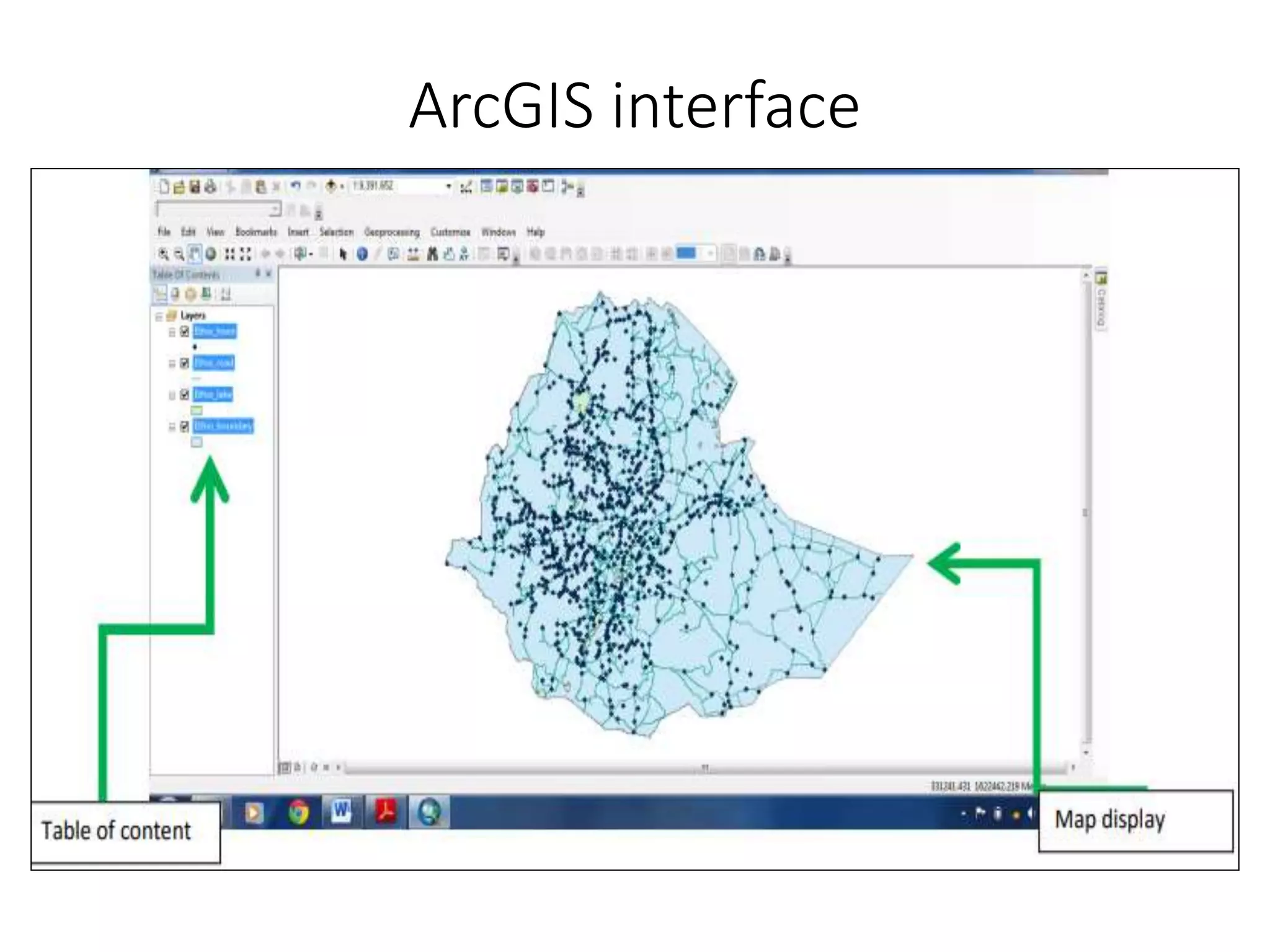
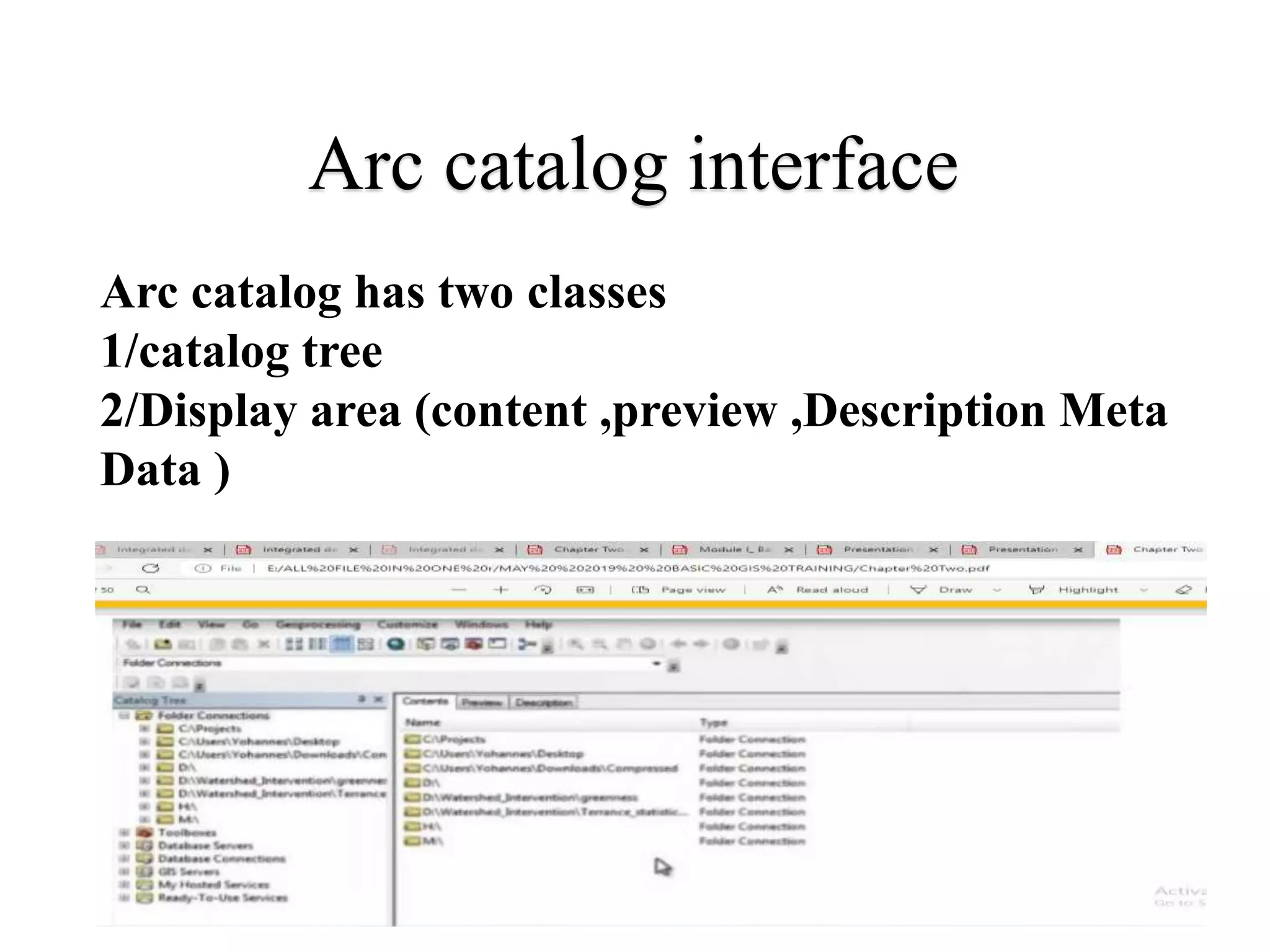
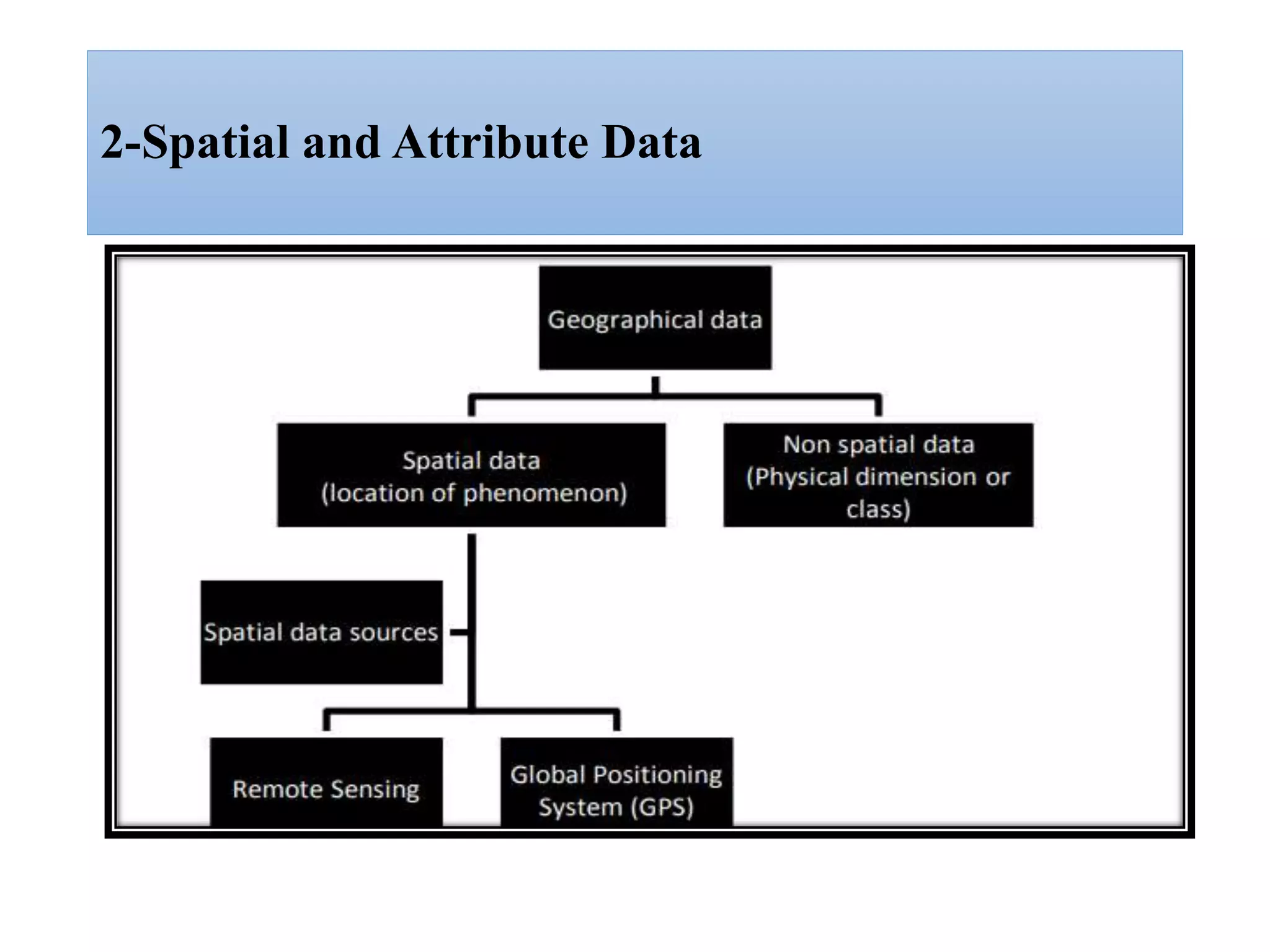
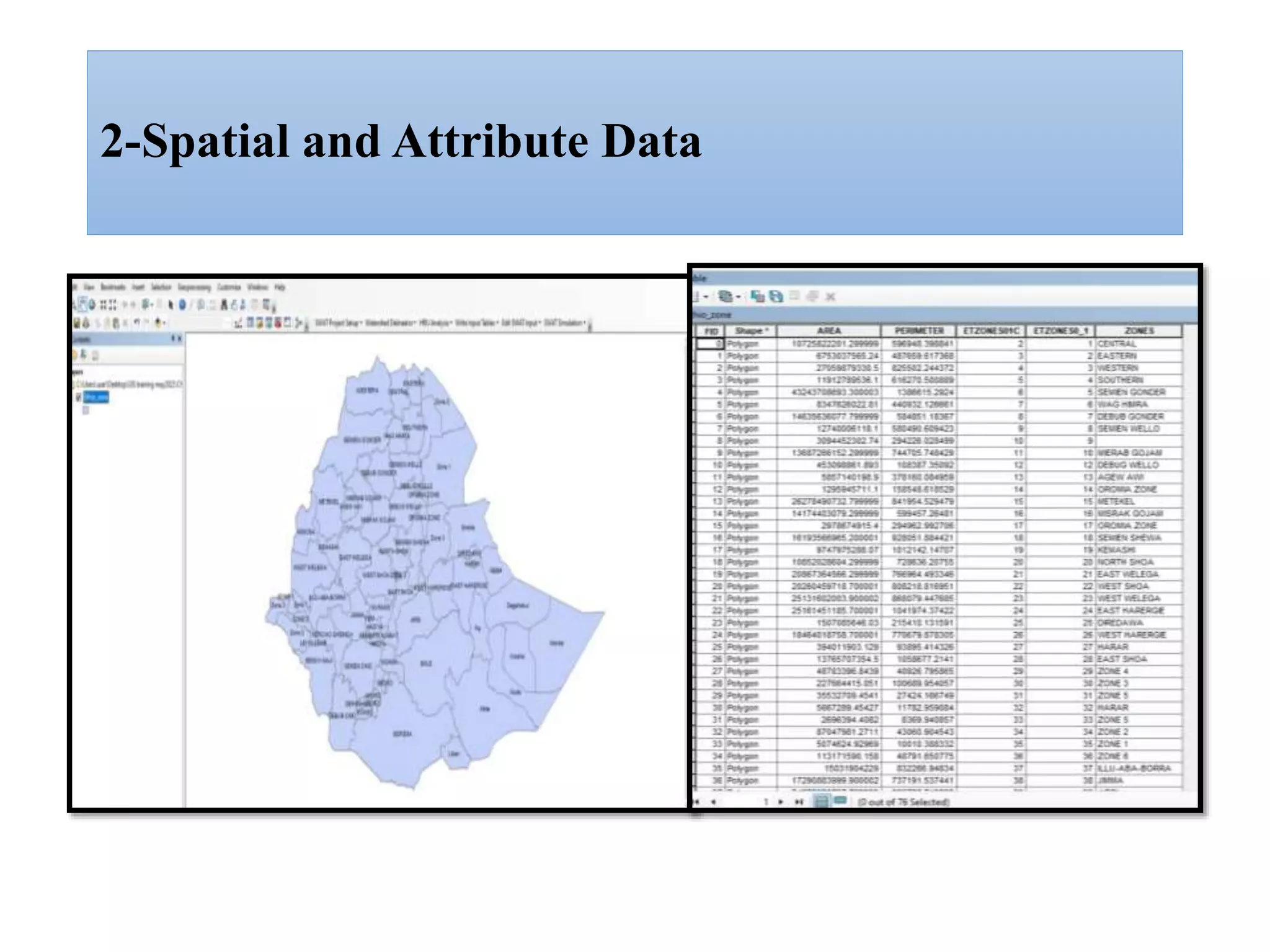
