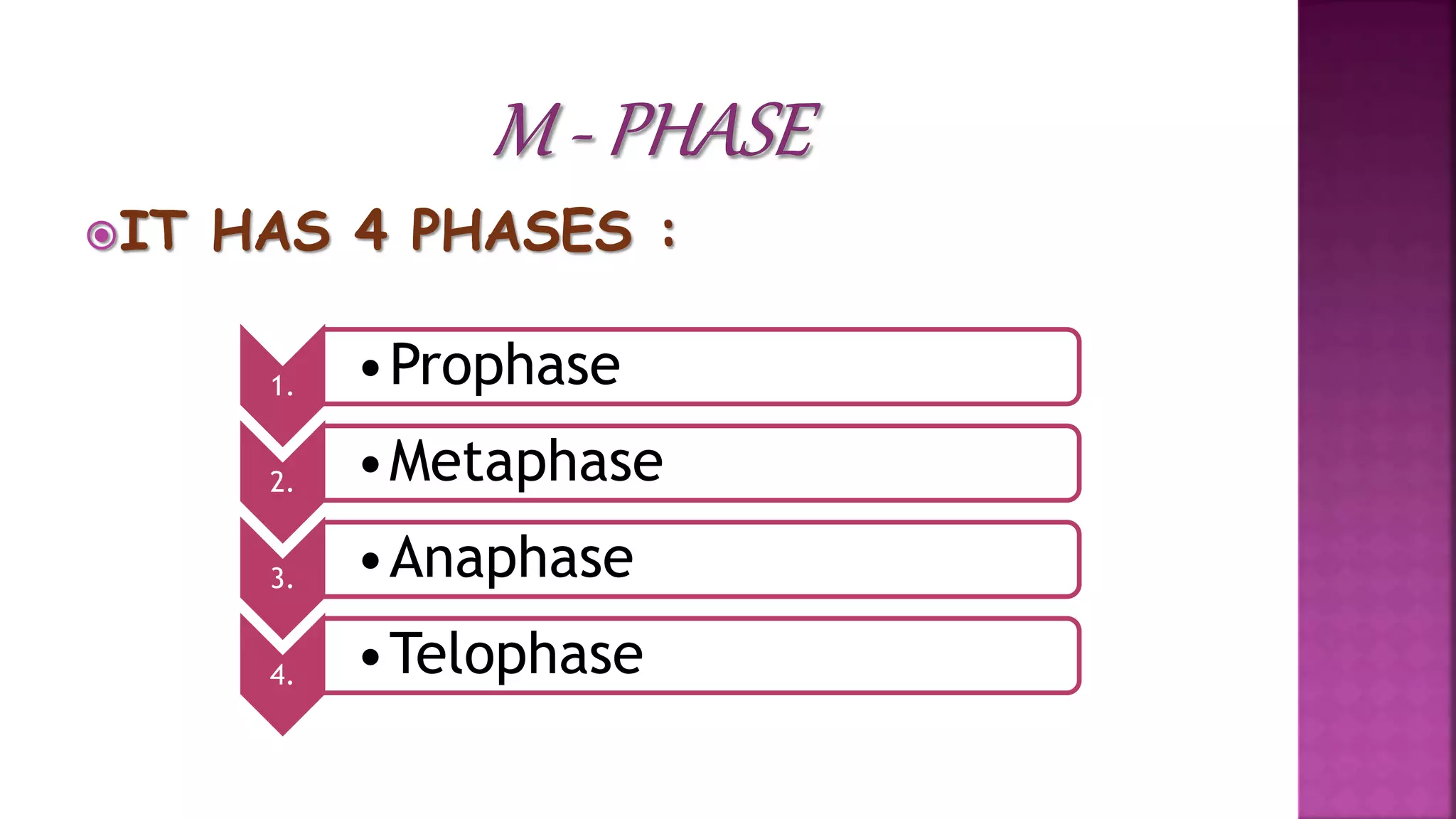
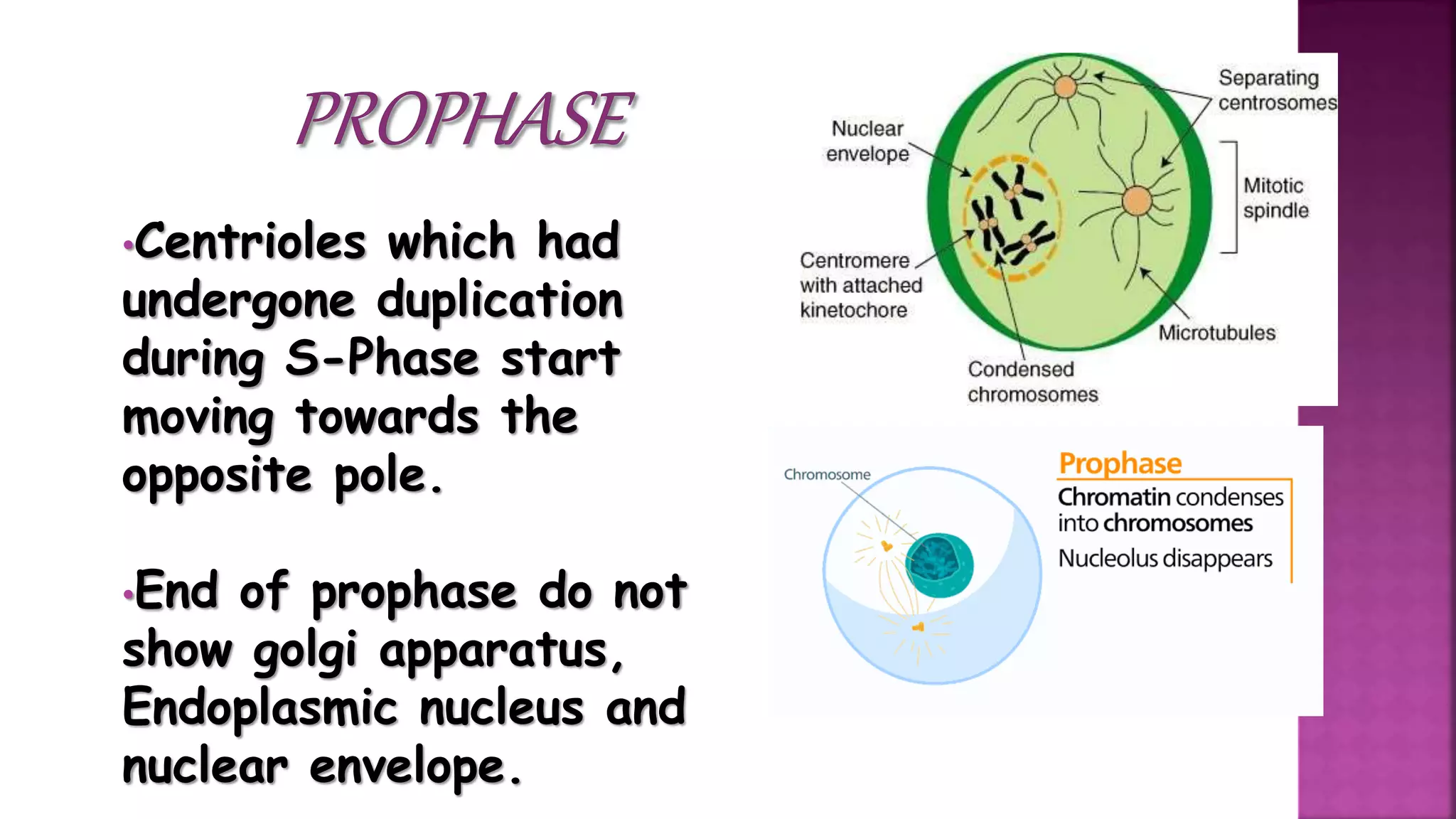
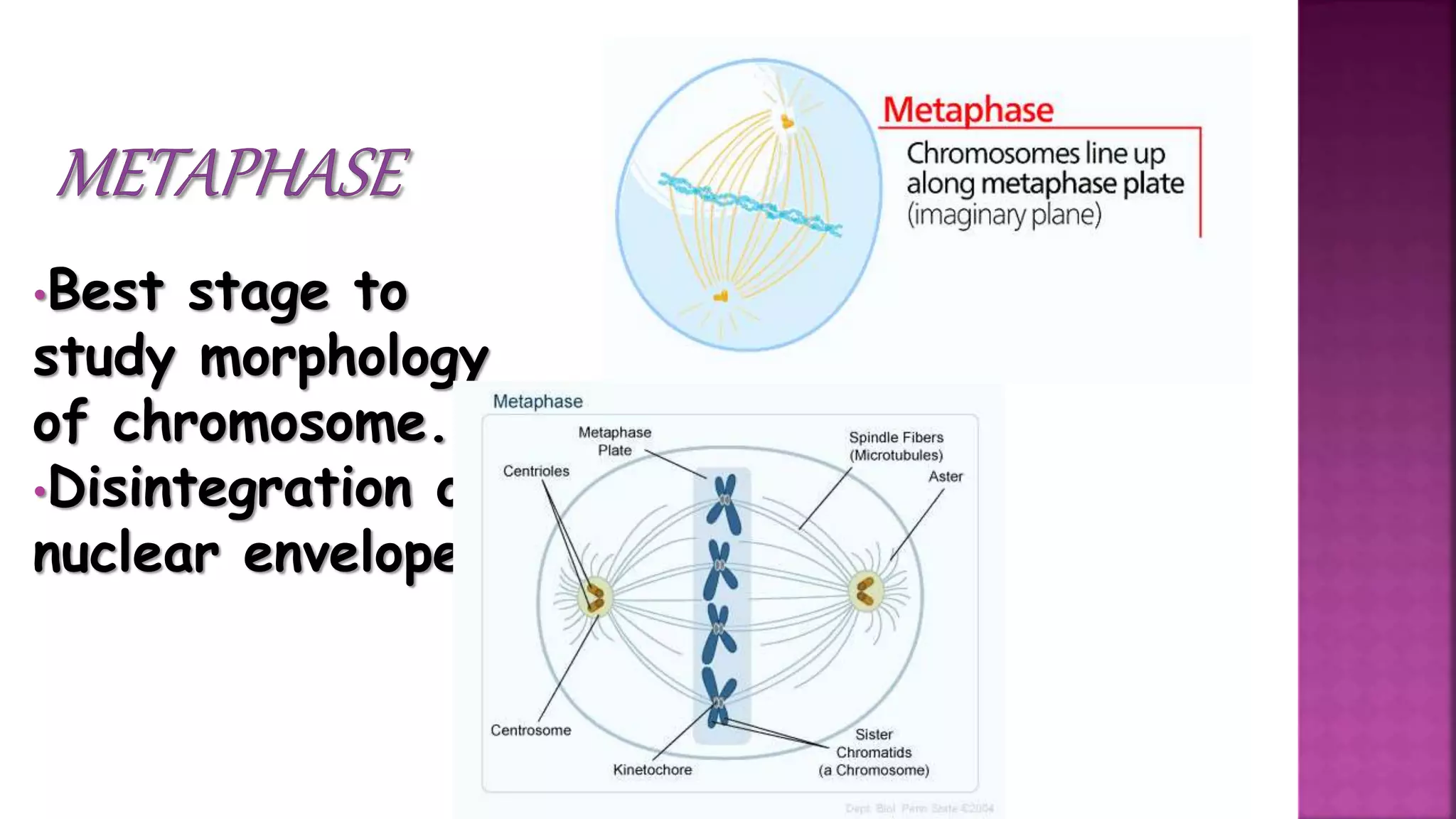
