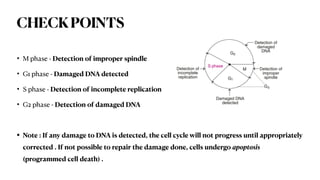
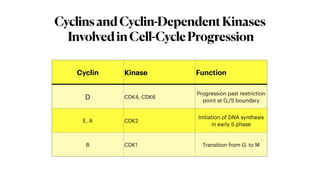
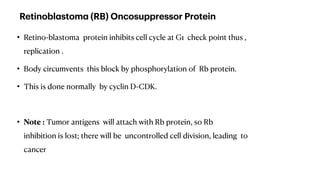
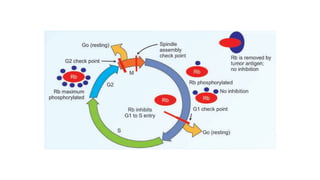
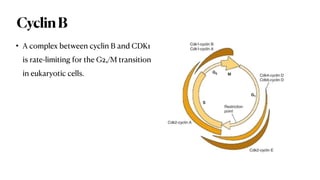
The document summarizes the key phases and checkpoints of the cell cycle, as well as the roles of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) in regulating progression through the cell cycle. It notes that the cell cycle consists of M (mitosis), G1, S (DNA synthesis), and G2 phases, with checkpoints to detect errors and damage. Cyclins activate CDKs to phosphorylate proteins and drive progression, with Cyclin D activating CDK4/6 to promote G1/S transition, Cyclin E and A activating CDK2 to initiate DNA synthesis, and Cyclin B activating CDK1 for G2/M transition. The Rb protein also regulates the G1 checkpoint