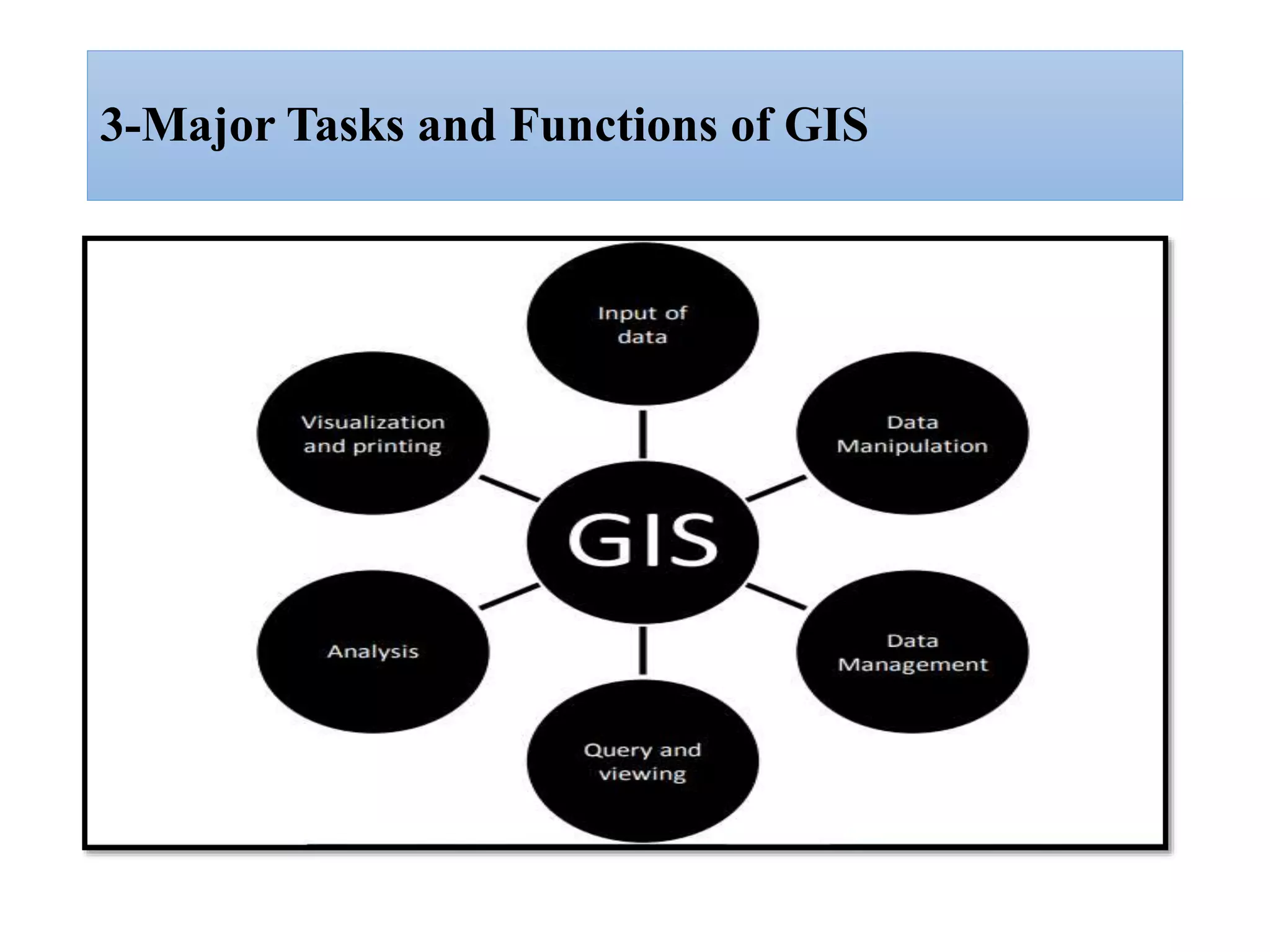
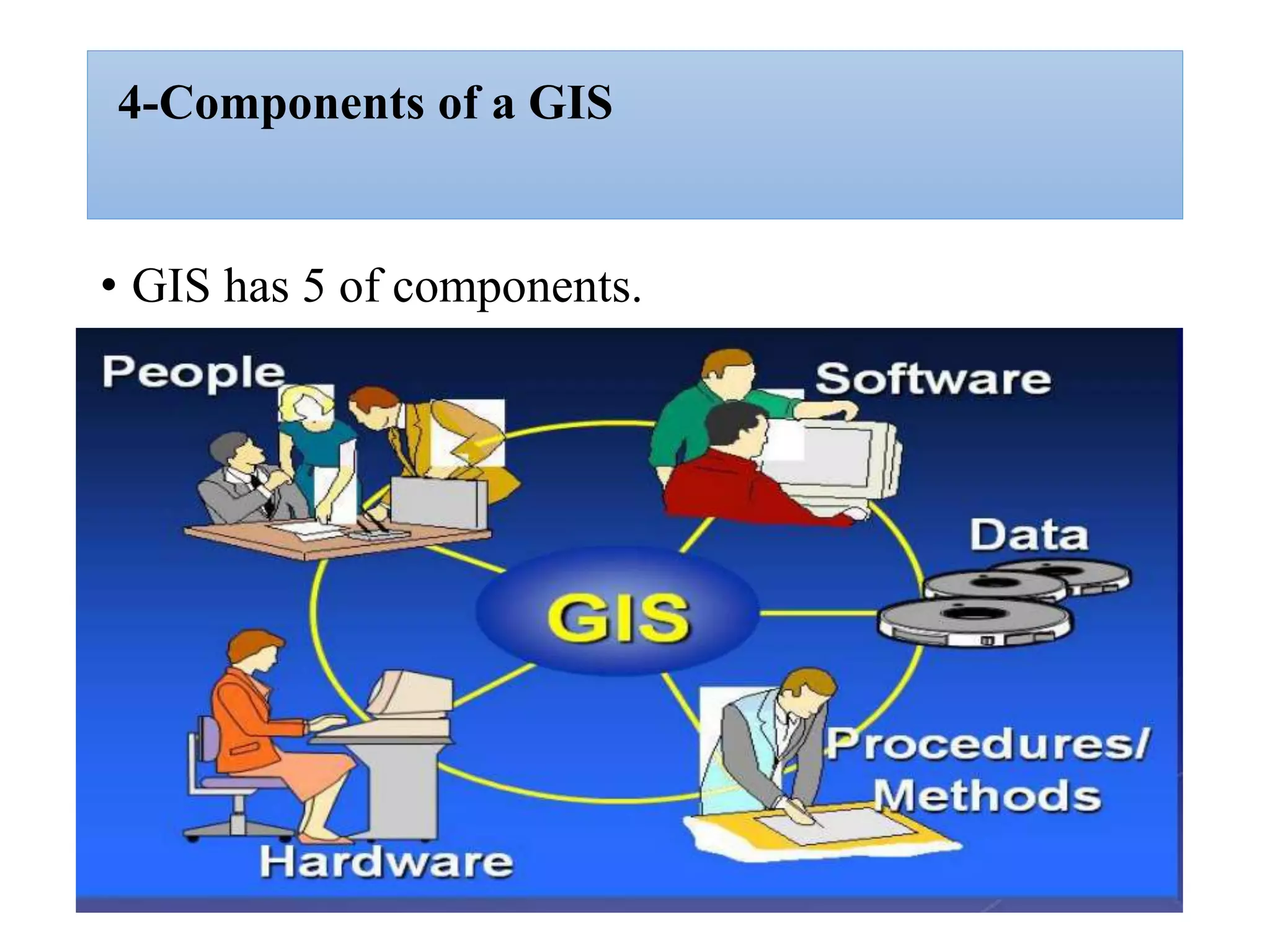
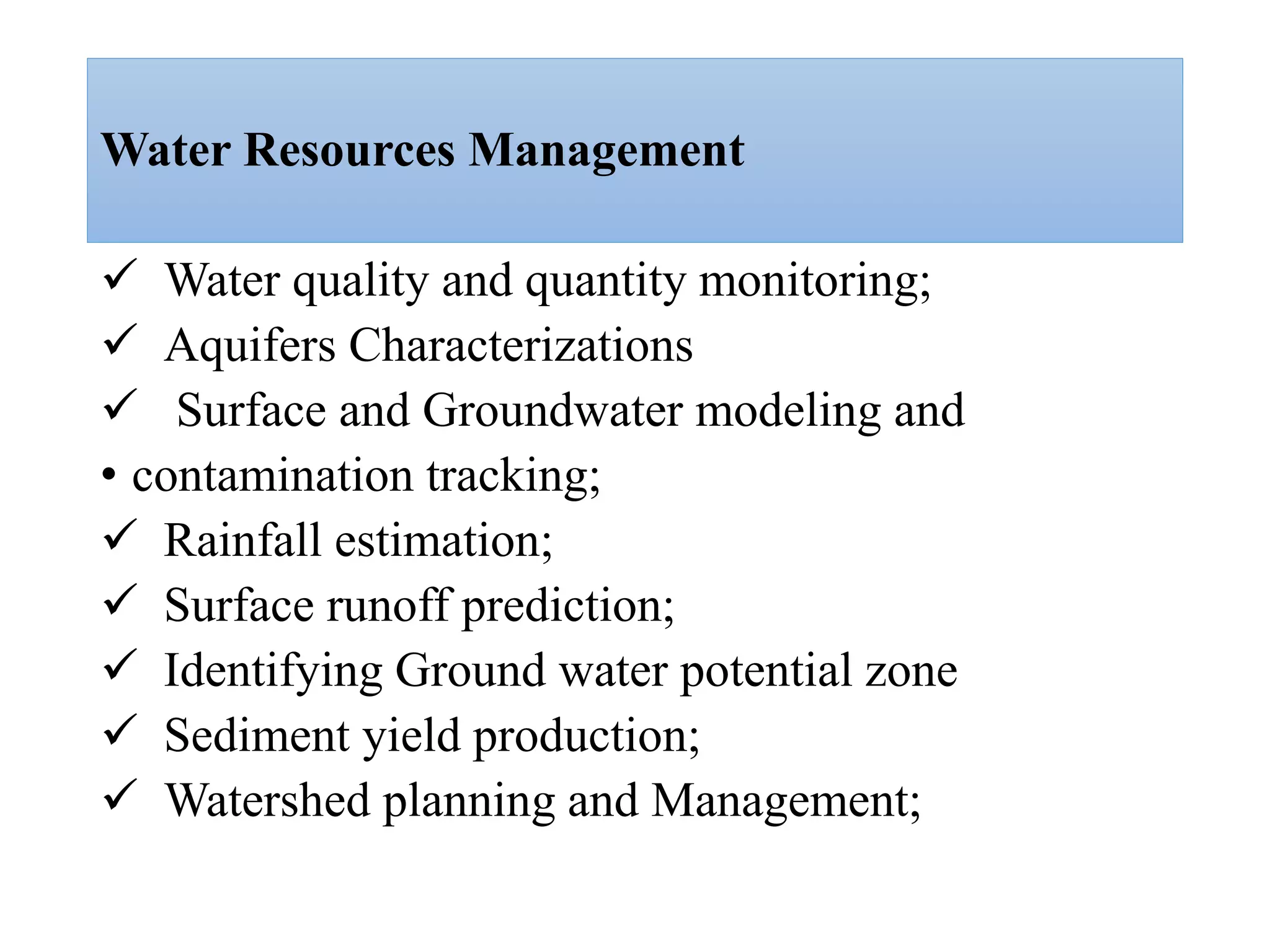
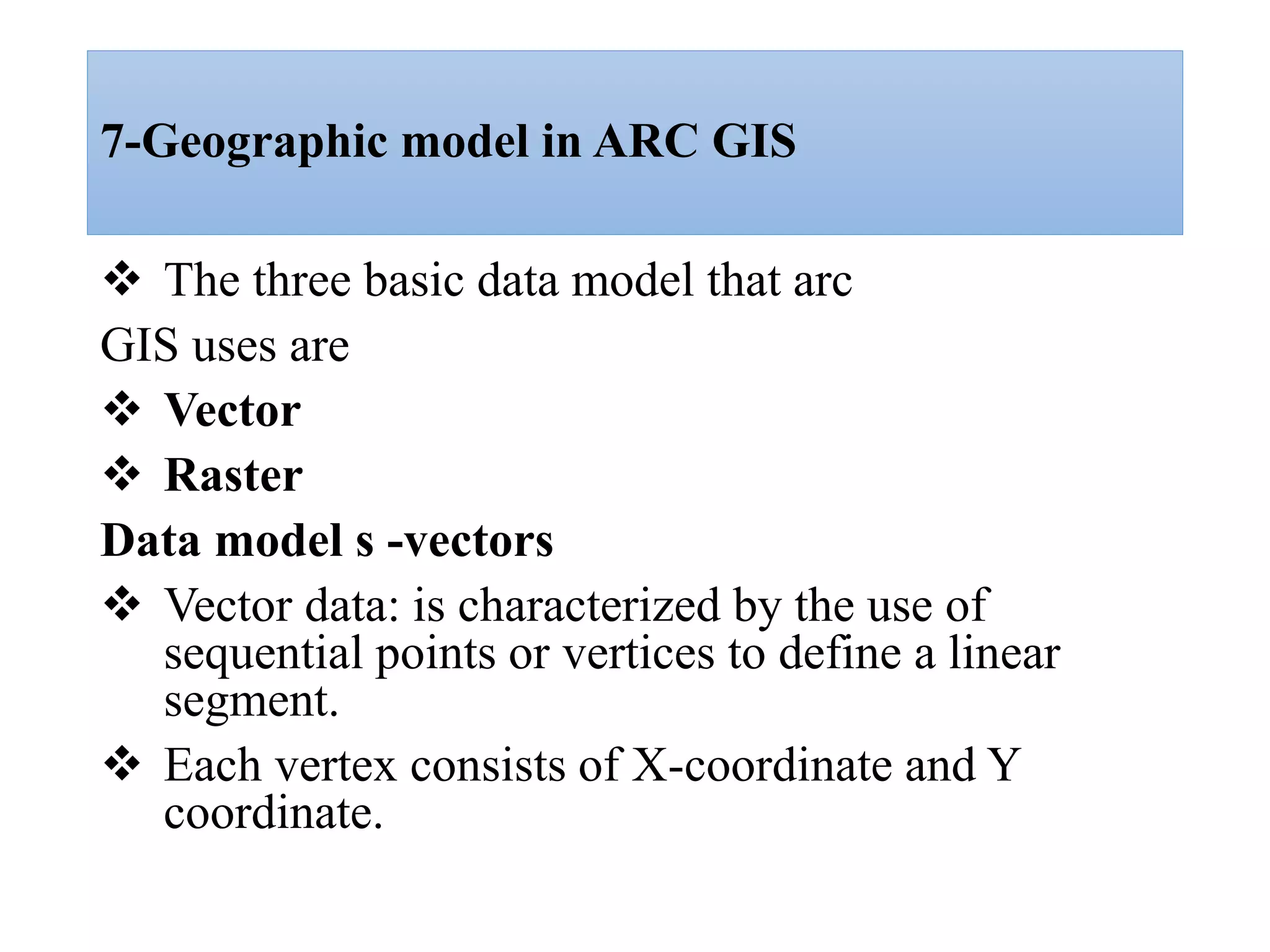