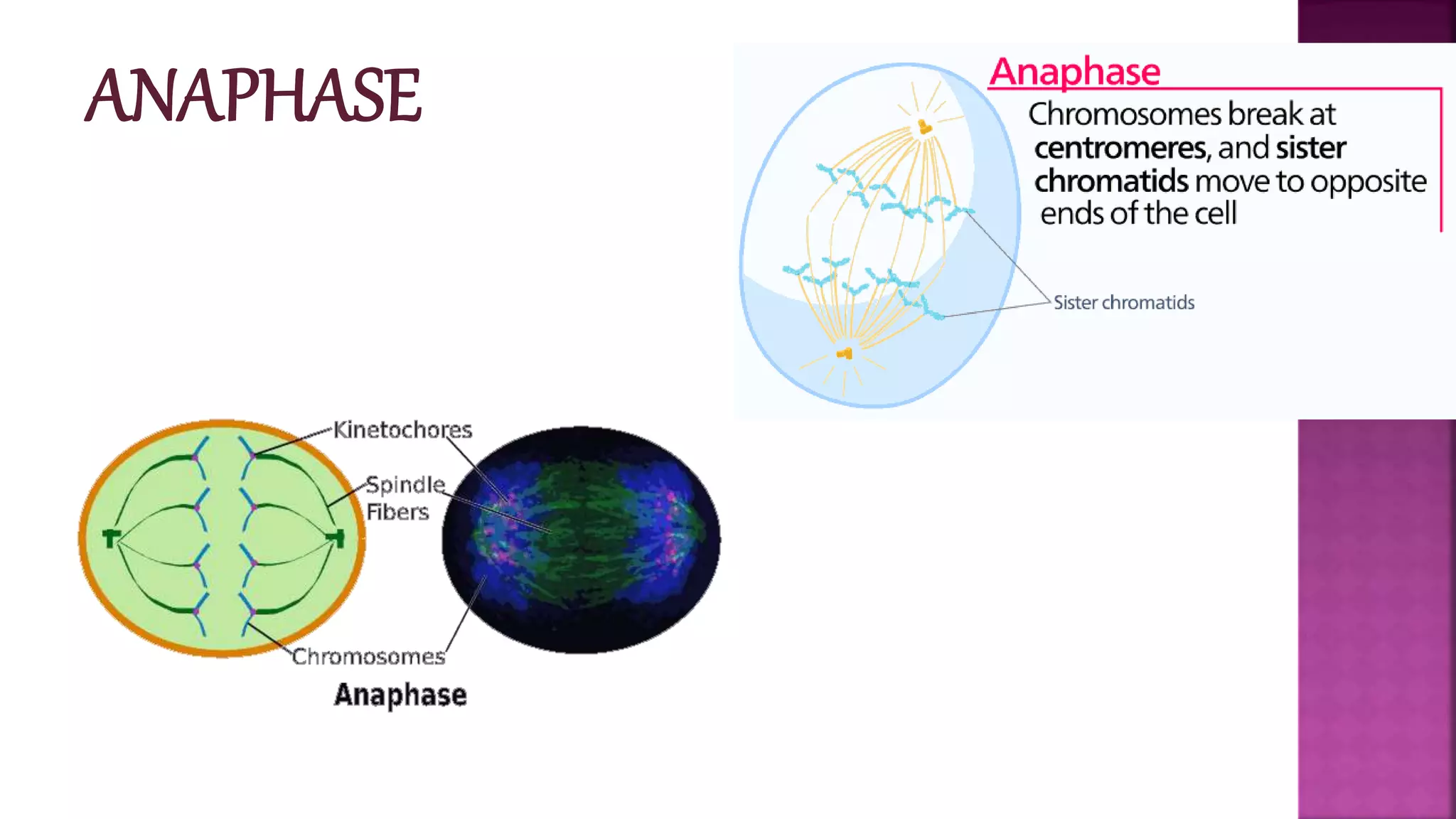
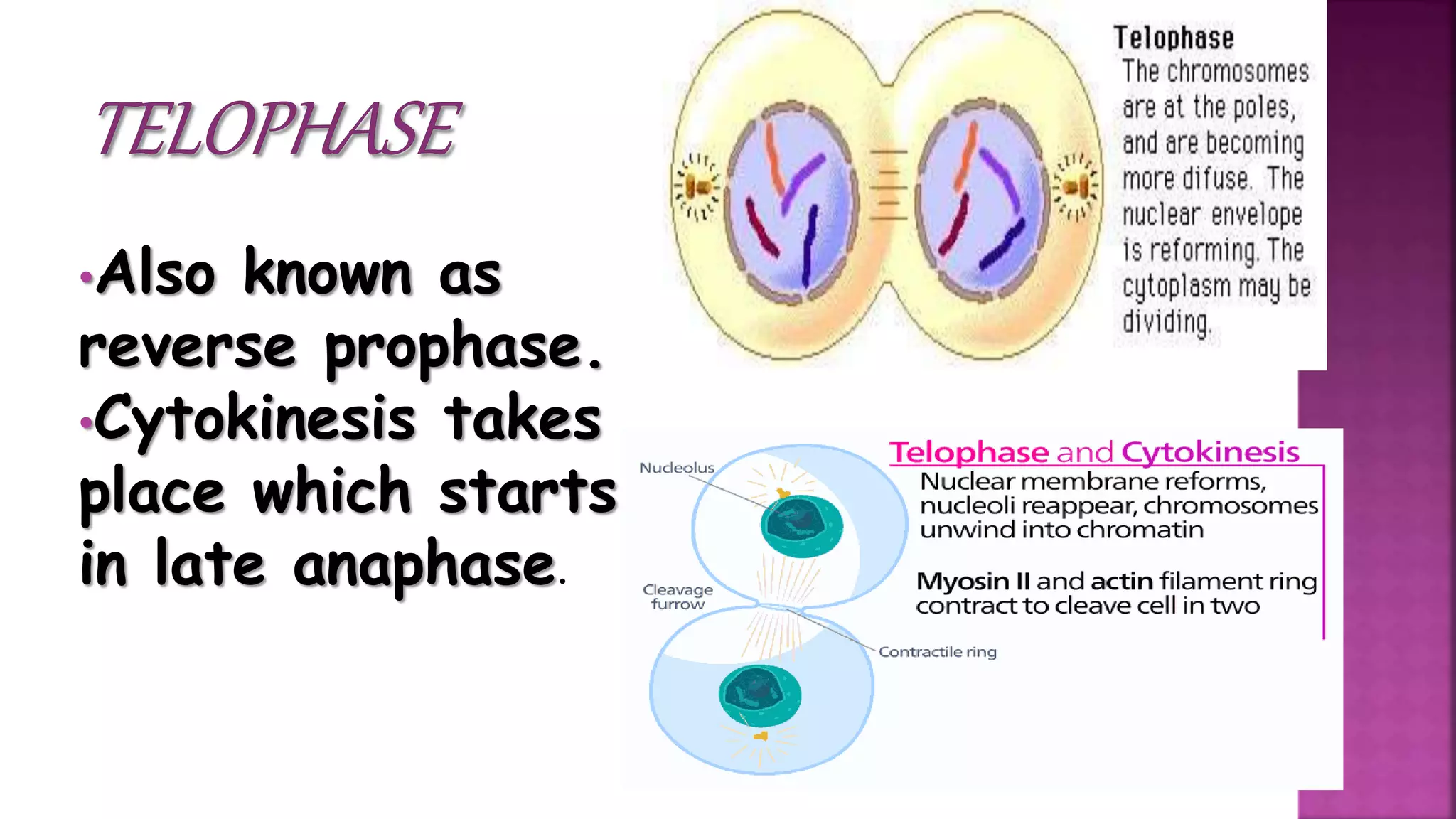
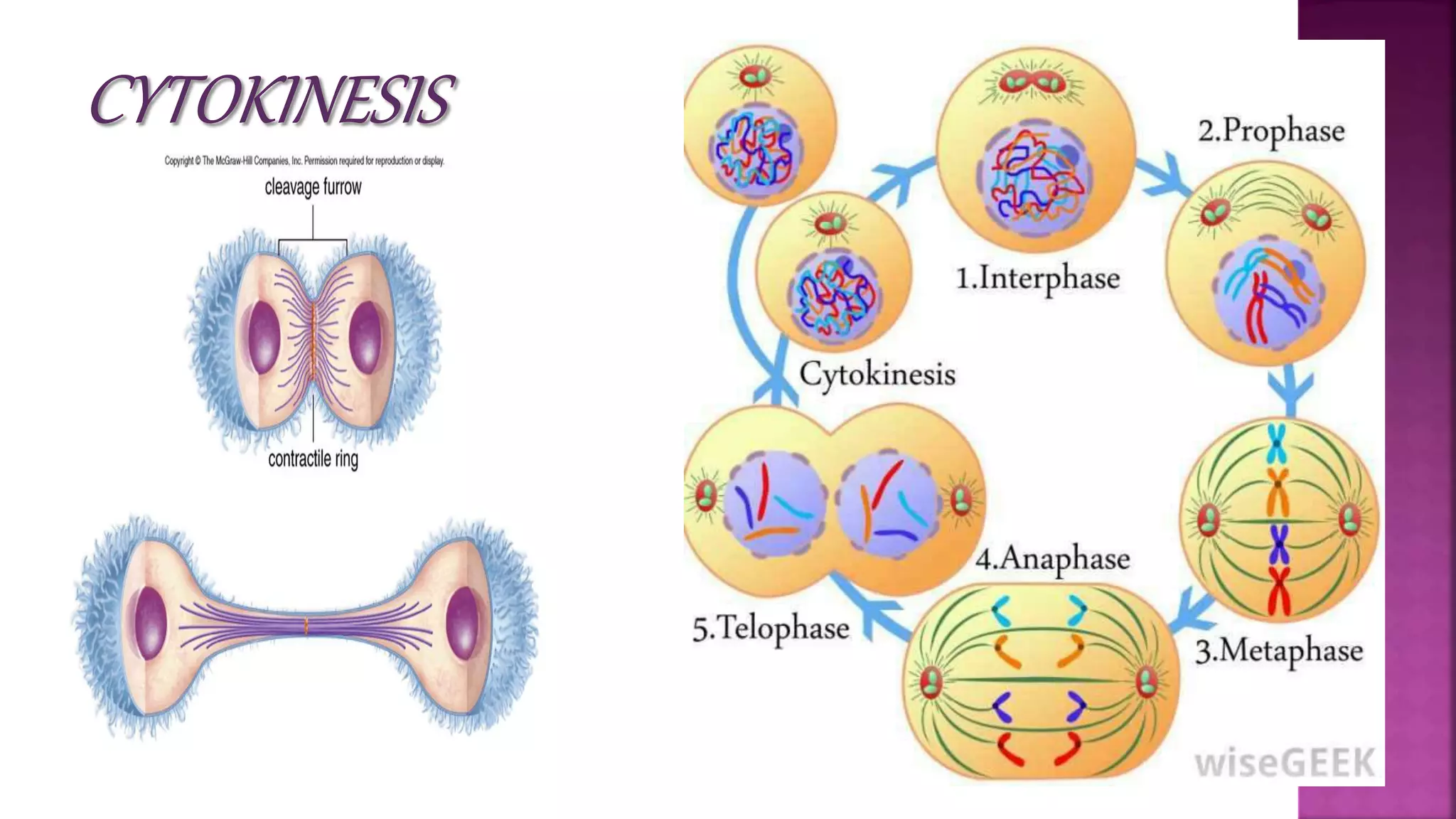
