This document provides an overview of computer networking concepts including:
1) It defines what a network is and describes the basic components of a network like cables, devices, and operating systems.
2) It discusses different types of networks including LANs, WANs, and examples of networking technologies and topologies used.
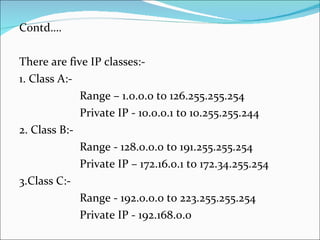
3) It covers IP addressing fundamentals like IP classes and private IP ranges.
4) It describes common networking devices like switches, routers, and their functions.
5) It provides steps for basic router configuration and setting up RIP routing protocol.