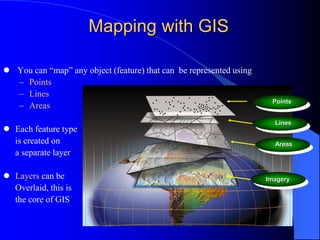
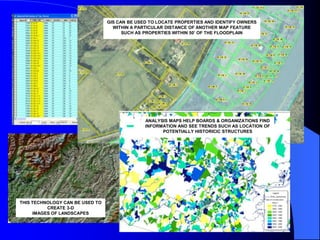
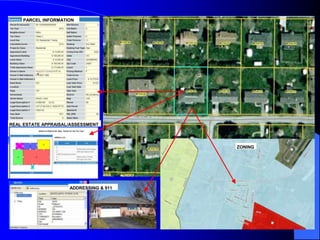
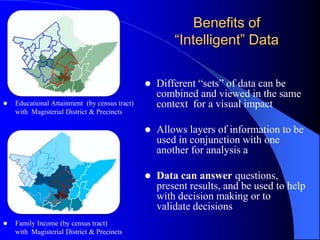
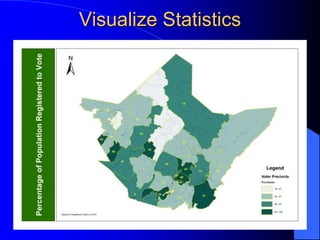
The document discusses the critical role of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in government, highlighting its history, current applications, and future possibilities. GIS enables the mapping of various features and the integration of intelligent data to aid in decision-making for local governments, with the emphasis on local accuracy and relevance. It also explores the organizational and funding strategies necessary for successful GIS implementation and management within county departments.