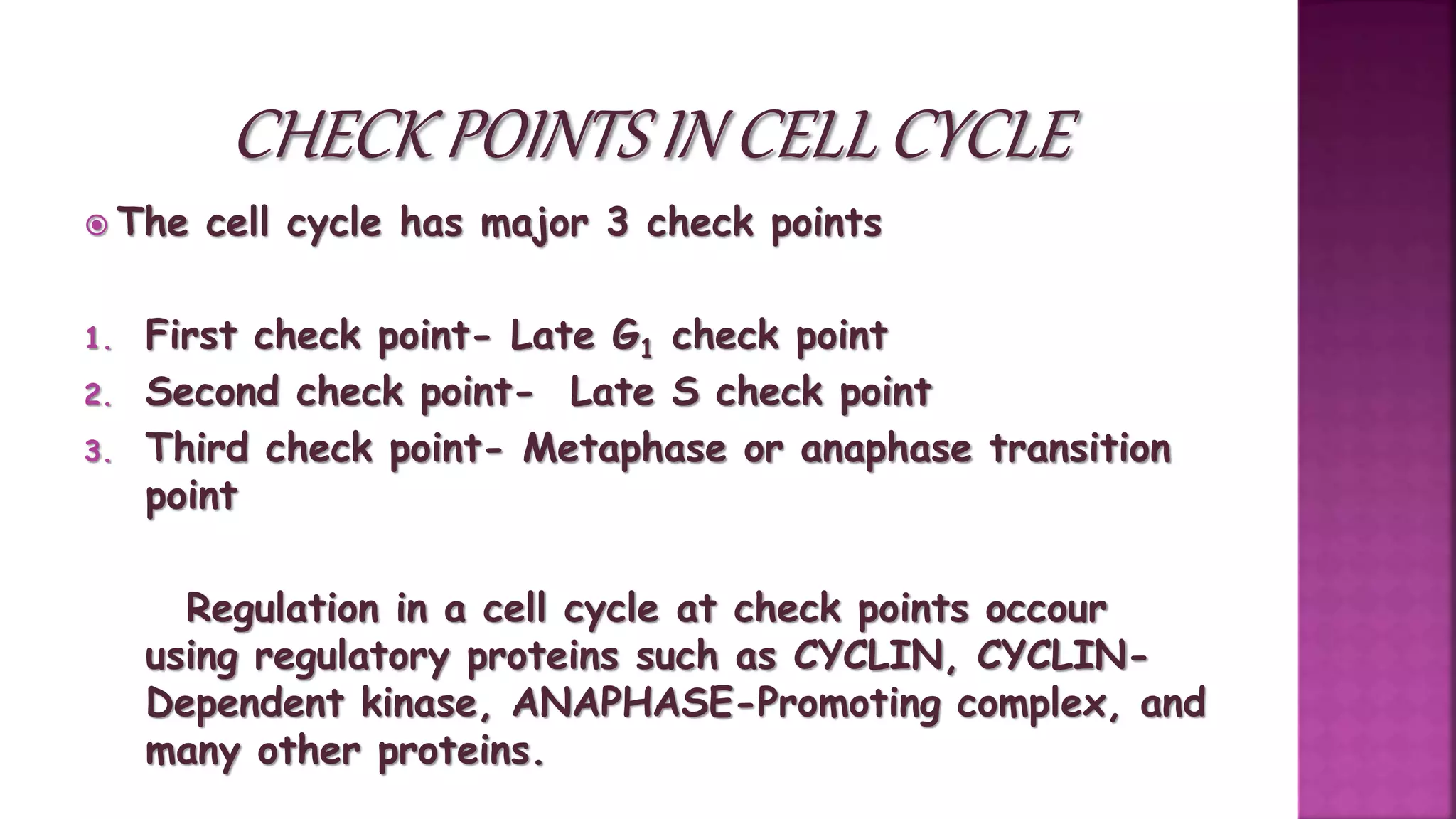
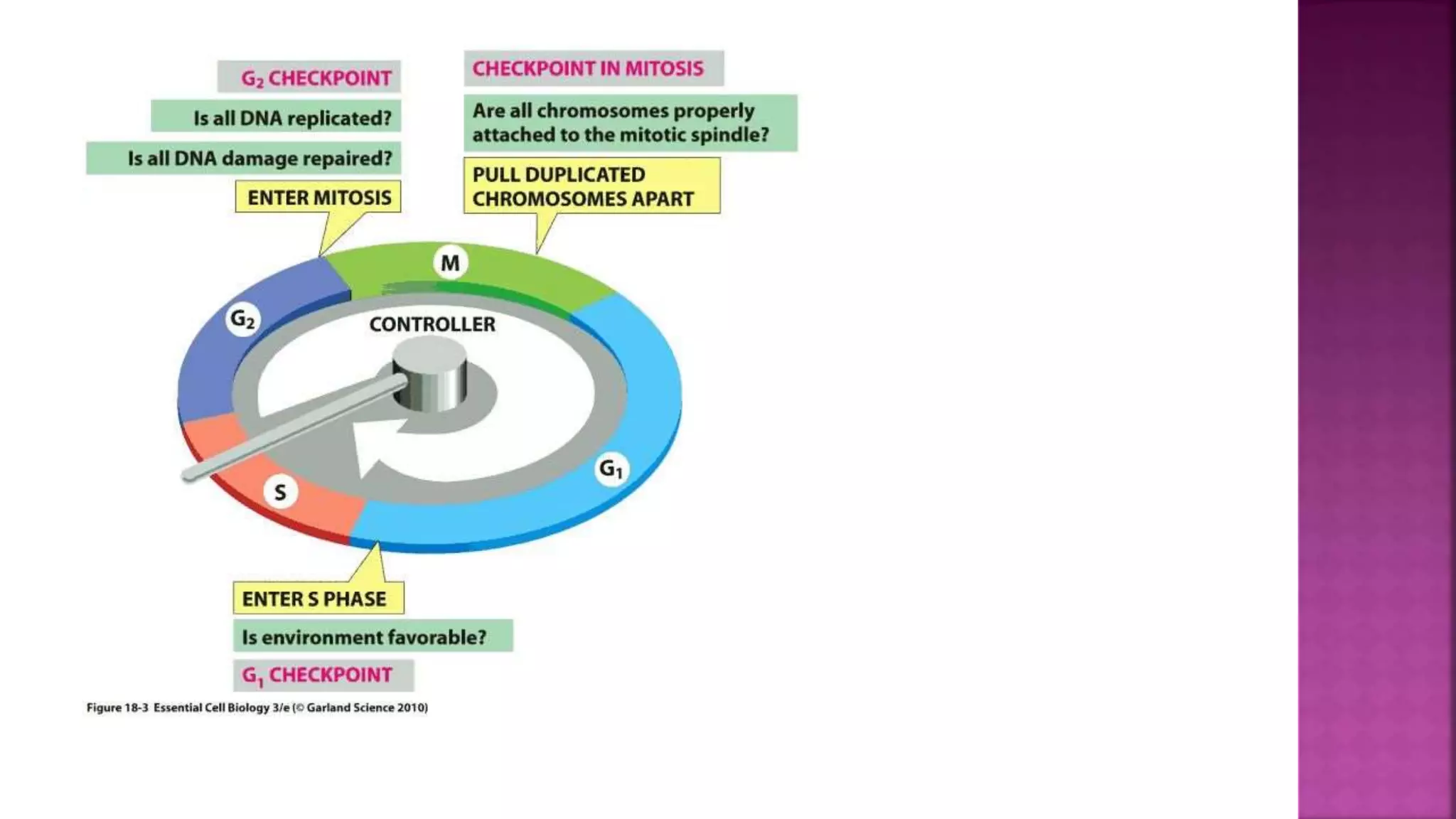
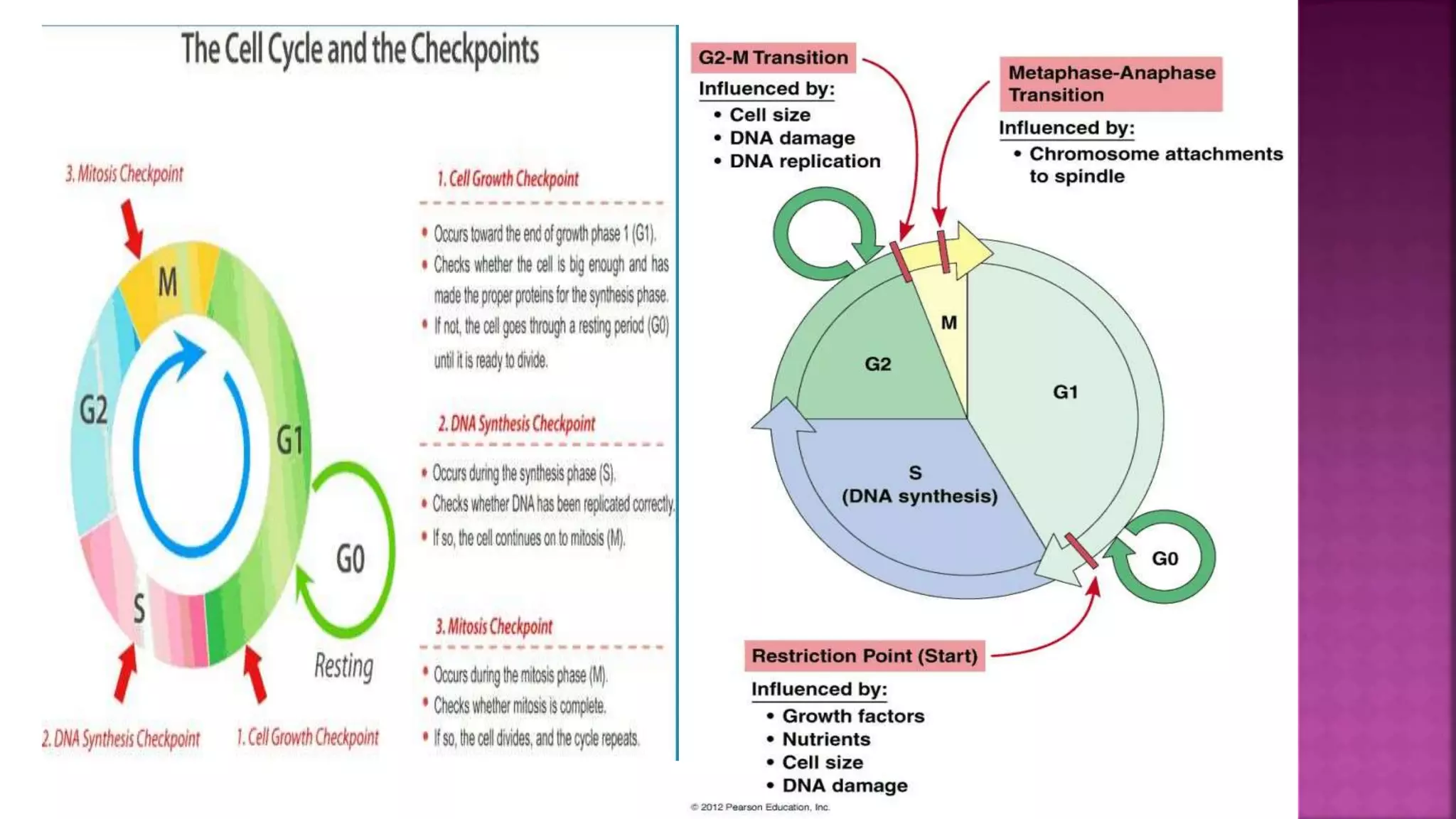
