This document provides an overview of various networking concepts including:
- Types of networks like LAN, MAN, and WAN
- Networking devices like hubs, switches, routers, and their functions
- Network addressing concepts like subnetting, supernetting, and CIDR
- Dynamic routing protocols like RIP and EIGRP
- Router configuration including accessing modes and deleting configurations
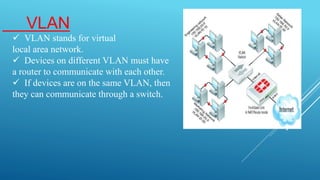
- VLAN concepts and how devices on different VLANs require a router to communicate














![DYNAMIC ROUTING
A routing protocol is the communication used between
routers.
A routing protocol allows one router to share information
with other routers.
The information a router gets from another router, using a
routing protocol, is used to build & maintain a routing
table.
Examples of routing protocols:
1). RIP [ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL]
2.) EIGRP[ENHANCED INTERIOR GATEWAY
ROUTING PROTOCOL]
3. OSPF[OPEN SHORTEST PATH FIRST]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/banknetworkdesign-230108084407-c2bb4406/85/bank-network-design-pptx-15-320.jpg)