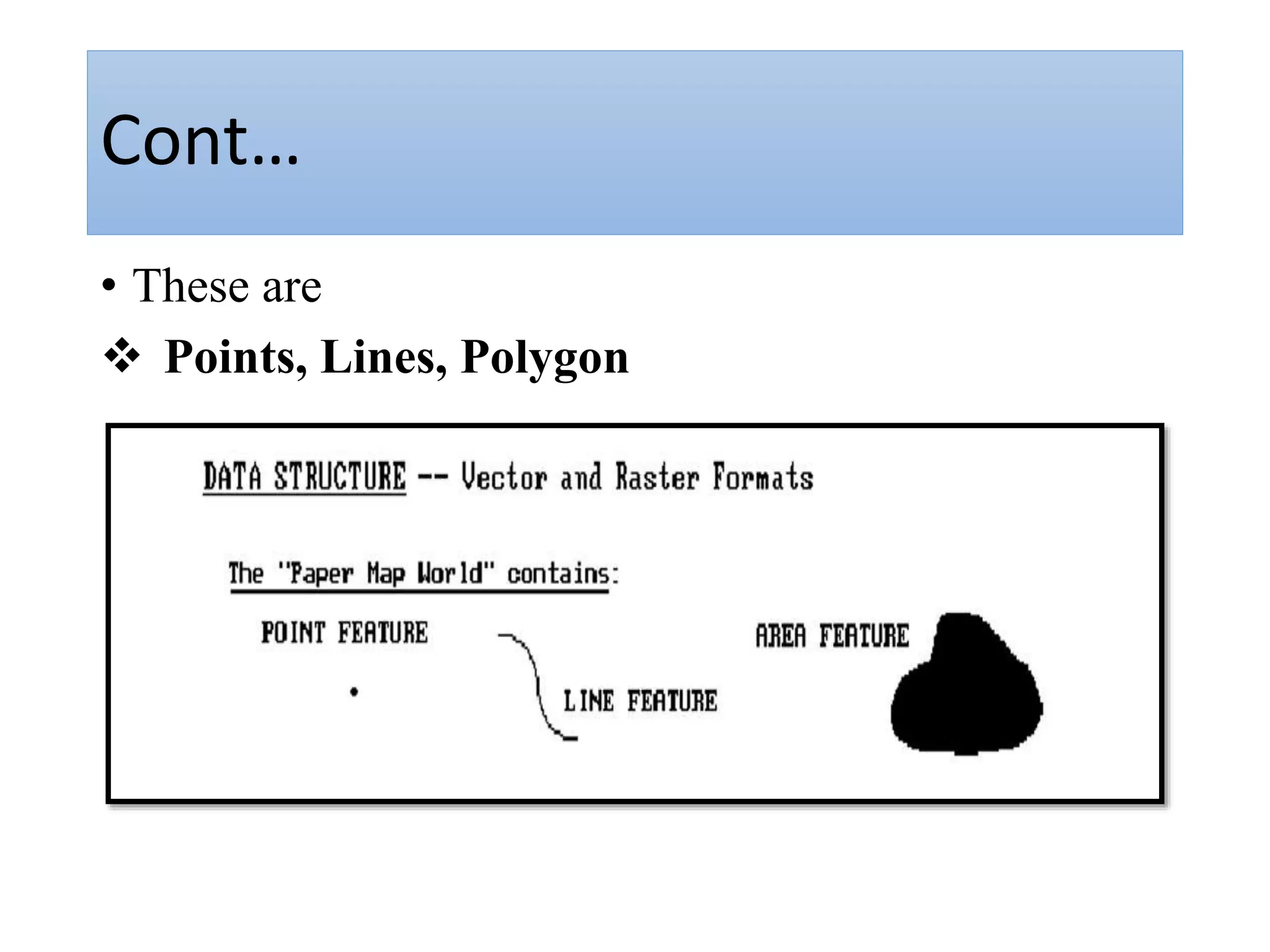
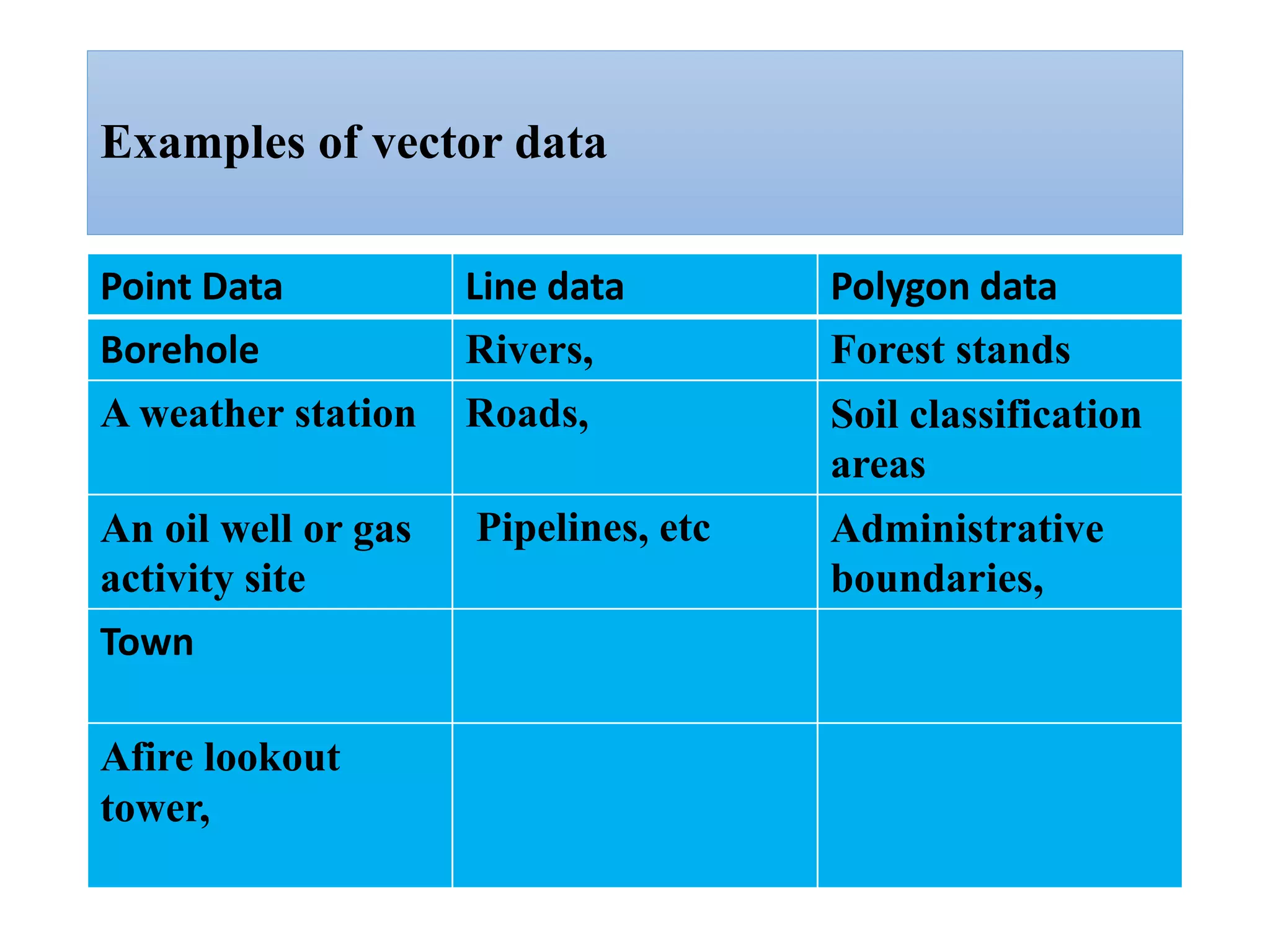
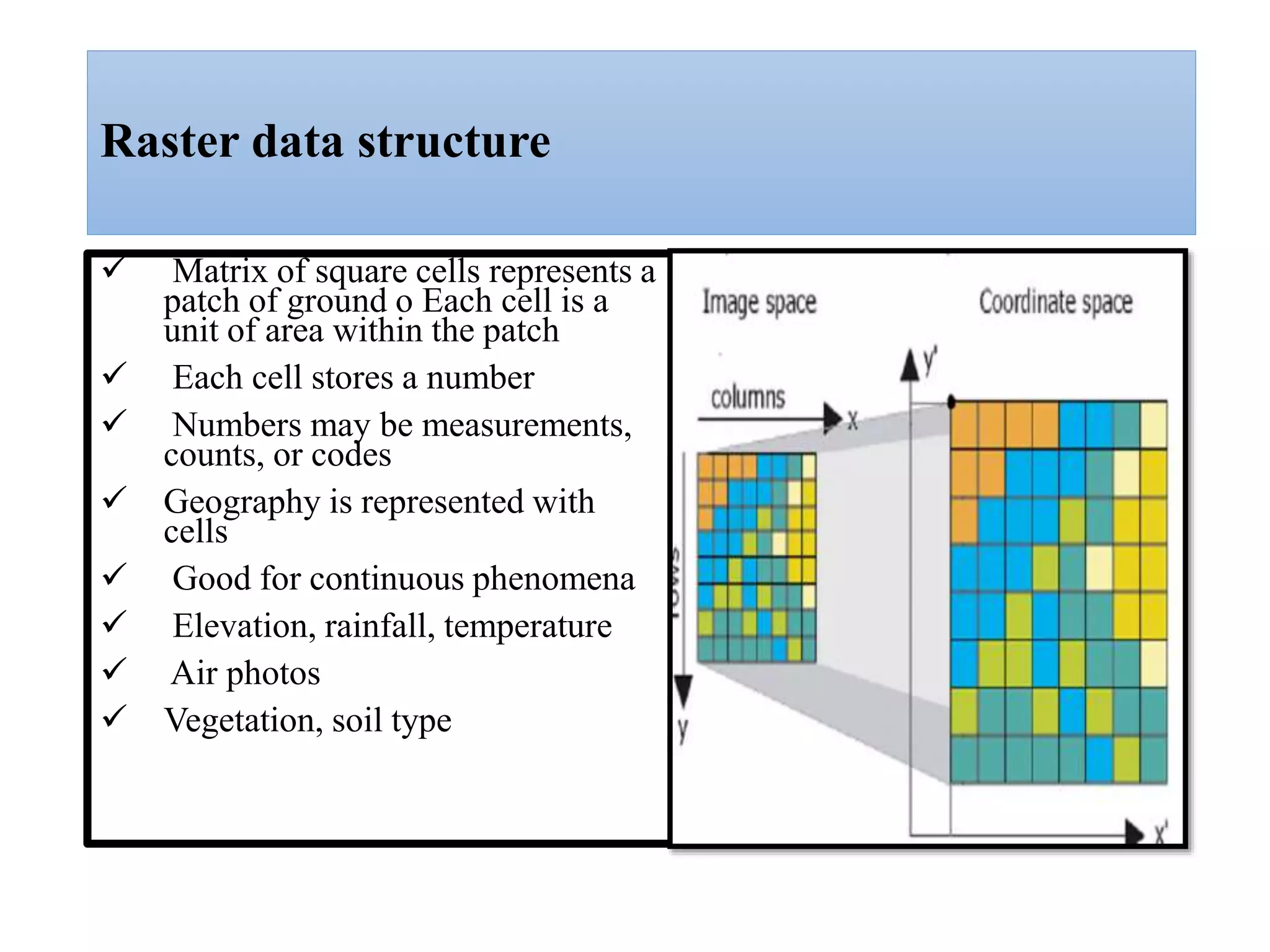
