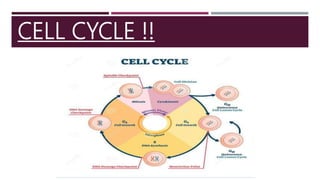
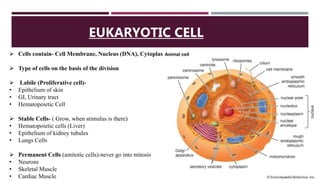
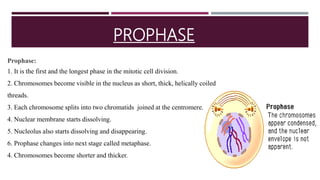
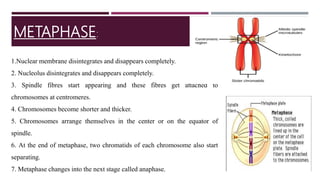
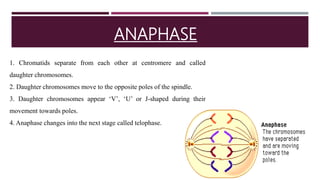
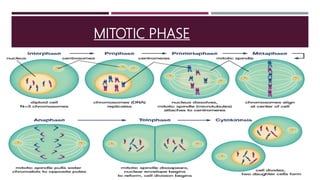
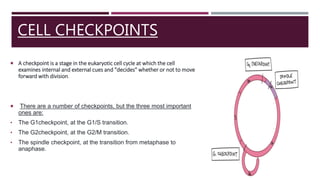
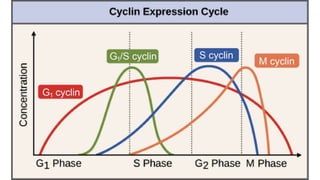
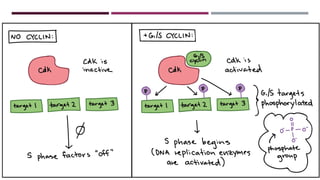
The document discusses the eukaryotic cell cycle, detailing its phases (G1, S, G2, and M) and the types of cells involved (labile, stable, and permanent). It explains the process of mitosis and the stages within it (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase), as well as the significance of cell checkpoints and regulators like cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) in regulating cell division. The overview highlights the importance of these mechanisms for proper cellular function and division.