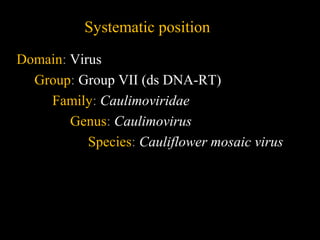
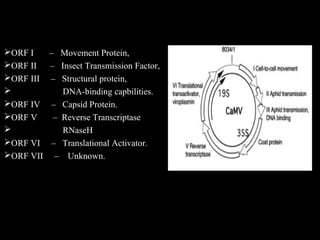
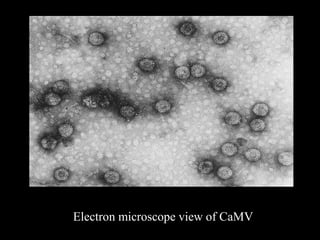
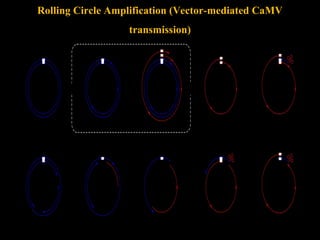
Cauliflower mosaic disease is caused by the Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV). It infects cruciferous plants like cauliflower and cabbage. CaMV is a pararetrovirus with a circular double-stranded DNA genome. It is transmitted by the aphid Myzus persicae in a semi-persistent and non-circulative manner. Symptoms include mosaic patterns, leaf deformation, stunting and yellowing. The disease causes significant yield losses worldwide. Management involves controlling the aphid vector through insecticide application.