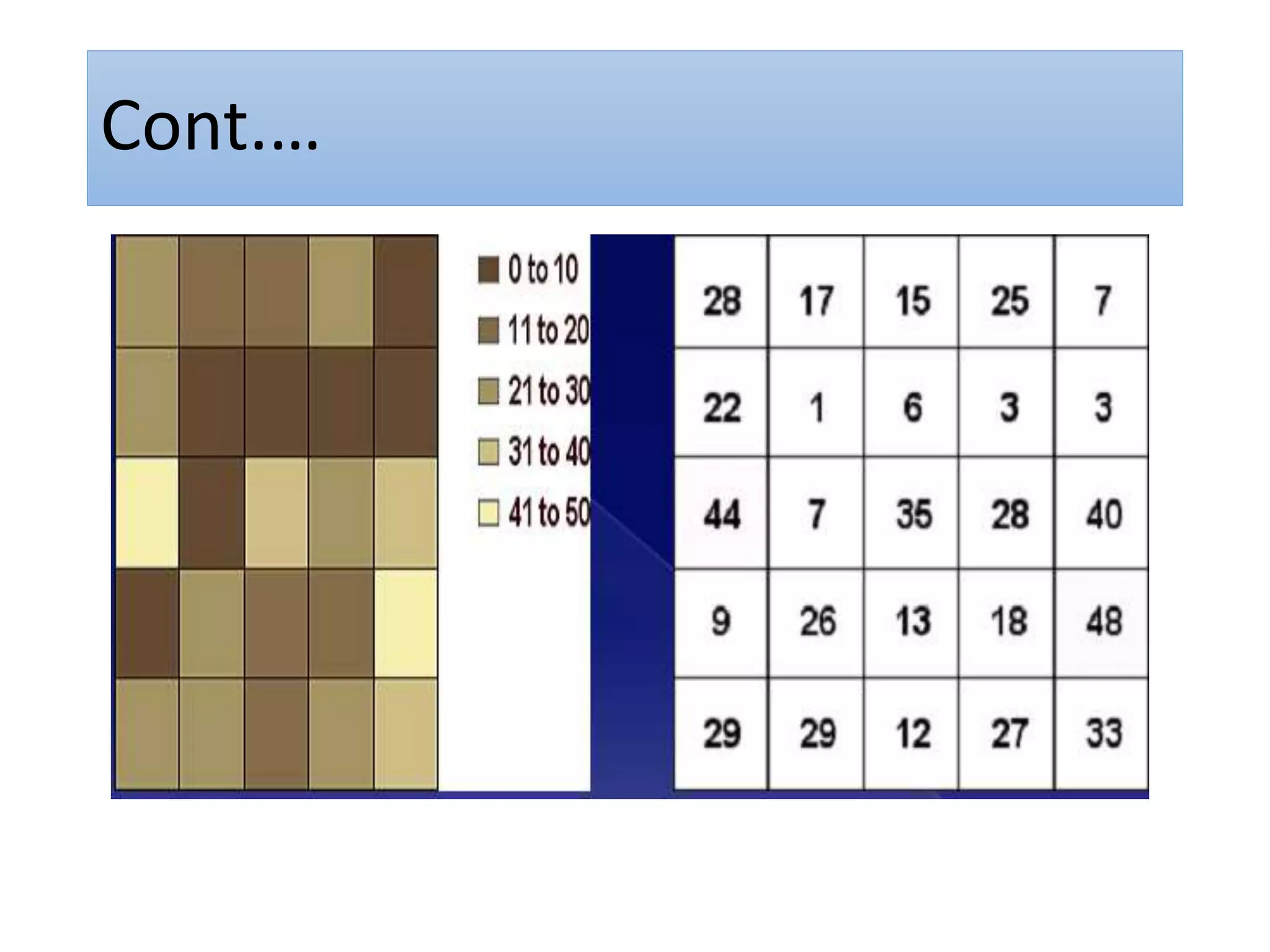
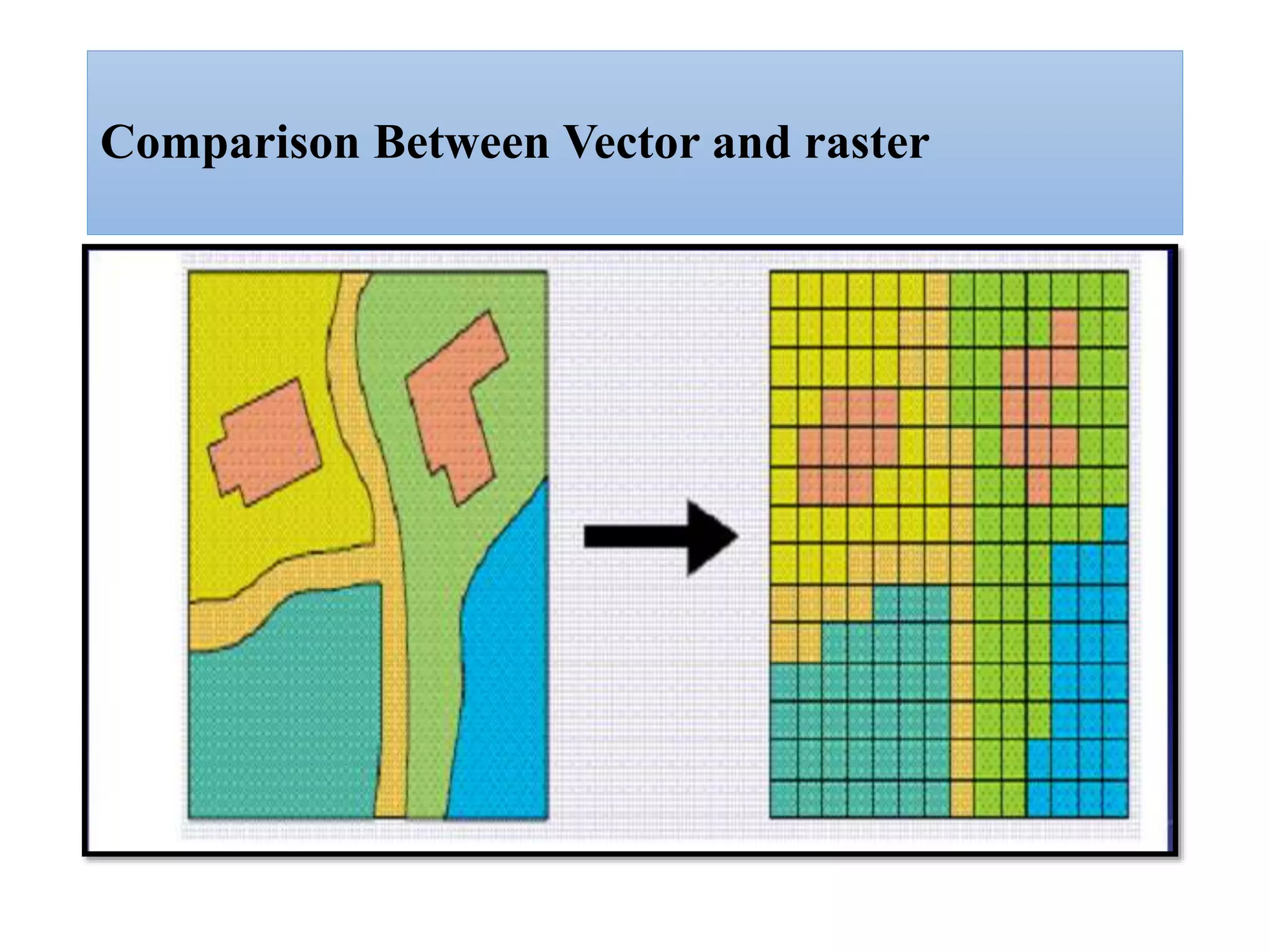
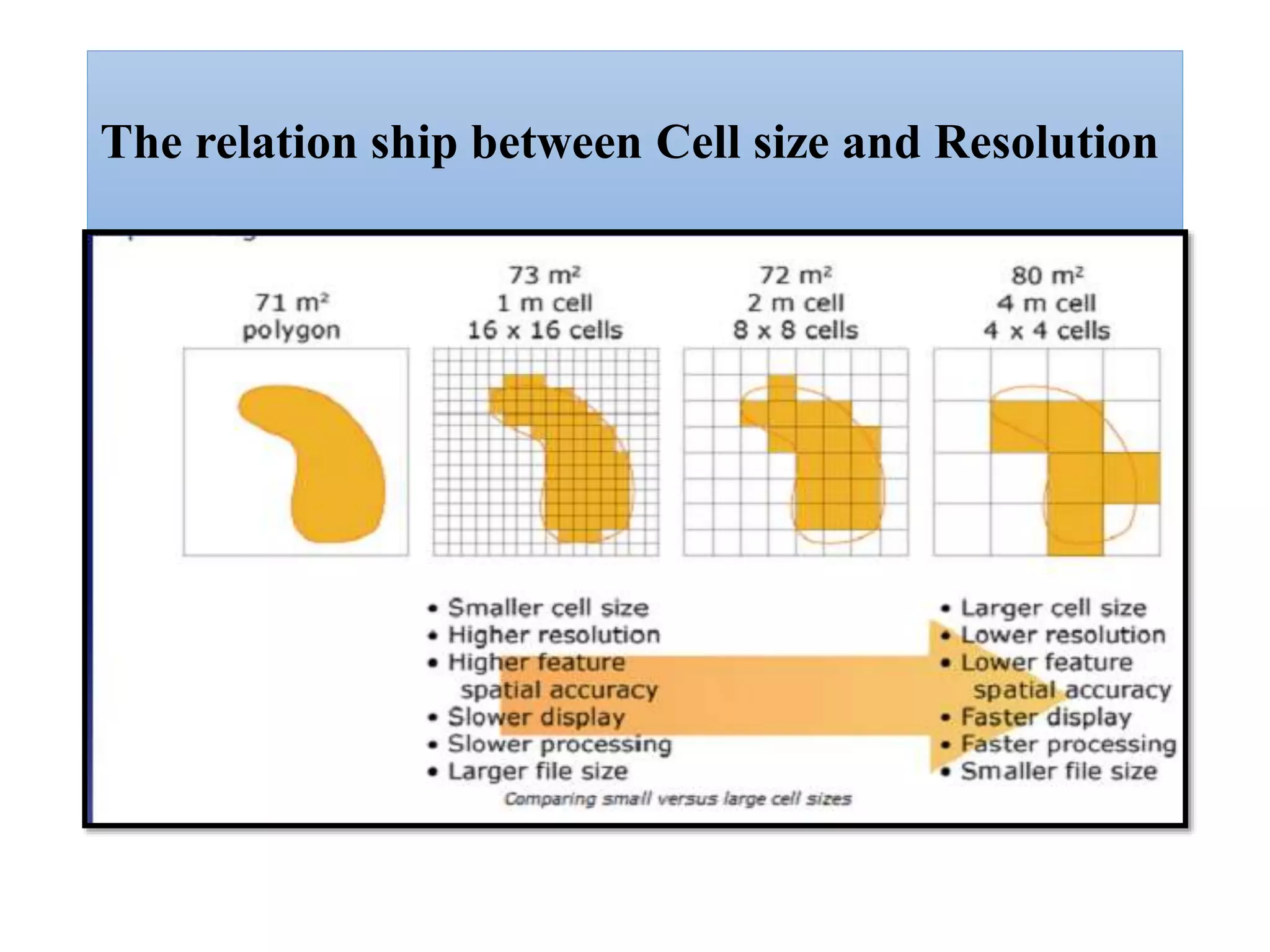
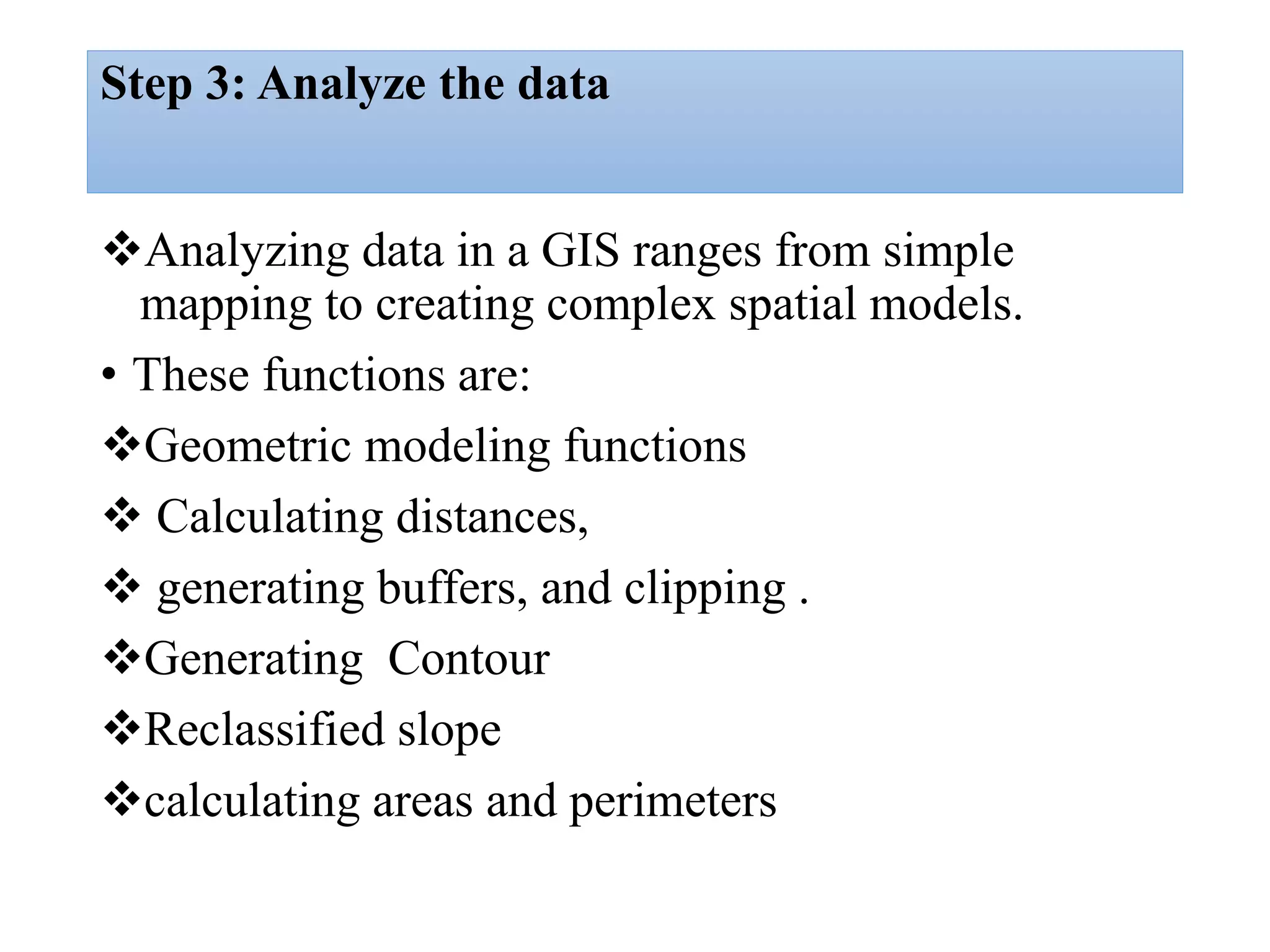