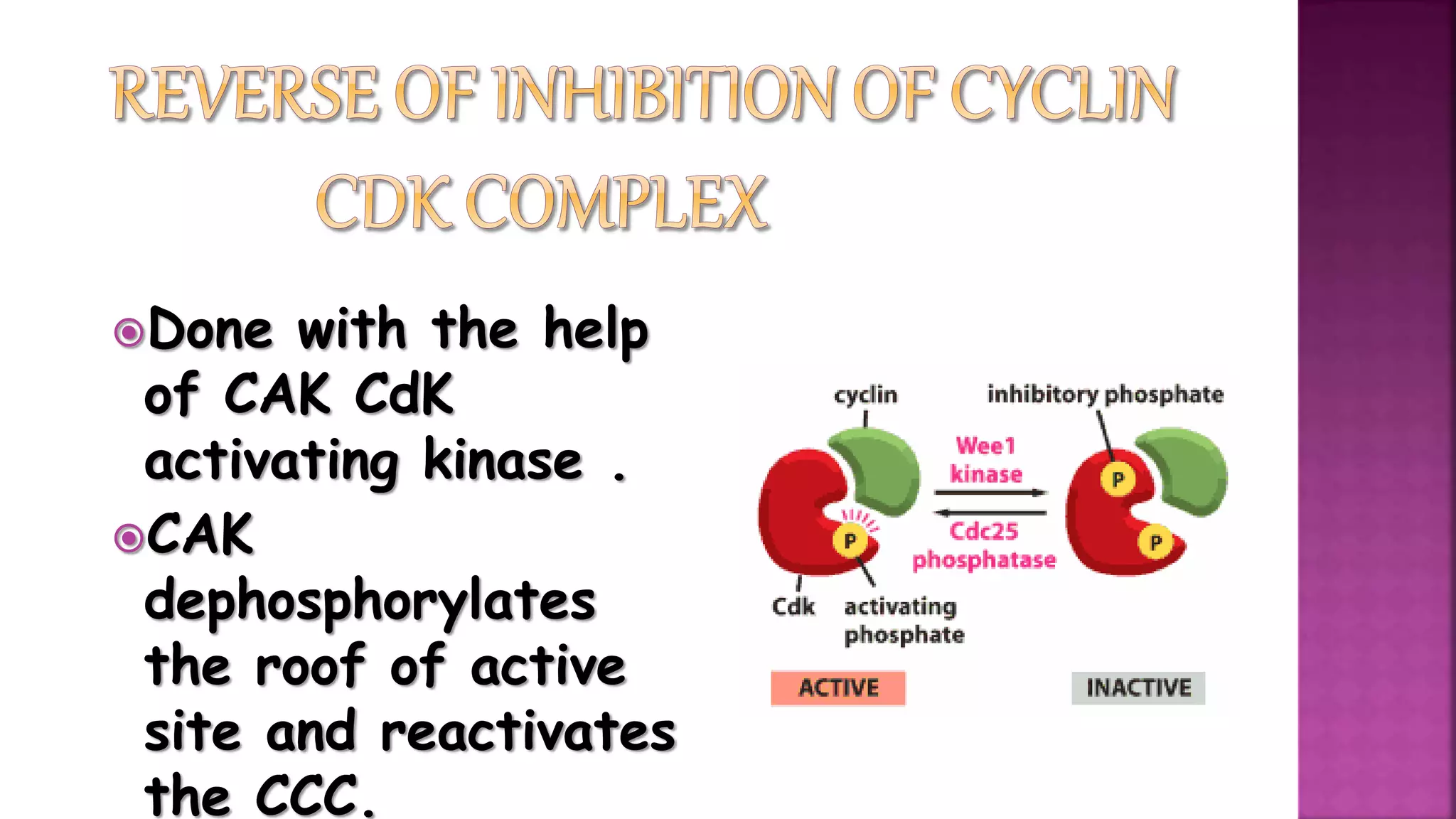
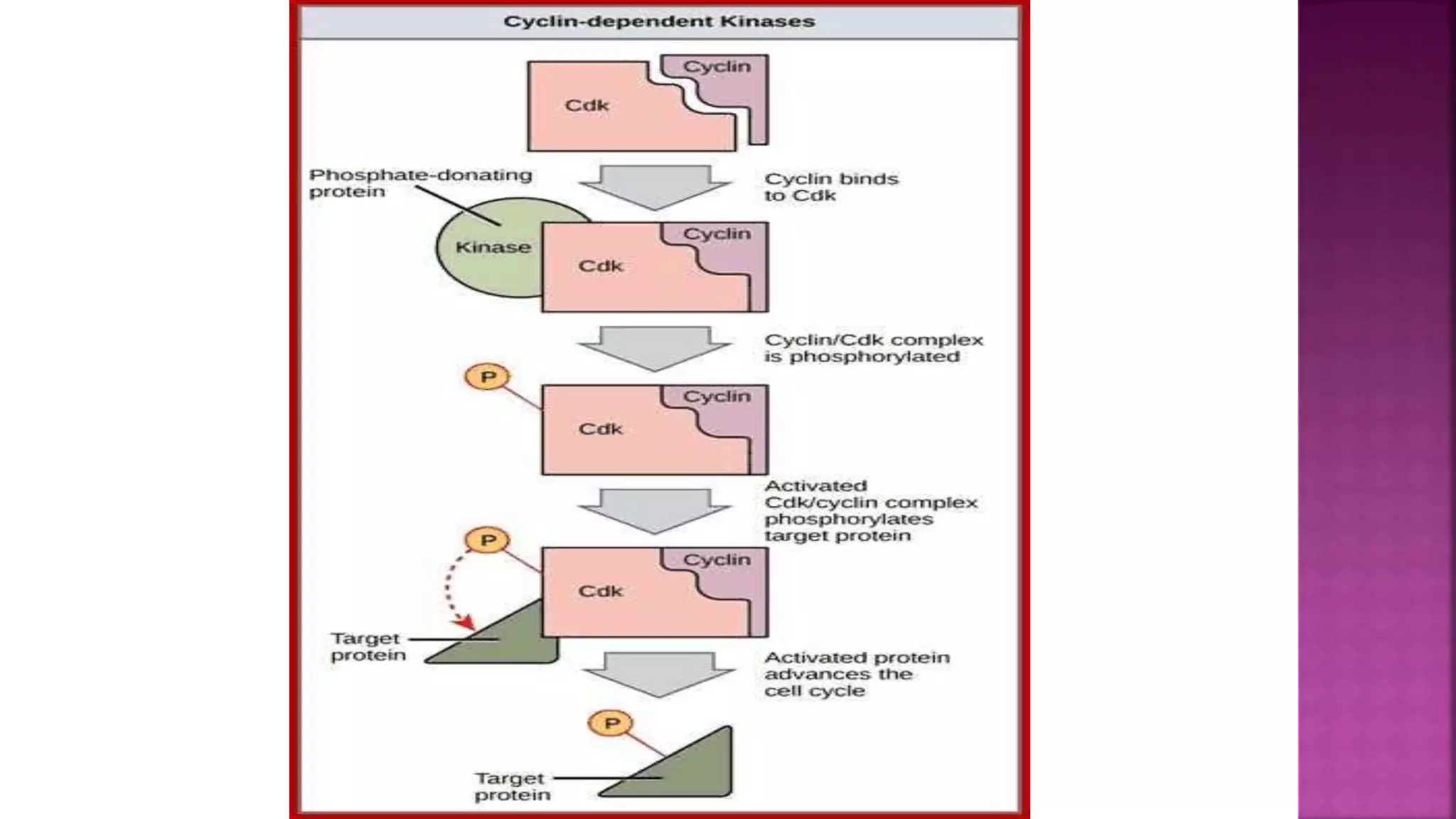
This document summarizes the cell cycle and its regulation. It describes that the cell cycle consists of interphase and M-phase. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. M-phase is where the cell divides. Regulation occurs through cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and checkpoint proteins that control phase transitions. CDK activity is regulated by binding with cyclins to form active complexes, or being inactivated through phosphorylation. Precise coordination of these elements ensures orderly cell division and replication.