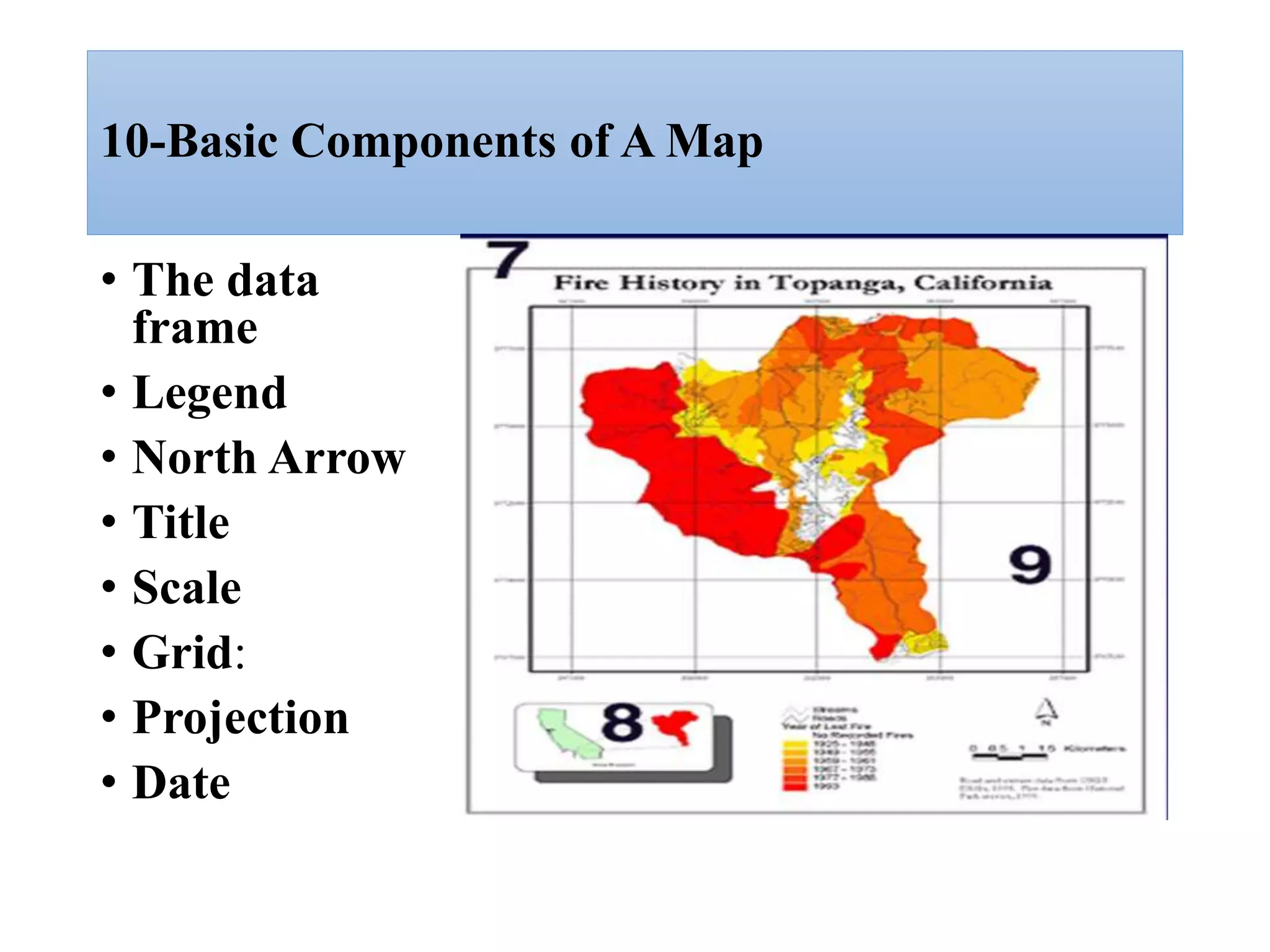
This document provides an introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). It outlines 12 topics: (1) what GIS is and its components; (2) spatial and attribute data; (3) major GIS tasks and functions; (4) where GIS data comes from; (5) benefits of using GIS; (6) why GIS is studied; (7) geographic models in ArcGIS; (8) the steps in a GIS project; (9) basic ArcMap components; (10) the ArcGIS software window and platforms; (11) the ArcCatalog interface; and (12) a practical exercise on implementing ArcGIS and performing tasks like importing data, digitizing features, and map layout